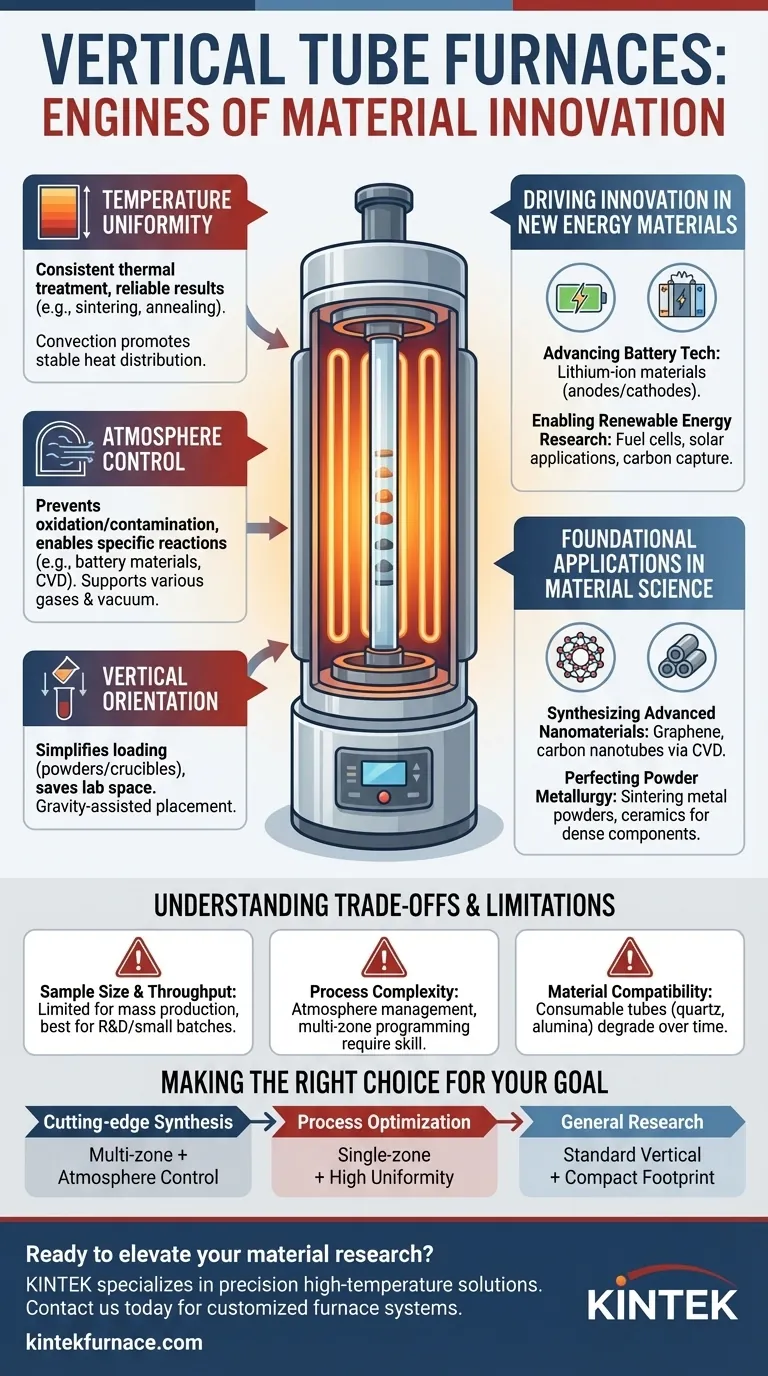
At their core, vertical tube furnaces are the engines of modern material innovation. They contribute to scientific and industrial advancements by providing an exceptionally uniform and precisely controlled high-temperature environment, which is essential for synthesizing and processing the high-performance materials that define next-generation technology.
The true value of a vertical tube furnace is not simply its ability to get hot. It is the precise combination of temperature uniformity, atmospheric control, and a vertical orientation that allows researchers and engineers to create materials with specific, repeatable properties that are unattainable with other methods.
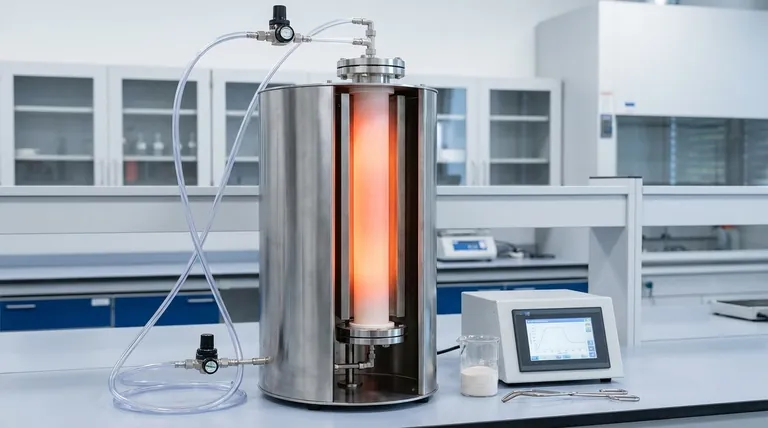

The Core Principles of Operation
The unique capabilities of a vertical tube furnace stem from three fundamental design advantages that work in concert. Understanding these principles is key to grasping their impact.
