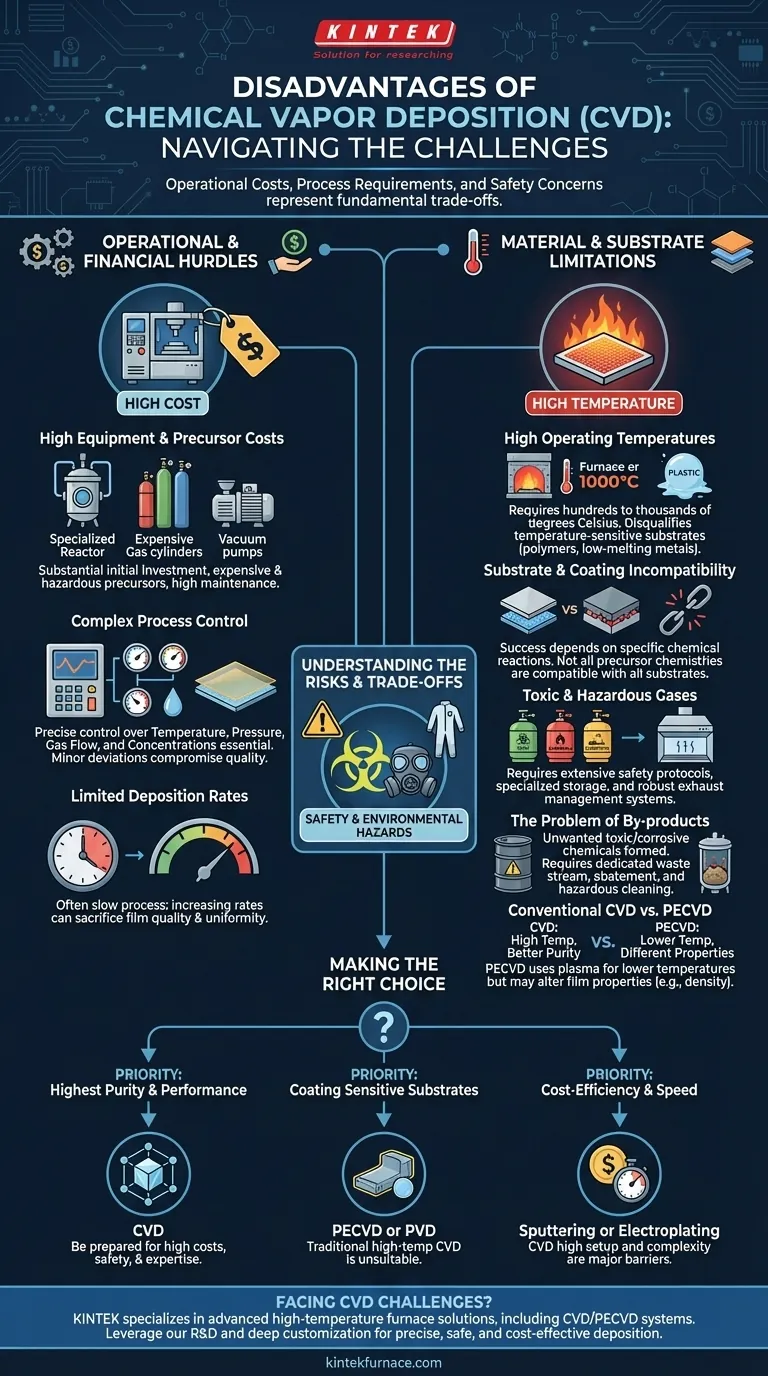
The primary disadvantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) are its high operational costs, demanding process requirements, and significant safety concerns. These challenges stem from the high temperatures needed for the chemical reactions, the expensive and often hazardous precursor gases used, and the complexity of controlling the deposition environment to achieve a uniform, high-quality film.
While Chemical Vapor Deposition is unparalleled for producing high-purity, high-performance thin films, its drawbacks are not minor inconveniences. They represent fundamental trade-offs in cost, safety, and operational complexity that must be carefully weighed against the desired material properties.

Operational and Financial Hurdles
To understand if CVD is a viable process for your goal, you must first account for its significant operational and financial demands. These factors often represent the highest barrier to entry.
