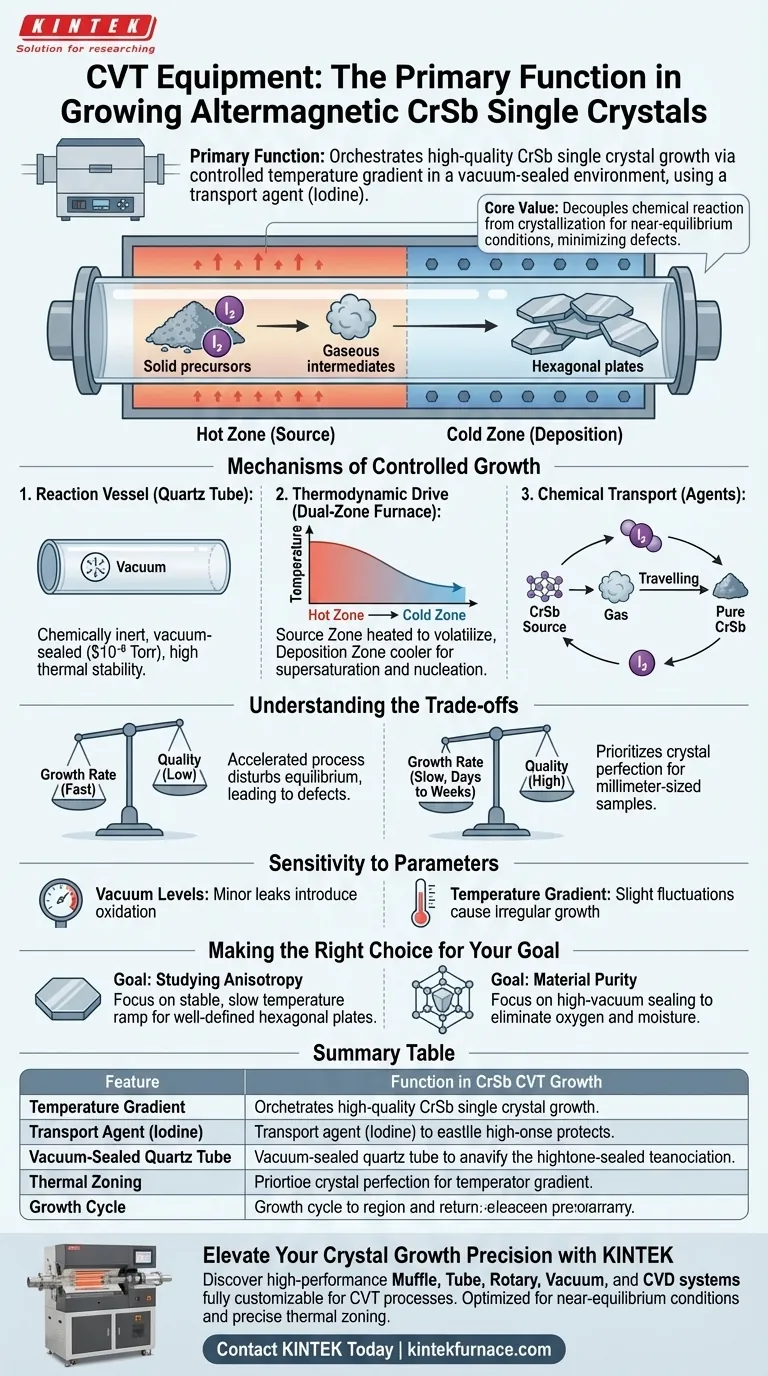
The primary function of Chemical Vapor Transport (CVT) equipment is to orchestrate the growth of high-quality CrSb single crystals by establishing a strictly controlled temperature gradient within a vacuum-sealed environment. By employing a transport agent such as iodine, the equipment converts solid precursors into a gaseous phase at a high temperature, forcing them to migrate and recrystallize at a cooler deposition zone. This method is indispensable for producing millimeter-sized crystals with specific orientations, such as hexagonal plates, which are required to study anisotropic transport properties.
The core value of CVT equipment lies in its ability to decouple the chemical reaction from the crystallization process through thermal zoning. This ensures that CrSb crystals grow under near-equilibrium conditions, minimizing defects and maximizing the purity required for advanced altermagnetic research.