Achieving Exceptional Temperature Uniformity
A vertical furnace design naturally promotes convection, leading to highly stable and uniform heat distribution along the length of the process tube.
This uniformity is critical. It ensures that every part of a sample receives the exact same thermal treatment, eliminating inconsistencies and leading to reliable, repeatable results in processes like sintering and annealing.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere Management
Modern material synthesis rarely happens in open air. These furnaces are designed to be sealed, allowing for the introduction of specific gases or the creation of a vacuum.
This atmosphere control prevents unwanted oxidation or contamination and enables specific chemical reactions. It is essential for producing high-purity materials like battery cathodes or for processes like carbonization.
The Advantage of Vertical Orientation
The vertical setup simplifies the loading and unloading of samples, especially for powders, crucibles, or components that benefit from gravity-assisted placement.
This orientation is also ideal for certain growth processes and helps conserve valuable laboratory space due to its smaller footprint compared to a horizontal furnace of similar capacity.
Driving Innovation in New Energy Materials
Vertical tube furnaces are indispensable in the race for cleaner energy. Their precision is a prerequisite for developing the next generation of energy storage and production materials.
Advancing Battery Technology
They are central to producing and testing materials for lithium-ion batteries. Processes like the graphitization of anodes and the synthesis of high-performance cathode materials require the exact temperature and atmospheric conditions that these furnaces provide.
Enabling Renewable Energy Research
From preparing materials for fuel cells to conducting biomass pyrolysis for biofuel production, vertical tube furnaces offer the controlled environment needed to test and validate new concepts. They are also used to develop materials for solar applications and carbon capture technologies.
Foundational Applications in Material Science
Beyond energy, these furnaces are a cornerstone of fundamental materials research and development across numerous fields.
Synthesizing Advanced Nanomaterials
The creation of materials like graphene and carbon nanotubes often relies on a process called chemical vapor deposition (CVD), for which a tube furnace is the standard instrument. The controlled environment is perfect for growing these highly structured materials.
Perfecting Powder Metallurgy and Sintering
In powder metallurgy, vertical furnaces are used to sinter compacted metal powders into solid, high-precision parts. In ceramics, they provide the uniform heat needed to create dense, durable components with consistent structural integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, vertical tube furnaces are not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires understanding their limitations.
Sample Size and Throughput
These furnaces are typically designed for research, development, and small-batch production. Their tube diameter and heated zone length inherently limit the size and quantity of material that can be processed at one time, making them less suitable for mass industrial production.
Process Complexity
Achieving and maintaining a specific atmosphere requires careful management of gas flow, pressure, and sealing. Multi-zone furnaces, while offering superior temperature profiling, add another layer of complexity to operation and programming.
Material Compatibility and Lifespan
The process tube, often made of quartz, alumina, or silicon carbide, is a consumable component. It can be degraded by extreme temperatures, rapid heating/cooling cycles, or reactions with the sample materials, requiring periodic replacement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting and using a vertical tube furnace effectively depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is cutting-edge material synthesis (e.g., nanomaterials, batteries): Prioritize a multi-zone furnace with advanced atmosphere control to achieve precise temperature gradients and ensure absolute material purity.
- If your primary focus is process optimization and quality control: A high-quality single-zone furnace is ideal, as its exceptional temperature uniformity ensures high repeatability for consistent batch processing.
- If your primary focus is general research in a constrained lab: The versatility and compact footprint of a standard vertical tube furnace make it a highly efficient and capable tool for a wide range of thermal processing tasks.
Mastering the capabilities of this instrument is fundamental to unlocking the next generation of material performance.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Uniformity | Ensures consistent thermal treatment for reliable results | Sintering, annealing, material synthesis |
| Atmosphere Control | Prevents contamination and enables specific reactions | Battery material production, CVD processes |
| Vertical Orientation | Simplifies loading/unloading and saves lab space | Powder handling, growth processes, R&D labs |
Ready to elevate your material research with precision high-temperature solutions? KINTEK specializes in advanced furnace systems tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your experimental requirements are met with reliability and innovation. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can drive your advancements in material science and industrial production!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety



















