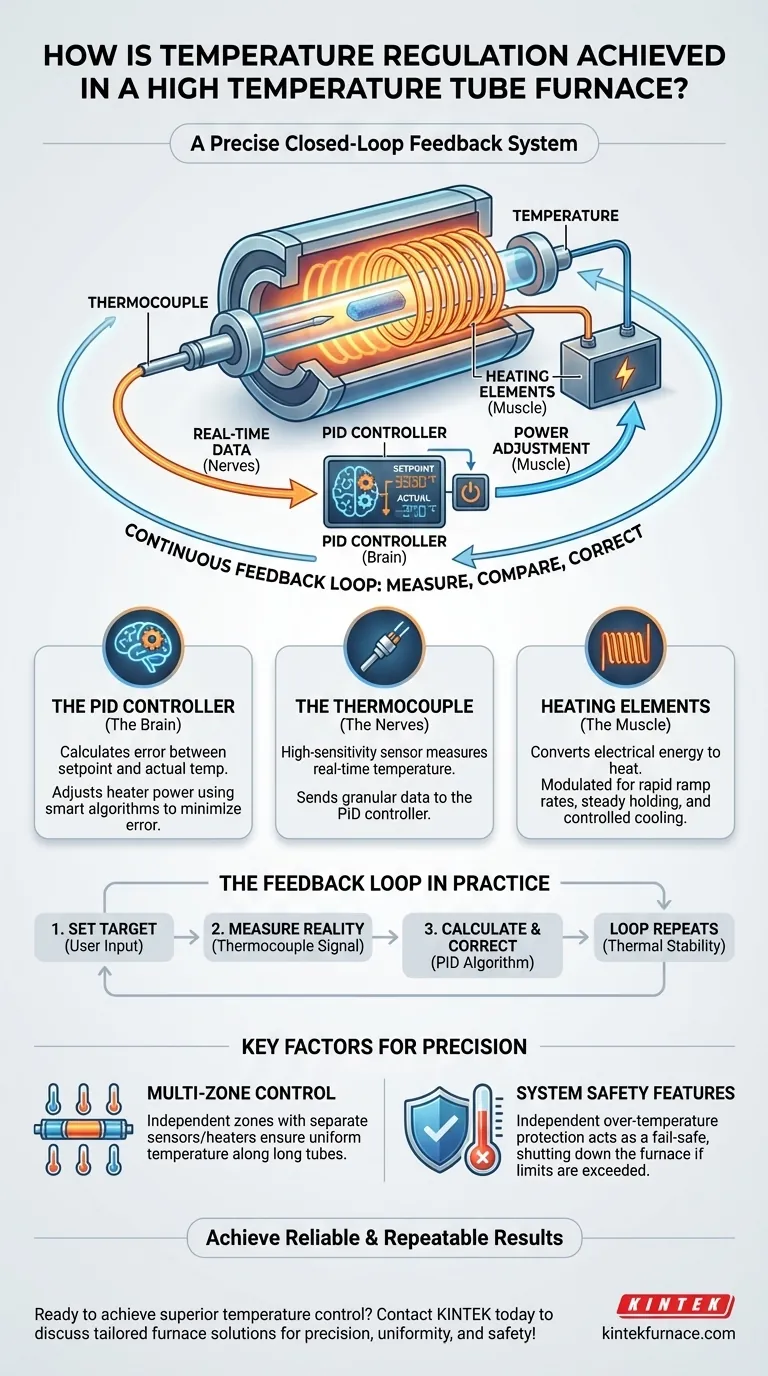
At its core, temperature regulation in a high-temperature tube furnace is achieved through a precise, closed-loop feedback system. The system's "brain," a PID controller, uses constant feedback from its "nerves," a thermocouple sensor, to precisely manage the power sent to the heating elements, ensuring the furnace temperature accurately matches the user's setpoint.
The key to understanding furnace temperature control is to see it not as a simple heater, but as an intelligent system. It constantly measures, compares, and corrects itself in a continuous feedback loop to maintain thermal stability with remarkable accuracy.

