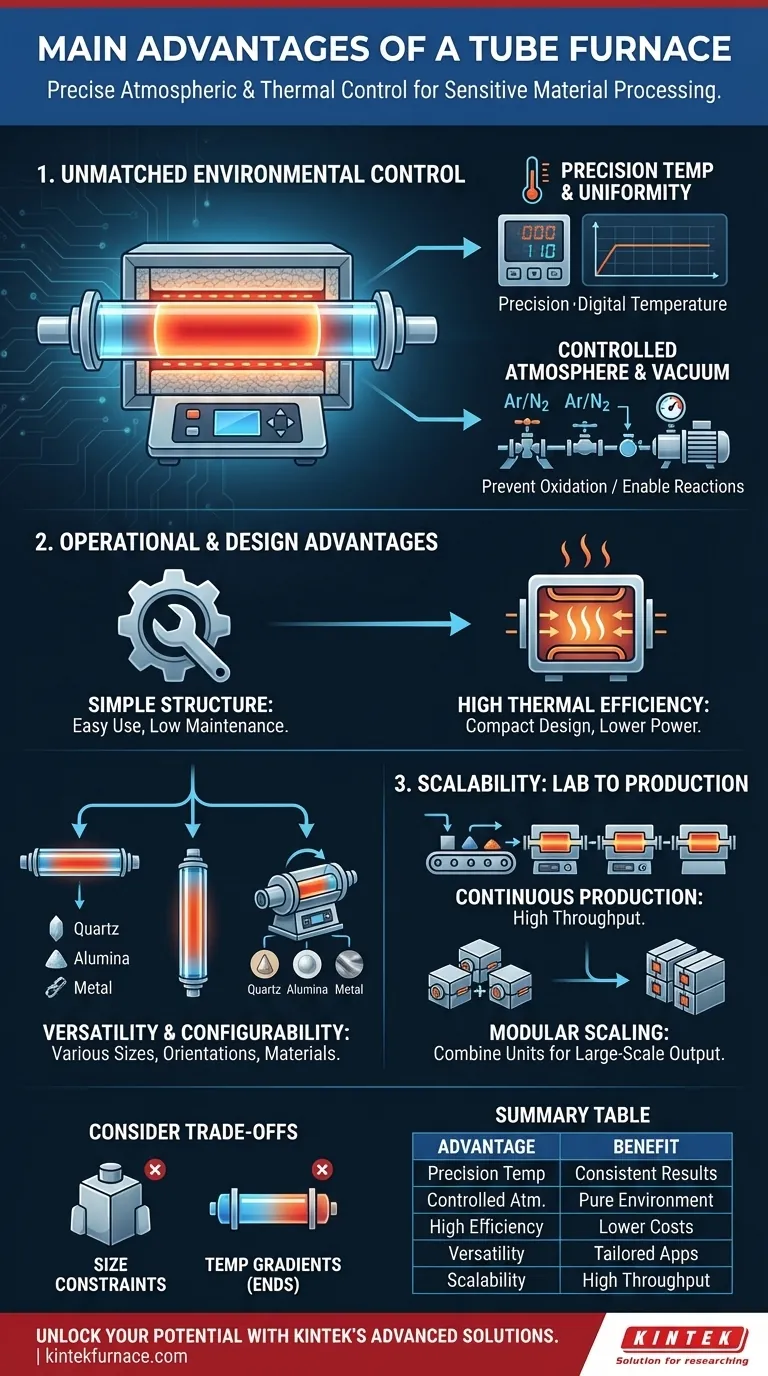
At their core, the primary advantages of a tube furnace stem from its ability to provide precise atmospheric and thermal control within an isolated environment. This unique capability, combined with its simple structure and operational versatility, makes it an indispensable tool for a wide range of sensitive material processing applications.
The true value of a tube furnace is not just its heating ability, but its power to create a highly controlled and pure environment. This makes it the superior choice for processes where preventing contamination and ensuring repeatable results are non-negotiable.

The Foundation: Unmatched Environmental Control
The defining characteristic of a tube furnace is the containment of the process within a sealed tube. This design is the source of its most significant advantages.
