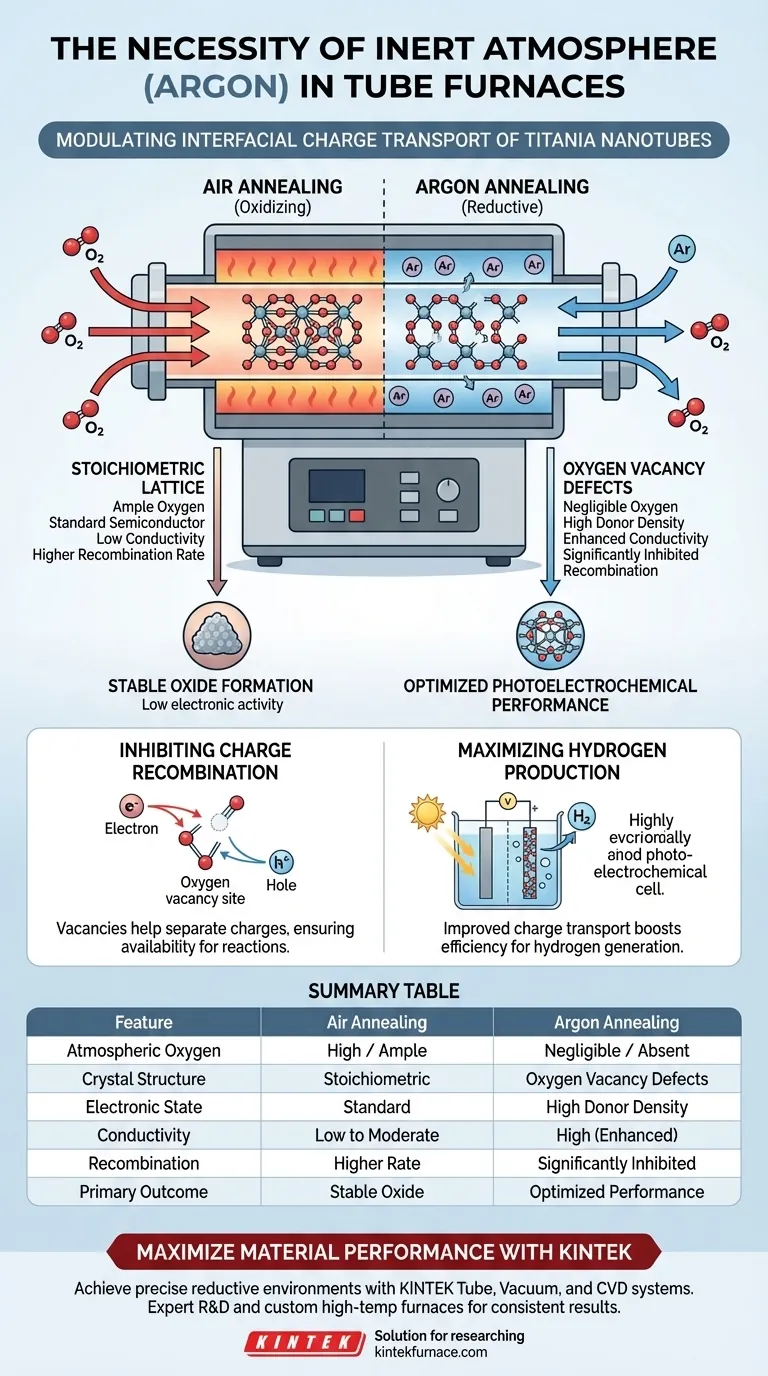
The primary necessity of introducing an inert atmosphere like argon into a tube furnace is to create a controlled, oxygen-deficient environment during the annealing process. By excluding atmospheric oxygen, you force the titania nanotubes to undergo a reductive change, leading to the deliberate formation of structural imperfections known as oxygen vacancies.
Core Takeaway Introducing argon prevents the oxidation that would naturally occur in air, instead fostering a reductive environment that generates oxygen vacancy defects. These specific defects are the key to unlocking higher electronic conductivity and minimizing charge recombination, directly resulting in superior photoelectrochemical hydrogen production.

The Mechanism of Defect Engineering
Creating a Reductive Environment
Standard annealing in air supplies ample oxygen to the material, creating a stoichiometric (perfectly balanced) crystal lattice.
