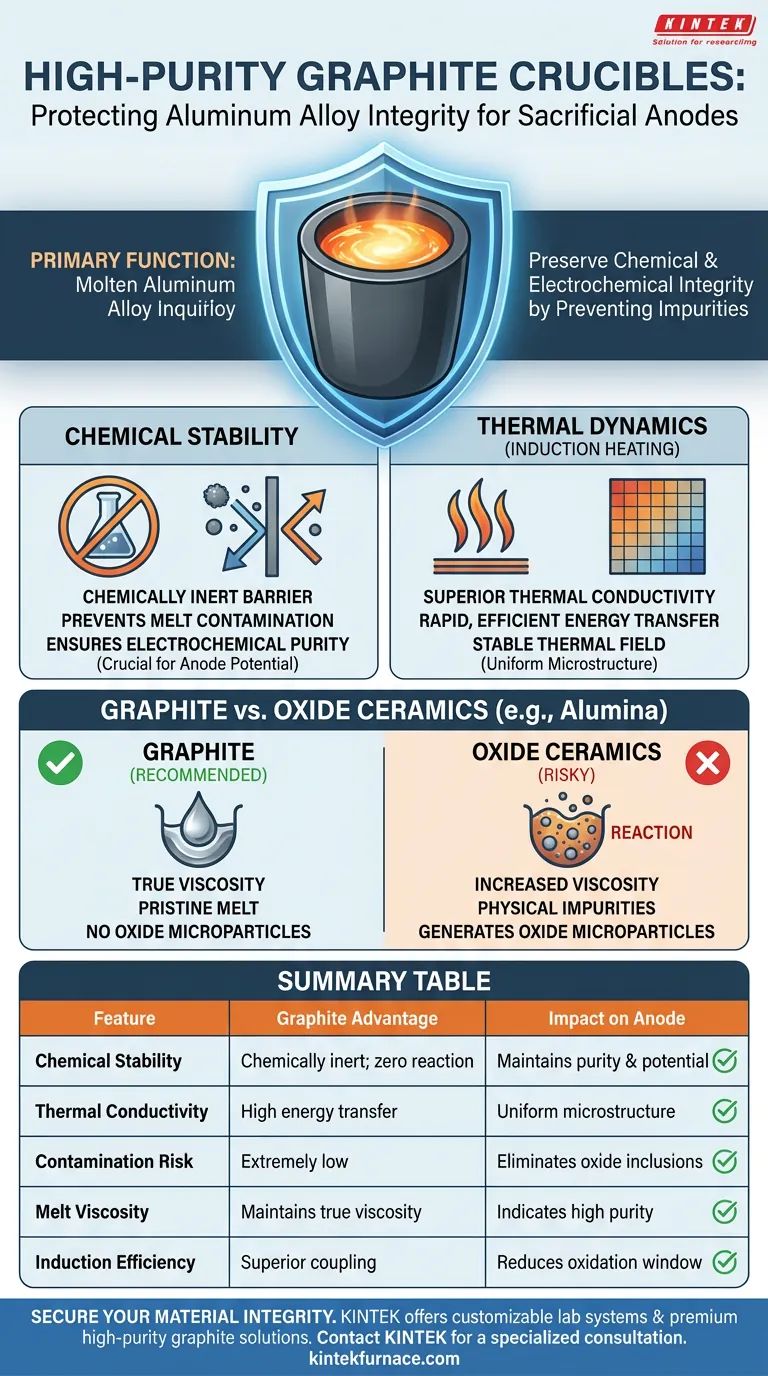
The primary function of high-purity graphite crucibles is to preserve the chemical and electrochemical integrity of the aluminum alloy during the melting process. By providing exceptional chemical stability and thermal conductivity, these crucibles prevent the introduction of impurities that would otherwise degrade the performance of the sacrificial anode.
The effectiveness of a sacrificial anode relies entirely on its material purity. High-purity graphite crucibles act as a chemically inert barrier, ensuring the molten alloy retains its specific electrochemical properties by preventing reactions between the vessel and the melt.

The Critical Role of Chemical Stability
Preventing Melt Contamination
Molten aluminum is highly reactive at the temperatures required for casting. High-purity graphite is distinct because of its chemical inertness.
