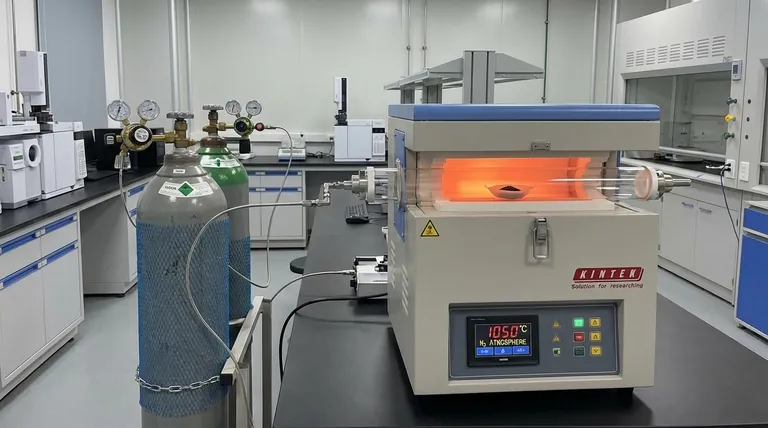
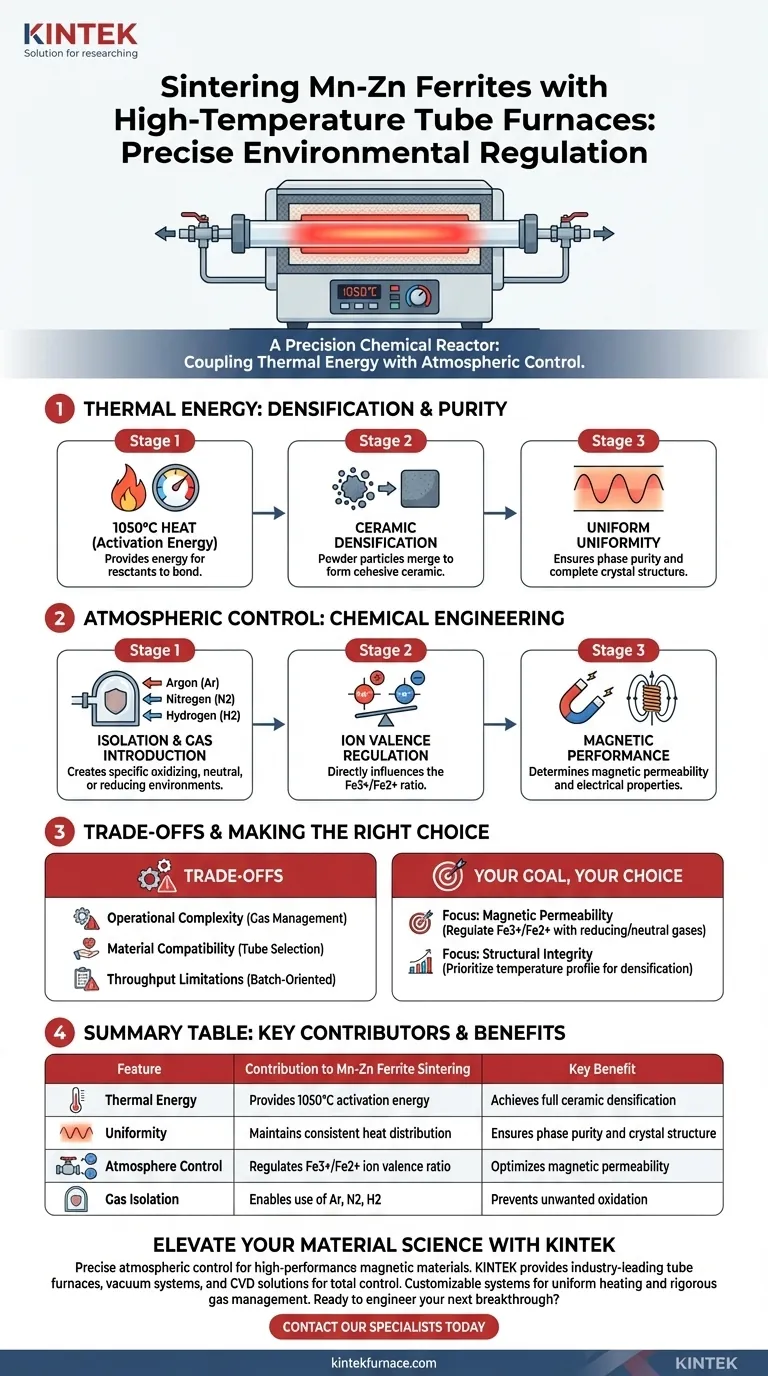
Precise environmental regulation is the primary contribution of a high-temperature tube furnace to the sintering of Mn-Zn ferrites. This equipment provides a stable 1050°C thermal environment necessary for ceramic densification while simultaneously controlling the chemical atmosphere. By introducing specific gases, the furnace regulates the oxidation state of metal ions, directly engineering the material's final magnetic and electrical properties.