High Equipment and Precursor Costs
The initial investment in a CVD reactor and its associated systems (vacuum pumps, gas delivery, exhaust treatment) is substantial. These systems require specialized engineering to handle high temperatures and corrosive chemicals.
Furthermore, the precursor gases—the chemical building blocks for the film—can be extremely expensive, especially those required for high-purity or exotic materials. Ongoing maintenance costs for these complex machines also contribute to a high total cost of ownership.
Complex Process Control
Achieving a perfect film requires precise, simultaneous control over multiple variables, including temperature, pressure, gas flow rates, and chemical concentrations.
Even minor deviations can compromise the film's thickness, uniformity, and composition. This complexity demands sophisticated control systems and highly skilled operators, adding to the operational overhead.
Limited Deposition Rates
CVD is often a relatively slow process. The chemical reactions on the substrate surface take time, which can limit throughput for large-scale manufacturing. While rates can be increased, this often comes at the expense of film quality or uniformity.
Material and Substrate Limitations
Beyond the operational costs, CVD has inherent physical and chemical limitations that restrict its application.
High Operating Temperatures
Traditional CVD processes operate at very high temperatures, often several hundred to over a thousand degrees Celsius, to provide the energy needed for the chemical reactions.
This heat requirement immediately disqualifies many temperature-sensitive substrates, such as polymers or certain low-melting-point metals. The high heat can damage or destroy the very material you intend to coat.
Substrate and Coating Incompatibility
The success of CVD depends on specific chemical reactions occurring on the substrate surface. Not all precursor chemistries are compatible with all substrate materials, which can limit the possible combinations of coatings and parts.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Inherent Risks
The "disadvantages" of CVD are deeply intertwined with the very chemistry that makes it so effective. Understanding these trade-offs is key to determining its suitability.
Safety and Environmental Hazards
Many precursor gases used in CVD are highly toxic, flammable, or corrosive. This necessitates extensive safety protocols, specialized storage, and robust exhaust management systems to neutralize hazardous by-products before they are released.
The risk of leaks or improper handling poses a significant danger to personnel and the environment, making safety infrastructure a non-negotiable expense.
The Problem of By-products
The chemical reactions that form the desired film also create unwanted chemical by-products. These substances can be toxic and corrosive, requiring a dedicated waste stream and abatement system. Over time, these by-products can also build up inside the reactor, necessitating periodic, hazardous cleaning cycles.
Conventional CVD vs. Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
To overcome the temperature limitation, variants like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) were developed. PECVD uses plasma to energize the precursor gases, allowing deposition to occur at much lower temperatures.
However, this introduces its own trade-off. While enabling work with sensitive substrates, PECVD films may have different properties (like lower density or incorporated hydrogen) compared to their high-temperature counterparts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a deposition method requires aligning its capabilities and drawbacks with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible film purity and performance: CVD is often the superior choice, but you must be prepared to invest heavily in the required equipment, safety infrastructure, and process expertise.
- If your primary focus is coating temperature-sensitive substrates (e.g., plastics): Traditional high-temperature CVD is entirely unsuitable; you must investigate lower-temperature variants like PECVD or alternative technologies like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency or rapid, flexible production: The high setup costs, process complexity, and safety overhead of CVD make other methods, such as sputtering or electroplating, a more practical choice.
Understanding these disadvantages is the first step toward leveraging Chemical Vapor Deposition for its strengths while respecting its significant limitations.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage Category | Key Issues |
|---|---|
| Operational & Financial | High equipment and precursor costs, complex process control, limited deposition rates |
| Material & Substrate | High operating temperatures, substrate incompatibility |
| Safety & Environmental | Toxic/hazardous gases, by-product management, safety infrastructure needs |
| Trade-offs | Temperature limitations vs. film quality (e.g., PECVD alternatives) |
Facing CVD challenges? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD systems, with deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing for precise, safe, and cost-effective thin-film deposition. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of PECVD tube furnaces compared to CVD tube furnaces? Lower Temp, Faster Deposition, and More
- What is the role of temperature in PECVD? Optimize Film Quality and Substrate Protection
- How does a CVD system ensure the quality of carbon layers? Achieving Nanometer Precision with KINTEK
- What are gas barrier films, and how is PECVD involved in their creation? Discover Advanced Packaging Solutions
- What is the difference between PVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Coating Technology



















