Defining accurate heat transfer coefficients and thermal contact resistance is the cornerstone of reliable thermal stress analysis in slag simulations. Without these precise parameters, it is impossible to correctly simulate the dynamic heat exchange between the slag and the mold, particularly as physical gaps form during the solidification process.
Core Insight: Accurate thermal parameters are the only way to account for the insulating air gaps caused by volume shrinkage. This precision is required to calculate the exact temperature gradients that drive thermal stress and ultimately cause cracking.

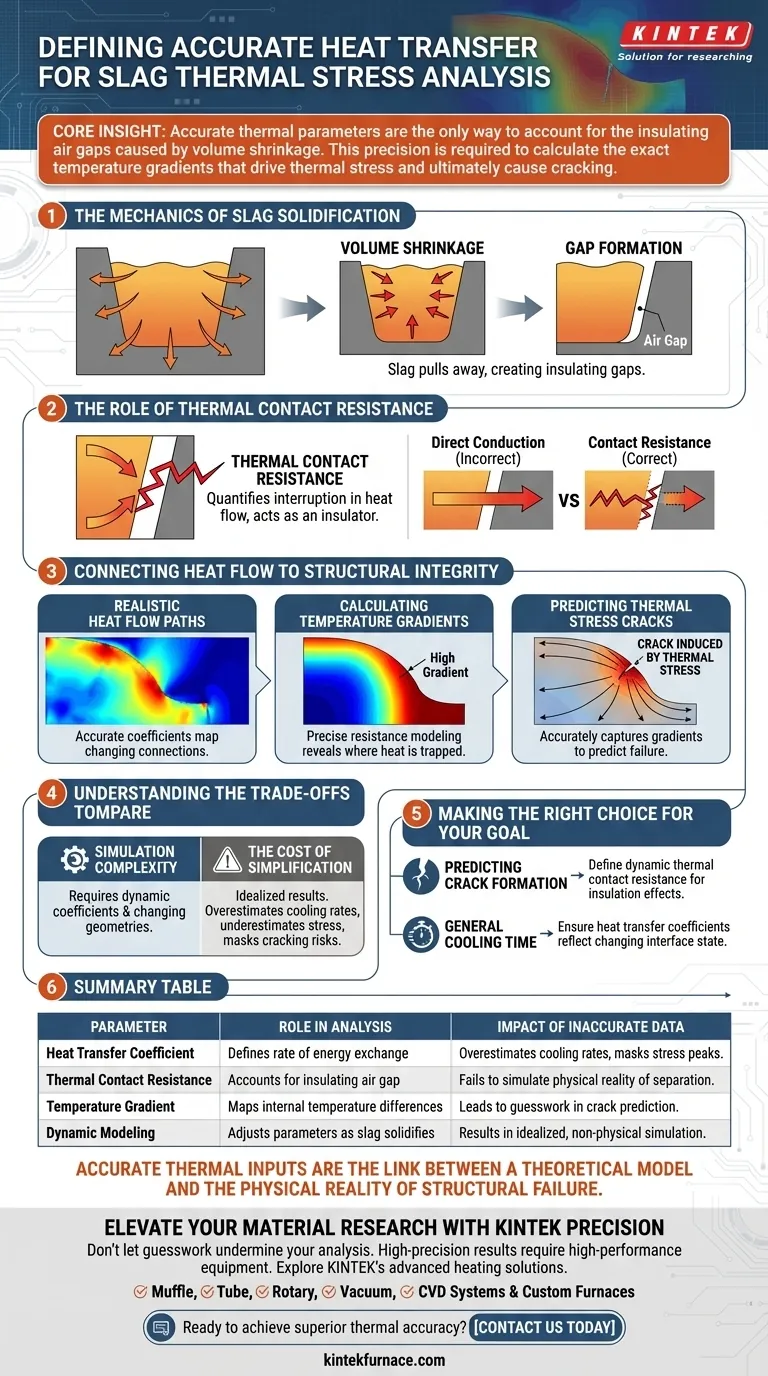
The Mechanics of Slag Solidification
Volume Shrinkage and Gap Formation
As slag cools and solidifies, it undergoes significant volume shrinkage. This is not a uniform process; it creates physical changes in the geometry of the casting environment.
