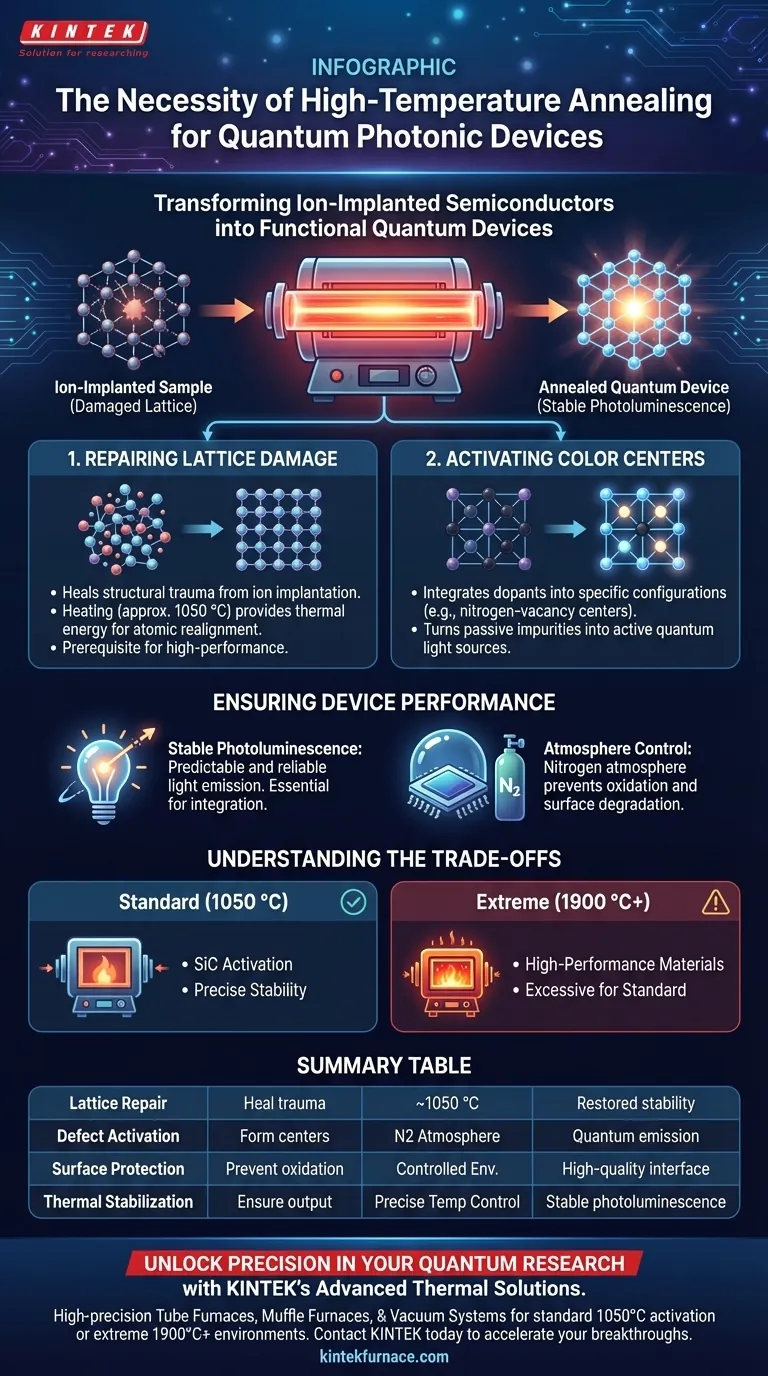
High-temperature tube furnaces are the critical enabling technology for transforming ion-implanted semiconductors into functional quantum devices. Specifically, annealing at temperatures around 1050 °C in a nitrogen atmosphere is necessary to repair crystal lattice damage and activate the specific defects—such as color centers—that generate quantum light.
The annealing process serves a dual purpose: it heals the structural trauma caused by ion implantation and activates the quantum properties of the material. Without this thermal treatment, the material lacks the stable photoluminescence required to operate as an effective photonic device.

The Role of Thermal Treatment in Quantum Fabrication
Repairing Lattice Damage
Ion implantation is a violent process at the atomic level. While it successfully introduces necessary foreign atoms into the material, it disrupts the host crystal structure.
