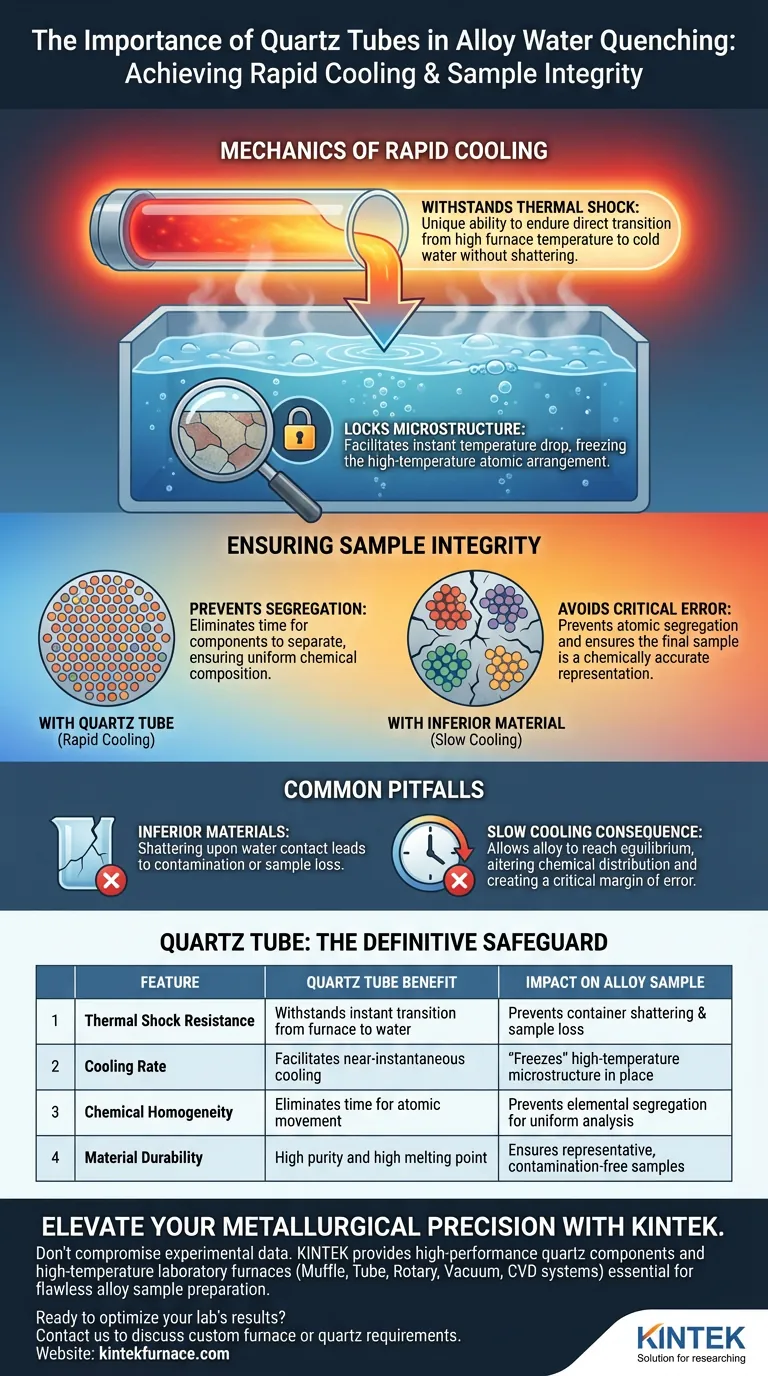
The primary importance of a quartz tube in water quenching is its unique ability to withstand extreme thermal shock, enabling the instantaneous cooling of molten metal. By functioning as a robust vessel that can transition directly from high furnace temperatures into cold water without shattering, it allows for the immediate preservation of the alloy's state.
The quartz tube acts as a critical thermal barrier that permits rapid cooling, effectively "freezing" the alloy's high-temperature microstructure. This prevents atomic segregation and ensures the final sample is a chemically accurate representation of the melt for experimental analysis.
The Mechanics of Rapid Cooling
Withstanding Thermal Shock
The fundamental challenge in water quenching is the drastic temperature difference between the molten metal and the cooling medium. Quartz allows this transition to happen instantly.