The high-temperature tube furnace functions as a precision chemical reactor, coupling thermal energy with atmospheric control. Its ability to regulate the Fe3+/Fe2+ ratio during sintering is the deciding factor in achieving high magnetic permeability in Mn-Zn ferrites.

The Role of Thermal Energy in Densification
Providing Activation Energy
The fundamental role of the furnace is to generate high heat, specifically around 1050°C for this application. This thermal energy provides the activation energy required for the reactants to bond.
Ceramic Densification
At these temperatures, the material undergoes densification. The powder particles merge to form a solid, cohesive ceramic body, establishing the physical structure of the ferrite.
Ensuring Phase Purity
The tube furnace is designed to offer a high degree of temperature uniformity. This uniform heat distribution is critical for ensuring phase purity and a complete crystal structure throughout the synthesized product.
Atmospheric Control and Chemical Engineering
Managing the Reaction Environment
The defining feature of a tube furnace is its ability to isolate the sample from ambient air. Operators can introduce gases such as argon, nitrogen, or hydrogen to create specific oxidizing, neutral, or reducing environments.
Controlling Ion Valence
The atmosphere within the tube directly influences the chemical composition of the ferrite. Specifically, it regulates the valence balance of metal ions, most notably the Fe3+/Fe2+ ratio.
Defining Magnetic Performance
This control over ion ratios is not merely a chemical concern; it is a performance imperative. The balance between Fe3+ and Fe2+ determines the magnetic permeability and electrical properties of the finished Mn-Zn ferrite.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Operational Complexity
While tube furnaces offer precision, they introduce operational complexity regarding gas management. Users must precisely configure gas lines and flow rates, as slight deviations in the atmosphere can ruin the valence balance.
Material Compatibility
The physical setup requires careful selection of the tube material and size. Using an incorrect tube material for the required temperature or chemical atmosphere can lead to equipment failure or sample contamination.
Throughput Limitations
Compared to larger industrial conveyor furnaces, tube furnaces are often batch-oriented. They are excellent for precision and synthesis but may have limitations regarding high-volume production speed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of a high-temperature tube furnace in your sintering process, align your operational parameters with your specific material requirements:
- If your primary focus is magnetic permeability: Prioritize the precise control of reducing or neutral gases (like Nitrogen or Hydrogen) to strictly regulate the Fe3+/Fe2+ ratio.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity: Concentrate on the temperature profile and uniformity to ensure complete densification and crystal formation without thermal gradients.
Success in sintering Mn-Zn ferrites relies on treating the furnace not just as a heat source, but as a tool for atomic-level engineering.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Contribution to Mn-Zn Ferrite Sintering | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Energy | Provides 1050°C activation energy | Achieves full ceramic densification |
| Uniformity | Maintains consistent heat distribution | Ensures phase purity and crystal structure |
| Atmosphere Control | Regulates Fe3+/Fe2+ ion valence ratio | Optimizes magnetic permeability |
| Gas Isolation | Enables use of Argon, Nitrogen, or Hydrogen | Prevents unwanted oxidation |
Elevate Your Material Science with KINTEK
Precise atmospheric control is the difference between a standard ferrite and a high-performance magnetic material. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature tube furnaces, vacuum systems, and CVD solutions designed to give you total control over your sintering environment.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our customizable systems ensure uniform heating and rigorous gas management to meet your unique lab requirements. Ready to engineer your next breakthrough? Contact our specialists today to find the perfect furnace for your Mn-Zn ferrite research or production.
Visual Guide
References
- A. Faeghinia. Effects of sintering and pressing conditions on the properties of manganese ferrite. DOI: 10.53063/synsint.2025.53260
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a tube furnace in the pyrolysis of biomass? Achieve Precision in Material Research
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace play in STO thin film annealing? Unlock Neuromorphic Potential
- How is temperature regulation achieved in a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Master Precise Control for Your Lab
- What critical conditions does a tube furnace provide for TR-PBO membrane treatment? Achieve Perfect Thermal Rearrangement
- How do furnace chamber working conditions influence the choice of a tube furnace? Optimize Performance and Cost
- How is the sealing condition achieved in a vacuum tube experimental furnace? Master Precise Atmosphere Control
- Why is a high-precision tube furnace required during Fe-Mn catalyst synthesis? Control Morphology and CNF Quality
- What precautions should be taken regarding liquids and metals in a tube furnace? Ensure Safety and Prevent Damage



