The Core Components of Temperature Control
Achieving a stable and accurate temperature depends on three critical components working in perfect synergy. Each plays a distinct and irreplaceable role in the feedback loop.
The Brain: The PID Controller
A PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller is the advanced processing unit that governs the entire heating process. It's more than a simple thermostat; it uses a sophisticated algorithm to make intelligent decisions.
The controller continuously calculates the difference, or "error," between your desired temperature (setpoint) and the actual measured temperature. It then adjusts power to the heaters to minimize this error, preventing both overshooting and undershooting the target.
The Nerves: The Thermocouple
The thermocouple is the high-sensitivity temperature sensor inside the furnace. It functions as the nervous system, providing the real-time temperature data that the PID controller needs to make its calculations.
High-resolution thermocouples are essential for this process. They can detect minute temperature changes, providing the PID controller with the granular data required for precise adjustments.
The Muscle: The Heating Elements
The heating elements, typically coils of a resistant material wrapped around the furnace tube, are the components that do the physical work. They convert electrical energy into heat.
The PID controller doesn't just turn them on or off. It modulates the amount of power sent to the elements, allowing for rapid heating (ramp rate), steady holding temperatures, and even controlled, programmable cooling.
How the System Works: The Feedback Loop in Practice
The process of regulation is a dynamic, continuous cycle that happens many times per second to maintain thermal stability.
1. Setting the Target
The process begins when the user inputs a desired temperature profile into the fully programmable control system. This can be a single temperature or a complex series of steps over time.
2. Measuring the Reality
As the furnace heats up, the thermocouple constantly measures the actual temperature inside the process tube and sends this information back to the PID controller as a voltage signal.
3. Calculating the Error & Correcting
The PID controller compares the thermocouple's real-time reading to the programmed setpoint. Based on the size and direction of the error, its algorithm calculates the exact power adjustment needed.
This cycle of measure, compare, correct repeats continuously, ensuring the furnace temperature adheres tightly to the programmed profile throughout the entire process.
Understanding the Key Factors for Precision
While the core loop is simple in concept, several factors determine the ultimate performance and uniformity of the heat.
Multi-Zone Control
For longer furnace tubes, maintaining a perfectly uniform temperature along the entire length is a challenge. High-end furnaces solve this with multi-zone control.
These systems divide the furnace into several independent heating zones, each with its own heating element and thermocouple. The main controller manages each zone separately, ensuring a highly uniform temperature profile across the entire sample area.
System Safety Features
Precision is useless without safety. Modern furnaces incorporate critical safety mechanisms that operate alongside the primary control loop.
Over-temperature protection acts as a crucial fail-safe. It's an independent controller that monitors the temperature and will shut down the furnace completely if it exceeds a maximum safety limit, protecting both the sample and the equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the control system allows you to select a furnace that aligns directly with your research or production requirements.
- If your primary focus is process precision: Prioritize a furnace with a well-tuned PID controller and a high-resolution thermocouple to minimize temperature deviation.
- If your primary focus is sample uniformity: A furnace with multi-zone control is non-negotiable for ensuring consistent results across larger samples or along the length of the tube.
- If your primary focus is running long, automated processes: Demand robust safety features, especially independent over-temperature protection, for safe, unattended operation.
Mastering your furnace begins with understanding that its temperature control is an active and intelligent system, empowering you to achieve reliable and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role | Function |
|---|---|---|
| PID Controller | Brain | Calculates error and adjusts power using algorithms for precise temperature control |
| Thermocouple | Nerves | Measures real-time temperature and sends feedback to the controller |
| Heating Elements | Muscle | Converts electrical energy to heat, modulated for ramp rates and holding temperatures |
| Multi-Zone Control | Enhancer | Manages multiple zones for uniform temperature across long tubes |
| Safety Features | Protector | Includes over-temperature protection for safe, unattended operation |
Ready to achieve superior temperature control in your lab? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can enhance your precision, uniformity, and safety!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