High-temperature annealing provides the thermal energy required to heal this structural trauma. By heating the sample—often Silicon Carbide (SiC)—to approximately 1050 °C, the atoms are encouraged to realign.
This restoration of the lattice is a prerequisite for high-performance device operation.
Activating Color Centers
Merely implanting ions does not automatically create a quantum emitter. The dopants must be chemically and physically integrated into the lattice in a specific configuration.
The annealing process "activates" these centers. For example, it facilitates the formation of nitrogen-vacancy centers.
This activation turns a passive impurity into an active optical component capable of quantum interaction.
Ensuring Device Performance
Achieving Stable Photoluminescence
For a photonic device to be useful, it must emit light predictably and reliably.
Unannealed samples often exhibit unstable or weak optical properties due to residual defects.
The thermal treatment stabilizes the material's photoluminescence properties. This ensures the quantum light source can be successfully integrated into larger photonic structures.
The Importance of Atmosphere Control
Temperature is not the only variable; the environment inside the furnace is equally critical.
Standard processes typically utilize a nitrogen atmosphere during the 1050 °C cycle.
This prevents unwanted chemical reactions, such as oxidation, which could degrade the surface quality of the photonic device.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Standard vs. Extreme Capabilities
While 1050 °C is standard for many Silicon Carbide applications, not all furnaces are created equal.
Standard tube furnaces are sufficient for this specific activation process. However, specialized research sometimes requires exploring boundaries beyond standard protocols.
High-Performance Considerations
Some advanced tube furnaces are capable of reaching temperatures exceeding 1900 °C.
While this capacity is essential for fabricating high-performance materials under extreme conditions, it may be excessive for standard quantum emitter activation.
Using equipment with capabilities far beyond your needs can introduce unnecessary cost and complexity unless your research demands those specific extreme thresholds.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal processing strategy depends on the specific material constraints of your photonic device.
- If your primary focus is standard Silicon Carbide activation: Prioritize a furnace that offers precise temperature stability at 1050 °C within a controlled nitrogen atmosphere to ensure reliable defect activation.
- If your primary focus is experimental material research: Look for specialized furnaces capable of exceeding 1900 °C to handle extreme fabrication conditions not required for standard quantum emitters.
Ultimately, the furnace is not just a heater; it is the tool that transitions your material from a damaged crystal into a functional quantum light source.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Primary Objective | Key Parameter | Outcome for Device |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lattice Repair | Heal structural trauma from ion implantation | ~1050 °C Heating | Restored crystal stability |
| Defect Activation | Form functional color centers (e.g., NV centers) | Nitrogen Atmosphere | Active quantum light emission |
| Surface Protection | Prevent oxidation/chemical degradation | Controlled Environment | High-quality optical interface |
| Thermal Stabilization | Ensure predictable optical output | Precise Temp Control | Stable photoluminescence |
Unlock Precision in Your Quantum Research
Transform your ion-implanted semiconductors into high-performance quantum devices with KINTEK’s advanced thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-precision Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, and Vacuum Systems specifically engineered for the rigorous demands of photonic fabrication.
Whether you require standard 1050°C activation or extreme 1900°C+ environments, our customizable systems ensure the precise temperature stability and atmosphere control your materials demand. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique project needs and see how our laboratory high-temperature furnaces can accelerate your breakthroughs.
Visual Guide
References
- Sridhar Majety, Marina Radulaski. Wafer-scale integration of freestanding photonic devices with color centers in silicon carbide. DOI: 10.1038/s44310-024-00049-y
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- How does heating zone length impact tube furnace performance? Optimize Uniformity and Capacity
- How does a programmable tube furnace facilitate Al/SiC material transformation? Precision Heat for Ceramic Coatings
- What are the applications of a tube furnace? Master Precise Thermal Processing for Advanced Materials
- Why is a specific nitrogen flow rate necessary within a tube furnace during the carbonization of PVDF?
- How is heat transferred to the material inside a tube furnace? Master the 3-Stage Process for Precise Thermal Control
- Why is a high-precision tube furnace necessary for YIG thin films? Unlock Superior Magnetic Performance
- How should a quartz tube furnace be cleaned? Essential Steps for Safe, Contamination-Free Maintenance
- How does a tube furnace ensure uniform heating? Master Precise Temperature Control for Your Lab



