Consequently, the slag pulls away from the mold walls. This separation creates gaps between the material and the containment vessel.
The Role of Thermal Contact Resistance
Once a gap forms, the heat exchange mechanism changes fundamentally. Heat can no longer conduct directly from the slag to the mold.
Thermal contact resistance is the parameter that quantifies this interruption in heat flow. It creates a realistic representation of how the air gap acts as an insulator, slowing down the rate of heat loss in specific areas.
Connecting Heat Flow to Structural Integrity
Establishing Realistic Heat Flow Paths
Defining the correct heat transfer coefficients allows the simulation to map realistic heat flow paths.
If these coefficients are generic or static, the model assumes a constant connection between the slag and mold. This leads to a simulation that does not reflect the actual physical environment where the slag is detaching from the wall.
Calculating Temperature Gradients
Thermal stress is driven by differences in temperature within the material, known as temperature field gradients.
By accurately modeling the resistance at the mold interface, you can calculate these gradients with high precision. You can see exactly where the slag is cooling rapidly and where heat is trapped.
Predicting Thermal Stress Cracks
The ultimate goal of this analysis is predicting failure.
High temperature gradients lead to internal tension. If the simulation accurately captures these gradients via precise thermal parameters, it can successfully predict cracks induced by thermal stress. Without these inputs, crack prediction becomes guesswork.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Simulation Complexity vs. Reality
Incorporating dynamic heat transfer coefficients and contact resistance adds complexity to the model. It requires accounting for changing geometries (shrinkage) rather than static boundaries.
The Cost of Simplification
However, simplifying these parameters leads to idealized results. Ignoring the contact resistance caused by shrinkage gaps will usually result in an overestimation of cooling rates.
This inevitably leads to an underestimation of thermal stress, potentially masking the very cracking risks the simulation was designed to detect.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the value of your simulation, align your parameter precision with your specific analytical goals:
- If your primary focus is predicting crack formation: You must define dynamic thermal contact resistance to account for the insulation effects of gap formation during shrinkage.
- If your primary focus is general cooling time: You must ensure heat transfer coefficients are not static, but reflect the changing state of the slag-mold interface.
Accurate thermal inputs are not just data points; they are the link between a theoretical model and the physical reality of structural failure.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Role in Thermal Stress Analysis | Impact of Inaccurate Data |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Transfer Coefficient | Defines the rate of energy exchange between slag and mold. | Overestimates cooling rates and masks stress peaks. |
| Thermal Contact Resistance | Accounts for the insulating air gap created by volume shrinkage. | Fails to simulate the physical reality of material separation. |
| Temperature Gradient | Maps internal temperature differences that drive structural tension. | Leads to guesswork in predicting thermal stress cracks. |
| Dynamic Modeling | Adjusts parameters as the slag solidifies and detaches. | Results in idealized, non-physical simulation outcomes. |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Don't let guesswork undermine your thermal analysis. At KINTEK, we understand that high-precision results require high-performance equipment. Whether you are analyzing slag behavior or developing new materials, our expert R&D and manufacturing teams provide the tools you need to succeed.
We offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as other lab high-temperature furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique simulation and heat treatment requirements.
Ready to achieve superior thermal accuracy? Contact us today to discover how KINTEK’s advanced heating solutions can empower your lab's next breakthrough.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the process advantages of using PVT compared to solution methods for organic crystals? Enhance Purity & Uniformity
- What mechanisms generate heat in induction heating? Discover the Science of Efficient Material Processing
- How does temperature control in carbonization furnaces affect structural battery anodes? Optimize Fiber Performance
- Why is uniform thermal distribution critical for silica nanoparticle synthesis? Achieve 100% Phase Transformation
- What are the technical functions of carrier gases in VTD? Master Vapor Transport Deposition Control
- What role does activation treatment play in converting PPS waste? Unlock High-Performance Energy Storage Pores
- What is the technical value of using a vacuum drying oven? Master Platinum Catalyst Precision and Activity
- How does an annealing furnace work? A Guide to Controlled Heat Treatment



















