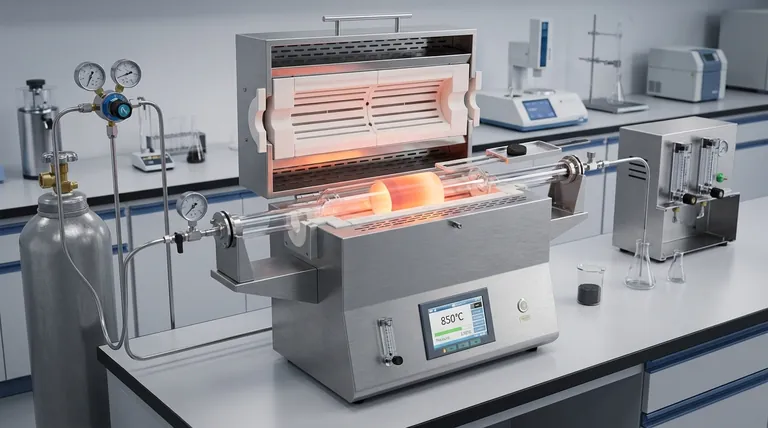
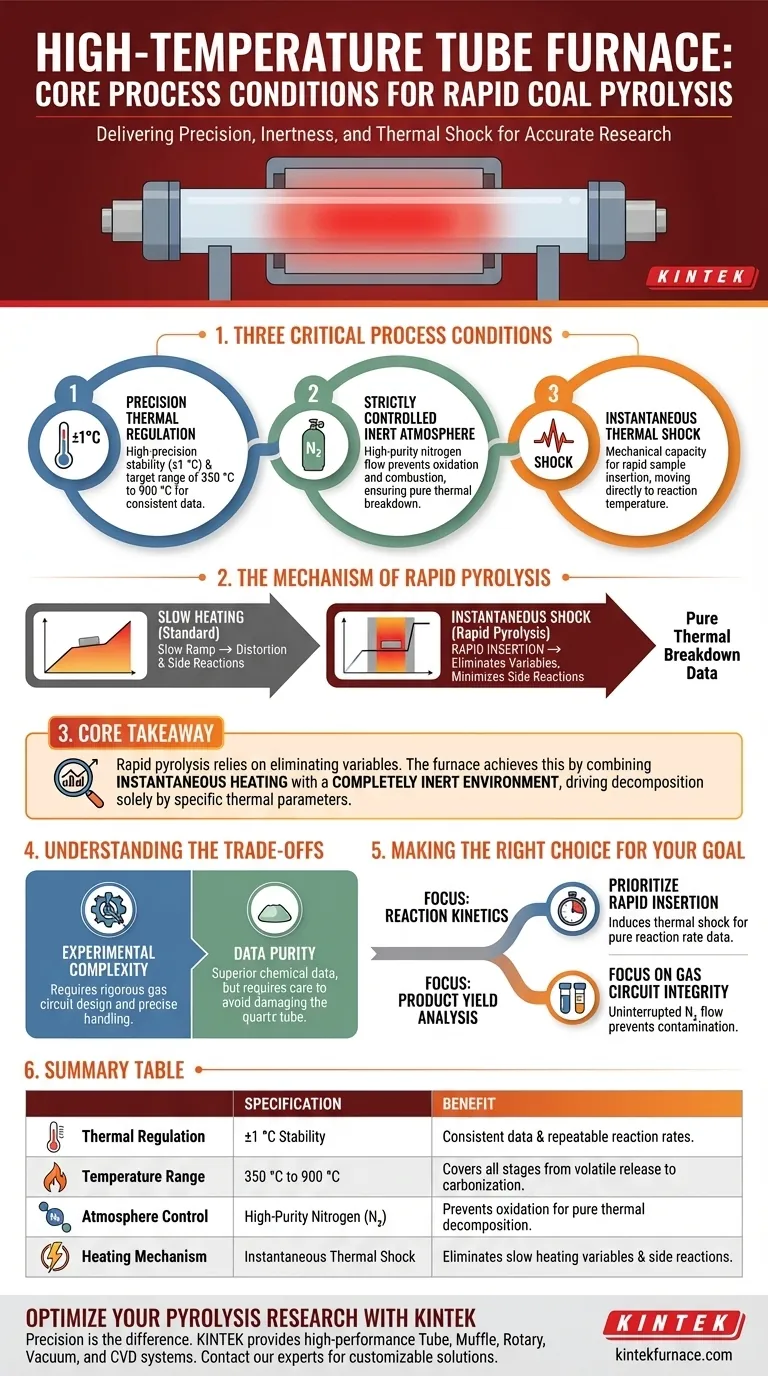
A high-temperature tube furnace delivers three critical process conditions: high-precision thermal regulation (±1 °C), a strictly controlled inert atmosphere using high-purity nitrogen, and the mechanical capacity for instantaneous thermal shock.
By utilizing a specialized quartz reaction tube and gas circuit system, the furnace isolates the coal sample from oxygen while allowing for rapid insertion into the central heating zone. This facilitates an immediate jump from pretreatment temperatures to reaction temperatures between 350 °C and 900 °C, ensuring the rapid pyrolysis occurs without interference from slow heating rates or oxidation.
