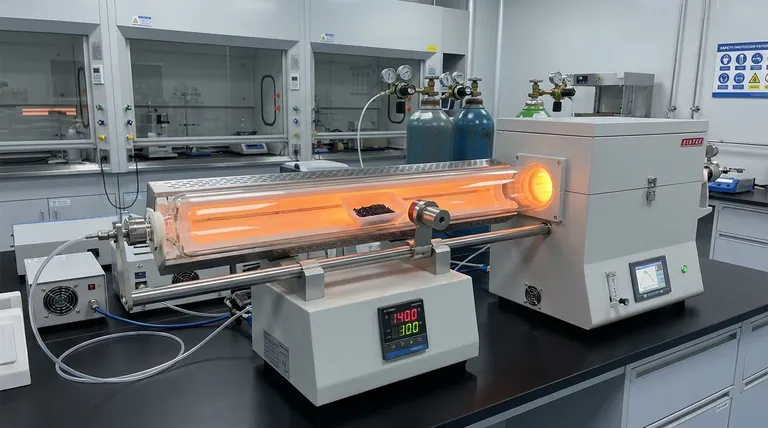
Precision control over reactant introduction and thermal history is essential for high-quality CVD growth. The positioning of the quartz boat dictates the gas diffusion path required for uniform deposition, while an external magnetic drive enables exact timing of the reaction onset. Together, these mechanisms allow you to isolate the specific single-phase monoclinic beta-Cu2-xSe structure by strictly managing the heating and cooling cycles.
By mechanically isolating the selenium source until the optimal temperature is reached—and withdrawing it instantly afterward—you effectively eliminate the thermal inconsistencies that lead to impure, multi-phase structures.

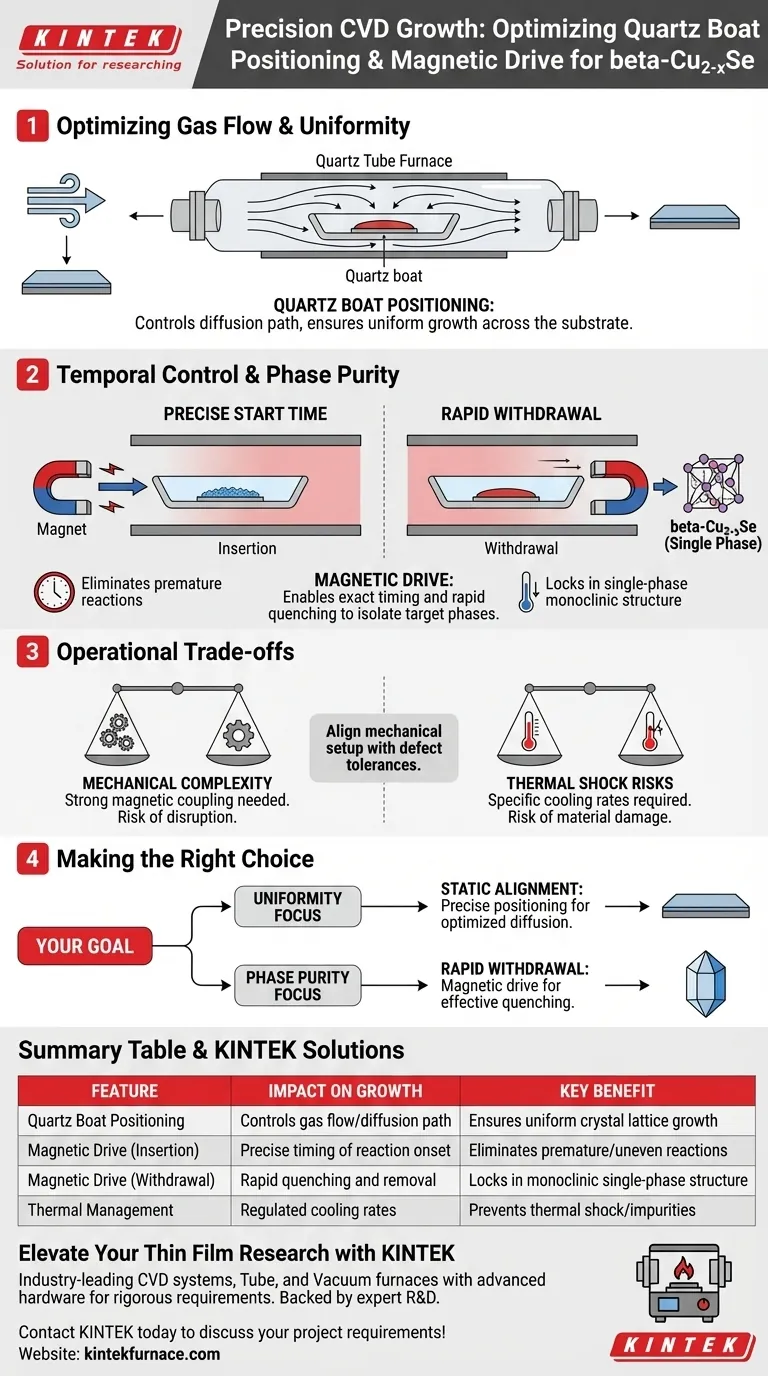
Optimizing Gas Flow and Uniformity
Defining the Diffusion Path
The physical location of the quartz boat within the furnace tube is not arbitrary; it acts as a primary variable in the deposition process.