Precision Temperature Control and Uniformity
The cylindrical geometry of the heating chamber naturally promotes a highly uniform temperature zone in the center of the tube. This uniformity is critical for processes that demand consistent thermal treatment across the entire sample.
Modern controllers allow for precise temperature regulation, ensuring that experimental or production parameters can be reliably replicated, leading to consistent data and high-quality results.
Controlled Atmosphere and Vacuum Capabilities
The sealed tube is the key to atmospheric control. It allows you to purge ambient air and introduce specific gases, creating an inert (e.g., argon, nitrogen) or reactive atmosphere.
This capability is essential for preventing unwanted oxidation of sensitive materials or for facilitating specific chemical reactions that require a particular gaseous environment. The tube can also be evacuated to create a vacuum for high-purity processing.
Operational and Design Advantages
Beyond its core function of environmental control, a tube furnace offers significant practical benefits in its design and operation.
Structural Simplicity and Ease of Use
Tube furnaces possess a mature technology and a straightforward structure. This simplicity translates into easy operation, intuitive controls, and less complex maintenance requirements compared to more intricate furnace systems.
High Thermal Efficiency
The compact design, where heating elements are positioned closely around the process tube, minimizes heat loss to the surrounding environment. This results in higher thermal efficiency and lower power consumption for a given temperature.
Versatility and Configurability
These furnaces are highly adaptable. They are available in various sizes and can be configured in horizontal, vertical, or rotary setups to meet different process needs.
Furthermore, a wide range of tube materials—such as quartz, alumina, or metal alloys—can be used, allowing the furnace to be tailored for different temperatures and chemical compatibilities.
The Scalability Factor: From Lab to Production
A tube furnace is not just a laboratory instrument; its design principles allow for a clear path to larger-scale operations.
Suitability for Continuous Production
Unlike a box furnace that operates in batches, a tube furnace is naturally suited for continuous or semi-continuous processing. Materials can be fed through one end of the tube and collected at the other, increasing throughput.
Pathway to Large-Scale Output
For industrial-scale needs, multiple tube furnaces can be combined and operated in parallel. This modular approach to scaling allows for a significant increase in production capacity while maintaining the precise process control of a single unit.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the tube furnace is not the universal solution for all heating applications. Understanding its limitations is crucial.
Sample Size and Geometry Constraints
The most obvious limitation is the internal diameter and length of the process tube. A tube furnace is unsuitable for processing large, bulky, or irregularly shaped objects that cannot fit within these geometric constraints. For such items, a chamber or box furnace is necessary.
Inherent Temperature Gradients
While the central zone of the tube is highly uniform, the temperature naturally drops off toward the cooler, unheated ends. This gradient must be accounted for by ensuring the sample is placed entirely within the uniform central hot zone for consistent results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right thermal processing equipment depends entirely on your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is material purity and controlled reactions: The ability to create a specific, sealed atmosphere is the most important advantage of a tube furnace.
- If your primary focus is process consistency and repeatability: The excellent temperature uniformity within the central hot zone is the critical feature you need.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and future growth: The suitability for continuous production and the ability to scale by combining units are its key strategic benefits.
Ultimately, a tube furnace excels by providing an exceptionally controlled micro-environment, ensuring the integrity of your process and the quality of your results.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Precision Temperature Control | Enables uniform heating and reliable replication of experimental parameters for consistent results. |
| Controlled Atmosphere & Vacuum | Allows inert or reactive gas environments and vacuum processing to prevent contamination and facilitate reactions. |
| High Thermal Efficiency | Compact design minimizes heat loss, reducing power consumption and operational costs. |
| Versatility & Configurability | Supports various sizes, orientations (horizontal, vertical, rotary), and tube materials for tailored applications. |
| Scalability for Production | Suitable for continuous processing and modular scaling to increase throughput from lab to industrial levels. |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable tube furnaces, muffle furnaces, vacuum & atmosphere furnaces, and CVD/PECVD systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