It refuses to react with the aluminum alloy melt, even under intense heat. This prevents the crucible material itself from breaking down and leeching foreign elements into the alloy.
Ensuring Electrochemical Purity
For a sacrificial anode to function, its internal chemistry must be precise. Any introduction of foreign impurities can alter the anode's electrical potential.
By eliminating the risk of reaction, graphite crucibles ensure the final product meets the strict electrochemical purity standards required for effective corrosion protection.
Thermal Dynamics in Induction Heating
Superior Thermal Conductivity
Graphite is an excellent conductor of heat. During the induction heating process, this property allows for rapid and efficient energy transfer to the metal.
This efficiency reduces the time the metal sits at high temperatures, further minimizing the window for potential oxidation or degradation.
Stabilizing the Thermal Field
Consistency is vital for creating a uniform alloy microstructure. High-purity graphite provides a stable thermal field throughout the melting cycle.
This stability prevents temperature fluctuations that could lead to uneven melting or segregation of alloy components.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Graphite vs. Oxide Ceramics
The Risks of Alternative Materials
It is crucial to understand why graphite is chosen over common alternatives like alumina (aluminum oxide).
Evidence shows that alumina crucibles can react with aluminum alloys—specifically Aluminum-Silicon melts—at high temperatures. This reaction generates oxide microparticles within the melt.
The Impact on Viscosity and Quality
When a crucible reacts with the melt, it creates physical impurities. These inclusions significantly increase the measured viscosity of the alloy.
This artificial increase in viscosity signals that the material is no longer pure. Graphite, by contrast, yields viscosity measurements closer to the material's theoretical true values, proving its superior ability to maintain a pristine melt.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection of your crucible material directly dictates the quality ceiling of your final casting.
- If your primary focus is electrochemical performance: Prioritize high-purity graphite to strictly eliminate foreign impurities and maintain the alloy's reactive potential.
- If your primary focus is thermal consistency: Leverage graphite’s superior conductivity to ensure a stable thermal field and uniform melting during induction heating.
Ultimately, the crucible is not merely a container; it is an active component in your quality control strategy that safeguards the fundamental chemistry of your product.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Graphite Crucible Advantage | Impact on Sacrificial Anodes |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Stability | Chemically inert; zero reaction with melt | Maintains electrochemical purity and potential |
| Thermal Conductivity | High energy transfer and heat distribution | Ensures uniform microstructure and rapid melting |
| Contamination Risk | Extremely low; prevents foreign inclusions | Eliminates oxide microparticles and impurities |
| Melt Viscosity | Maintains theoretical true viscosity | Indicates high material purity and flow quality |
| Induction Efficiency | Superior coupling and thermal field stability | Reduces oxidation window and energy waste |
Secure Your Material Integrity with KINTEK
Don't let crucible reactions compromise your sacrificial anode performance. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with premium high-purity graphite solutions tailored for your unique lab and high-temperature needs.
Take control of your alloy quality today—Contact KINTEK for a specialized consultation!
Visual Guide
References
- Xin Liu, Nian Liu. Effect of Bi on the Performance of Al-Ga-In Sacrificial Anodes. DOI: 10.3390/ma17040811
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a Type B thermocouple for 1600°C slag reduction? Precision in Ultra-High Heat
- What are the performance parameters of a circulating water vacuum pump? Optimize Your Lab's Vacuum Efficiency
- What is the water-saving benefit of using a water circulating vacuum pump? Save Over 10 Tons of Water Daily
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles used for phosphor synthesis? Ensure Maximum Luminescence and Spectral Purity
- What are the requirements for sealed quartz tubes for CVT? Ensure High Purity & Integrity for NiI2 and MnPS3 Growth
- Why are high-purity alumina grinding balls used for Al2O3/TiC milling? Master Chemical Consistency
- What is the sealing pipe requirement for inlet pressure in water circulating vacuum pumps? Ensure System Integrity Above 0.03 MPa
- How does the gas control system regulate the plasma nitriding process? Master Your N2/H2 Mixture for Superior Surfaces



