The boat's position determines the diffusion path of the gas flow.
Ensuring Uniform Growth
To achieve a consistent layer across the substrate, the gas must flow predictably.
Correct positioning ensures the reactants diffuse evenly, which is critical for the uniform growth of the crystal lattice.
Temporal Control and Phase Purity
Controlling Reaction Start Time
In standard setups, reactants often heat up gradually with the furnace, leading to premature or uneven reactions.
Utilizing an external magnetic drive solves this by keeping the selenium powder in a cool zone until the furnace is ready.
You can then push the boat into the preheated zone at the exact moment required, granting strict control over the reaction's start time.
The Necessity of Rapid Withdrawal
The magnetic drive provides a critical function at the end of the growth cycle as well.
It allows for the rapid withdrawal of the boat from the heat source immediately after the reaction is complete.
Locking in the Single Phase
This mechanical removal is combined with specific cooling rates to act as a physical safeguard.
Rapidly removing the heat prevents the material from settling into unwanted thermodynamic states.
This ensures the formation of single-phase monoclinic beta-Cu2-xSe, effectively avoiding the creation of inferior multi-phase products.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Mechanical Complexity
Introducing an external magnetic drive adds a moving mechanical variable to a sealed system.
You must ensure the magnetic coupling is strong enough to move the loaded boat without slipping, which could disrupt the critical timing of the process.
Thermal Shock Risks
While rapid withdrawal is necessary for phase purity, it introduces drastic thermal changes.
You must adhere to specific cooling rates to prevent thermal shock, which could damage the quartz ware or crack the newly grown crystal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your beta-Cu2-xSe growth, align your mechanical setup with your specific defect tolerances:
- If your primary focus is Uniformity: Prioritize the precise static alignment of the quartz boat to optimize the gas diffusion path over the substrate.
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Rely on the external magnetic drive to execute a rapid withdrawal, quenching the sample to prevent multi-phase contamination.
Mastering the physical movement of your reactants is just as critical as mastering the chemistry itself.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Impact on Growth | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Quartz Boat Positioning | Controls gas flow and diffusion path | Ensures uniform crystal lattice growth |
| Magnetic Drive (Insertion) | Precise timing of reaction onset | Eliminates premature/uneven reactions |
| Magnetic Drive (Withdrawal) | Rapid quenching and removal from heat | Locks in monoclinic single-phase structure |
| Thermal Management | Regulated cooling rates | Prevents thermal shock and multi-phase impurities |
Elevate Your Thin Film Research with KINTEK
Precision in CVD growth requires more than just chemistry; it demands advanced hardware. KINTEK provides industry-leading CVD systems, Tube, and Vacuum furnaces designed for the rigorous requirements of semiconductor and material science.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems offer the customizable zones and mechanical controls necessary for isolating complex phases like monoclinic beta-Cu2-xSe. Don't let thermal inconsistencies compromise your results. Whether you need a standard setup or a fully customized high-temperature furnace, KINTEK has the expertise to support your lab's unique needs.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Srijith Srijith, Gilbert Daniel Nessim. Chemical-Vapor-Deposition-Synthesized Two-Dimensional Non-Stoichiometric Copper Selenide (β-Cu2−xSe) for Ultra-Fast Tetracycline Hydrochloride Degradation under Solar Light. DOI: 10.3390/molecules29040887
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of using a CVD furnace? Achieve Atomic-Level Control for Superior Thin Films
- What are the disadvantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Key Challenges and Trade-offs
- What types of substrates are not suitable for CVD? Avoid Thermal and Geometric Pitfalls
- What role does a vacuum thermal evaporation system play in the fabrication of Cu13Se52Bi35 thin films? Expert Guide
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of LPCVD? Unlock Superior Film Quality for Complex Applications
- What are the advantages of using CVD for CNC machining? Boost Durability and Efficiency in Precision Parts
- How are CVD furnaces used in nanomaterial synthesis? Unlock High-Purity Materials for Advanced Applications
- What are the differences in film quality between PVD and CVD? Discover the Best Method for Your Application



