To modulate charge transport, you must disrupt this balance. Introducing argon creates a reductive atmosphere, starving the environment of oxygen while the material is heated.
Generating Oxygen Vacancies
Under these inert conditions, oxygen atoms act to leave the titania crystal lattice.
This removal creates oxygen vacancy defects. These are not errors, but calculated structural modifications required to alter the electronic behavior of the nanotubes.
Modulating Electronic Properties
Increasing Donor Density
The introduction of oxygen vacancies fundamentally changes the electronic structure of the titania.
These vacancies act as electron donors. Consequently, the donor density of the material increases significantly compared to samples annealed in oxygen-rich environments.
Enhancing Electronic Conductivity
A direct result of increased donor density is improved conductivity.
The oxygen vacancies facilitate the movement of electrons through the material. This boosts the overall electronic conductivity, making the nanotubes more efficient at transporting charge carriers.
Improving Photoelectrochemical Performance
Inhibiting Charge Recombination
One of the greatest challenges in photoelectrochemical systems is the tendency for photogenerated electrons and holes to recombine before they can do useful work.
The oxygen vacancies generated by the argon atmosphere effectively inhibit this recombination. They help separate the charges, ensuring they remain available for chemical reactions.
Maximizing Hydrogen Production
The ultimate output of these modifications is a tangible increase in reaction efficiency.
Because charge transport is improved and recombination is suppressed, the system achieves a substantial increase in photoelectrochemical hydrogen production efficiency.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
The Cost of Atmospheric Control
The necessity of an inert atmosphere implies a trade-off between process complexity and material performance.
You cannot achieve these high-conductivity states in an open-air furnace. If oxygen is present, it will "heal" the vacancies, returning the material to a less conductive, stoichiometric state. Therefore, strict environmental control is the unavoidable cost of high-performance charge transport.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if an argon atmosphere is required for your specific application, consider your performance metrics:
- If your primary focus is maximizing conductivity: You must use an inert atmosphere to generate the oxygen vacancies that increase donor density.
- If your primary focus is efficient hydrogen production: You need the reductive environment to inhibit electron-hole recombination, which is the primary loss mechanism in these systems.
By controlling the atmosphere, you transition titania from a simple semiconductor into a highly efficient charge-transport material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Air Annealing (Oxidizing) | Argon Annealing (Reductive) |
|---|---|---|
| Atmospheric Oxygen | High / Ample | Negligible / Absent |
| Crystal Structure | Stoichiometric (Perfect) | Oxygen Vacancy Defects |
| Electronic State | Standard Semiconductor | High Donor Density |
| Conductivity | Low to Moderate | High (Enhanced) |
| Recombination | Higher Rate | Significantly Inhibited |
| Primary Outcome | Stable Oxide Formation | Optimized Photoelectrochemical Performance |
Maximize Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Achieving the precise reductive environment for titania nanotube modulation requires uncompromising atmospheric control. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to maintain high-purity inert environments, ensuring consistent oxygen vacancy generation for your research.
Backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique experimental parameters. Don't let atmospheric interference compromise your results—partner with KINTEK to unlock superior electronic conductivity and hydrogen production efficiency.
Ready to elevate your thermal processing? Contact our experts today to find the perfect customized furnace solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
References
- Younggon Son, Kiyoung Lee. Interfacial Charge Transfer Modulation via Phase Junctions and Defect Control in Spaced TiO <sub>2</sub> Nanotubes for Enhanced Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting. DOI: 10.1002/solr.202500334
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- When did tube furnaces originate and what drove their development? Discover the Engineered Solution for Precise Heat
- How does the industrial tube furnace contribute to Fe-N-C catalyst synthesis? Master High-Temperature Carbonization
- What are the limitations of tube furnaces when cracking heavy materials? Overcome Coking and Boost Efficiency
- What are the benefits of independent temperature control in a three-zone furnace? Enhance Precision and Uniformity
- What are the objectives of using a tube furnace for dual-layer nanocomposite heat treatment? Maximize Coating Stability
- Why is a tube furnace with precise temperature control necessary for Fe7S8@CT-NS composites? Master Advanced Synthesis
- What problems existed with early tube furnace designs? Discover the Flaws That Hindered Performance
- What industries commonly use High Temperature Tube Furnaces? Essential for Material Science, Electronics, and More



