Core Takeaway Rapid pyrolysis relies on eliminating variables that distort data. The high-temperature tube furnace achieves this by combining instantaneous heating with a completely inert environment, preventing undesirable side reactions and ensuring that the resulting decomposition is driven solely by specific thermal parameters.

Precision Thermal Control
High-Precision Stability
The fundamental requirement for accurate pyrolysis study is thermal consistency. High-temperature tube furnaces provide a high-precision temperature control environment, maintaining stability within ±1 °C.
Target Temperature Range
These furnaces operate effectively across a broad thermal spectrum, specifically between 350 °C and 900 °C.
This wide range allows researchers to investigate various stages of coal decomposition, from initial volatile release to deep carbonization.
Atmospheric Regulation
The Necessity of an Inert Environment
Pyrolysis is defined by thermal decomposition in the absence of oxygen. To achieve this, the furnace utilizes a gas circuit control system to introduce high-purity nitrogen.
Preventing Oxidation
The design ensures a completely inert atmosphere within the quartz reaction tube.
This eliminates the risk of combustion or oxidation, ensuring that the liquid bio-oil, solid char, and gases produced are the result of pure thermal breakdown rather than reaction with ambient air.
The Mechanism of Rapid Pyrolysis
Instantaneous Thermal Shock
Unlike standard heating where a sample slowly ramps up in temperature, rapid pyrolysis requires an immediate transition.
The design of the central reaction zone allows for the rapid insertion of coal samples. This subjects the material to instantaneous thermal shock, moving it from low pretreatment temperatures directly to the target reaction temperature.
Minimizing Side Reactions
The speed of this transition is critical for chemical accuracy.
By bypassing the slow heating phase, the process minimizes undesirable intermediate side reactions. This ensures the final product distribution reflects the true pyrolysis behavior at the target temperature, rather than artifacts created during a slow temperature ramp.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Experimental Complexity vs. Data Purity
While the "rapid insertion" method provides superior chemical data, it introduces mechanical complexity.
Maintaining the integrity of the inert nitrogen atmosphere while physically moving a sample into the hot zone requires rigorous adherence to the gas circuit design.
Material Constraints
The use of a quartz reaction tube enables excellent thermal transparency and chemical inertness, but it also imposes physical limits.
Quartz is susceptible to thermal stress; therefore, the "shock" applies to the sample, not the tube itself. Operators must ensure the equipment is handled precisely to avoid damaging the core containment vessel during rapid sample loading.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of a high-temperature tube furnace, align your operational procedures with your specific research objectives.
- If your primary focus is Reaction Kinetics: Prioritize the rapid insertion mechanism to induce thermal shock, as this eliminates the variable of heating time and provides data on pure reaction rates.
- If your primary focus is Product Yield Analysis: Focus on the gas circuit integrity, ensuring high-purity nitrogen flow is uninterrupted to prevent oxygen contamination of the resulting oils and chars.
Success in rapid pyrolysis is defined by the ability to isolate the sample from everything except the specific heat and atmosphere you intend to study.
Summary Table:
| Process Condition | Technical Specification | Benefit for Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Regulation | ±1 °C Stability | Ensures consistent data and repeatable chemical reaction rates. |
| Temperature Range | 350 °C to 900 °C | Covers all stages from volatile release to deep carbonization. |
| Atmosphere Control | High-Purity Nitrogen (N₂) | Prevents oxidation, ensuring pure thermal decomposition. |
| Heating Mechanism | Instantaneous Thermal Shock | Eliminates variables from slow heating and minimizes side reactions. |
Optimize Your Pyrolysis Research with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between accurate kinetics and distorted data. KINTEK provides high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of rapid pyrolysis and material science. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our furnaces offer the precise thermal stability and advanced gas circuit control necessary for your laboratory's success.
Whether you need a specialized quartz reaction tube or a fully customizable high-temperature furnace, KINTEK delivers the reliability you require. Contact our technical experts today to discuss your unique research needs and discover how our customizable solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency.
Visual Guide
References
- Tao Xu, Zhifu Yang. Characteristics of Pyrolysis Products of Tar-Rich Coal Under Cryogenic Pretreatment with Liquid Nitrogen. DOI: 10.3390/pr13041064
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do vertical tube furnaces contribute to advancements in material science and industrial production? Unlock Precision in Material Innovation
- Why is heat treatment in a tube furnace or muffle furnace required after synthesizing magnesium hydroxide nano-precursors via electrochemical methods? Unlock the Full Potential of Your MgO Nanomaterials
- What is the importance of using a quartz tube for water quenching? Ensure Alloy Integrity with Thermal Shock Resistance
- What is the purpose of using a tube furnace during the reduction phase of graphite flake surface treatment?
- What are the two core technical functions of a vacuum tube sintering furnace? Mastering Porous Alloy Engineering
- What is a tube furnace and what are its primary uses? Essential for Controlled High-Temperature Processes
- What is the significance of using a tubular furnace in waste salt pyrolysis research? Precision for High-Fidelity Data
- Why is a tube furnace used for Solid State Polycondensation? Master Molecular Weight Control in SSP



