Unlike standard glass or ceramic, a quartz tube can endure the intense stress of being plunged into water while holding molten material. This durability is the physical prerequisite for achieving the high cooling rates necessary for accurate sampling.
Locking the Microstructure
The speed of cooling dictates the atomic structure of the solid sample. By using quartz to facilitate an instant temperature drop, you lock the high-temperature microstructure in place.
This preserves the specific arrangement of atoms as they existed in the liquid or semi-liquid state. It prevents the lattice changes that would naturally occur if the sample were allowed to cool gradually.
Ensuring Sample Integrity
Preventing Component Segregation
When alloys cool slowly, their chemical components often separate, leading to an uneven distribution of elements known as segregation.
The rapid cooling provided by the quartz tube method eliminates the time required for this separation to occur. This results in a sample where the chemical composition is uniform throughout, mirroring the homogeneity of the molten state.
Representative Analysis
For experimental data to be valid, the test sample must accurately reflect the material's properties at the target temperature.
By preventing segregation and freezing the microstructure, the quartz tube ensures the sample is truly representative. This validity is essential for subsequent metallurgical examinations and chemical analyses.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The Consequence of Slow Cooling
If a vessel with lower thermal shock resistance is used, the operator is forced to cool the sample more slowly to prevent the container from exploding.
This delay introduces a critical margin of error. During slower cooling, the alloy attempts to reach equilibrium, altering its chemical distribution and rendering the sample inaccurate for high-temperature studies.
Relying on Inferior Materials
Substituting quartz with standard borosilicate glass or lower-grade ceramics often leads to containment failure during the quench.
If the tube shatters upon contact with water, the sample is contaminated or lost entirely. Quartz provides the necessary reliability to ensure the physical survival of the sample during the aggressive quenching process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your alloy preparation yields valid scientific data, align your method with your analytical requirements.
- If your primary focus is microstructural fidelity: Use quartz to achieve the fastest possible quench rate, preserving the high-temperature crystal lattice without modification.
- If your primary focus is chemical homogeneity: Rely on the quartz tube's thermal shock resistance to prevent cooling delays that cause elemental segregation.
The use of a quartz tube is not merely a procedural step; it is the definitive safeguard against data corruption during alloy solidification.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Quartz Tube Benefit | Impact on Alloy Sample |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Withstands instant transition from furnace to water | Prevents container shattering and sample loss |
| Cooling Rate | Facilitates near-instantaneous cooling | "Freezes" high-temperature microstructure in place |
| Chemical Homogeneity | Eliminates time for atomic movement | Prevents elemental segregation for uniform analysis |
| Material Durability | High purity and high melting point | Ensures representative, contamination-free samples |
Elevate Your Metallurgical Precision with KINTEK
Don't compromise your experimental data with inferior materials. KINTEK provides the high-performance quartz components and high-temperature laboratory furnaces essential for flawless alloy sample preparation.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer a full range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique research specifications. Whether you need superior thermal shock resistance for quenching or precise atmosphere control for material synthesis, our technical team is ready to deliver the solution you need.
Ready to optimize your lab's results? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace or quartz requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Hyunjae Kim, Youn‐Bae Kang. Evaporation of Sn from Molten Fe–C–S Alloy Under Reduced Pressure at 1650 $$^\circ $$C for Developing Sustainable Ferrous Scrap Recycling Process. DOI: 10.1007/s11663-025-03579-8
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of using a tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thermal Control for Your Lab
- What core process conditions does a high-temperature tube furnace provide for the rapid pyrolysis of coal?
- What is a tube furnace and how is it designed? Achieve Precise, Uniform Heating for Your Lab
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace contribute to the atmosphere-controlled sintering of Mn-Zn ferrites?
- What is a horizontal electric furnace designed for? Achieve Precise Thermal Processing in Controlled Environments
- What are the key application features of a fluidized bed vertical tube furnace? Boost Efficiency and Uniformity
- What role does a tubular furnace play in the synthesis of Si:B nanowires? Driving Thermal Evaporation and Growth
- What are the primary functions of a high-precision tube resistance furnace? Optimize Chloride-Doped Composite Synthesis



