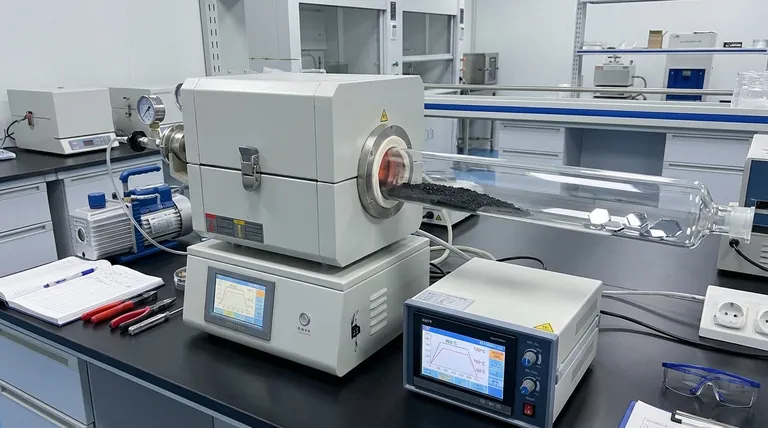

Mechanisms of Controlled Growth
The Role of the Reaction Vessel
The foundation of the CVT process is the quartz tube, which acts as a chemically inert reaction vessel.
This tube is vacuum-sealed to create a high-purity environment, preventing raw materials from reacting with atmospheric oxygen or moisture.
It must possess high thermal stability to withstand the elevated temperatures required for the reaction without contaminating the growing CrSb crystal.
Establishing the Thermodynamic Drive
CVT equipment, typically a dual-zone furnace, generates the necessary driving force for crystal growth by maintaining a precise temperature difference.
The "source zone" is heated to a higher temperature to volatilize the precursors, while the "deposition zone" is kept cooler to trigger supersaturation.
This gradient forces the gaseous material to migrate naturally from the hot end to the cold end, where nucleation occurs.
Chemical Transport via Agents
Since CrSb precursors are solid, the equipment relies on a transport agent, specifically iodine, to facilitate movement.
The agent reacts with the solid source material to form gaseous intermediates.
These gases travel down the tube and decompose at the cooler end, depositing pure CrSb and releasing the iodine back to transport more material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Growth Rate vs. Quality
CVT is an inherently slow process, prioritizing crystal perfection over speed.
High-quality single crystal growth can take several days or even weeks (e.g., up to 10 days for similar materials) to produce millimeter-scale samples.
Accelerating this process often disturbs the equilibrium, leading to polycrystals or structural defects that ruin the sample's utility for magnetic study.
Sensitivity to Parameters
The equipment requires rigorous control over pressure and vacuum levels.
Even a minor leak or insufficient vacuum (failure to reach levels like $10^{-6}$ Torr) can introduce oxidation that compromises the metallic luster and purity of the crystal.
Furthermore, slight fluctuations in the temperature gradient can alter the transport rate, resulting in irregular crystal sizes or unwanted morphologies.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the yield and quality of your CrSb crystals, you must tailor the equipment settings to your specific research objectives.
- If your primary focus is studying anisotropy: Prioritize a stable, slow temperature ramp to encourage the formation of well-defined hexagonal plates with specific crystallographic orientations.
- If your primary focus is material purity: Ensure your quartz tube preparation includes a high-vacuum sealing step to eliminate all traces of oxygen and moisture before the furnace is activated.
Success in growing altermagnetic CrSb relies not just on the equipment, but on the precise calibration of the thermal environment to support orderly atomic stacking.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in CrSb CVT Growth |
|---|---|
| Temperature Gradient | Drives gaseous precursors from source zone to deposition zone |
| Transport Agent (Iodine) | Converts solid precursors into gaseous intermediates for migration |
| Vacuum-Sealed Quartz Tube | Provides an inert, high-purity environment ($10^{-6}$ Torr) to prevent oxidation |
| Thermal Zoning | Decouples chemical reaction from crystallization for near-equilibrium growth |
| Growth Cycle | Requires several days to weeks to ensure structural perfection and purity |
Elevate Your Crystal Growth Precision with KINTEK
To achieve the near-equilibrium conditions and precise thermal zoning required for altermagnetic research, you need equipment engineered for stability. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a wide range of high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all of which are fully customizable to meet the unique pressure and temperature demands of CVT processes. Whether you are growing CrSb hexagonal plates or specialized semiconductor materials, our advanced lab furnaces provide the reliability your research deserves.
Ready to optimize your lab’s high-temperature capabilities?
Visual Guide
References
- B. Rai, Nitesh Kumar. Direction‐Dependent Conduction Polarity in Altermagnetic CrSb. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202502226
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) and how does it relate to CVD? Unlock Precision Thin Film Technology
- What is the process for synthesizing transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) using CVD tube furnaces? Master High-Quality Thin Film Growth
- Why is gas flow distribution critical in LPCVD alpha-MnSe synthesis? Master Precise Nanosheet Morphology
- How does the chemical Vapour deposition method work? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision Coating
- Why are CVD furnaces indispensable in material science? Unlock Atom-Level Precision for Superior Materials
- What role does a vacuum thermal evaporation system play in the fabrication of Cu13Se52Bi35 thin films? Expert Guide
- What are the structural advantages of a customized AP-SCVD system? High-Throughput WO3 Thin Film Production
- What are the advantages of chemical vapour deposition? Achieve Superior, Uniform Coatings on Complex 3D Surfaces



















