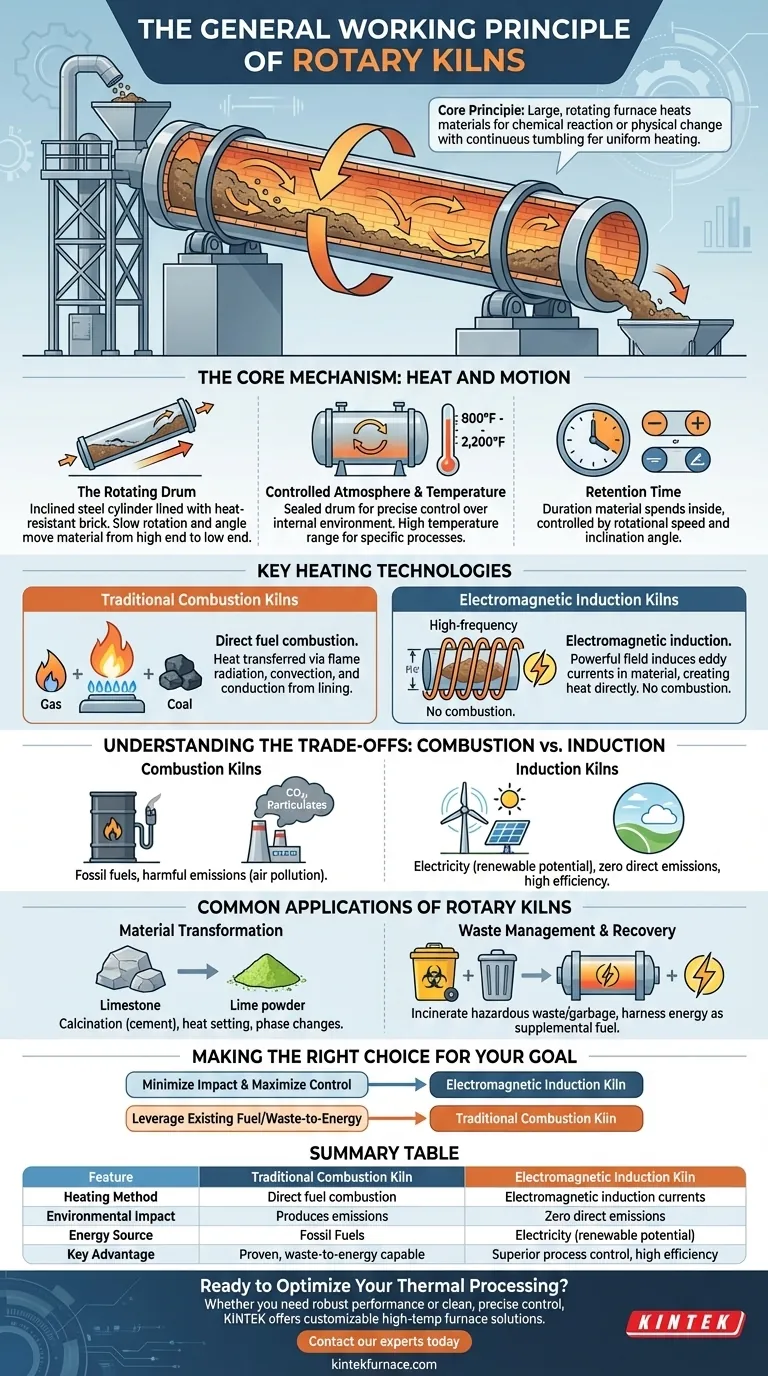
At its core, a rotary kiln is a large, rotating industrial furnace designed to heat solid materials to very high temperatures. This process is used to induce a specific chemical reaction or a physical change, with the constant tumbling motion ensuring every particle is heated uniformly.
The fundamental principle of a rotary kiln is controlled thermal processing. By combining intense heat with continuous, gentle agitation inside an inclined, rotating cylinder, it creates a highly controlled environment to transform raw materials into processed products.

The Core Mechanism: Heat and Motion
A rotary kiln's effectiveness comes from the elegant combination of a few simple physical principles working in concert.
The Rotating Drum
The main body of the kiln is a long steel cylinder lined with heat-resistant brick. It is mounted at a slight angle to the horizontal.
This incline, combined with slow rotation, causes material fed into the higher end to gradually travel down to the lower end, ensuring a consistent flow.
Controlled Atmosphere and Temperature
The drum is sealed at both ends. This allows operators to maintain precise control over the internal atmosphere and temperature, which is critical for achieving the desired chemical reactions.
Kilns operate across a wide temperature range, typically from 800°F to over 2,200°F, depending on the specific process.
Retention Time
The duration a material spends inside the kiln is called retention time. This is a critical variable controlled by adjusting the kiln's rotational speed and angle of inclination.
Key Heating Technologies
How a kiln generates its intense heat is a primary distinction between different types of systems.
Traditional Combustion Kilns
This is the most established method, relying on the direct combustion of fuel like natural gas or coal.
A burner injects a flame into the kiln, and heat is transferred to the material through flame radiation, convection from hot gases, and conduction from the hot refractory brick lining.
Electromagnetic Induction Kilns
This modern approach uses electromagnetic induction heating technology, similar to a household induction cooktop.
High-frequency electrical currents create a powerful electromagnetic field. This field induces eddy currents within the material itself (if it's conductive) or a metal conductor, directly converting electrical energy into heat without any combustion.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Combustion vs. Induction
The choice of heating technology has significant operational and environmental consequences.
Environmental Impact
Combustion kilns inherently produce harmful emissions, including greenhouse gases and particulate matter, which contribute to air pollution.
Electromagnetic induction is a much cleaner process. Because it involves no burning of fuel, it eliminates the emission of harmful byproducts, making it a more environmentally friendly option.
Energy Source and Efficiency
Traditional kilns rely on fossil fuels. In contrast, induction kilns run on electricity, which can be sourced from renewable grids.
Induction heating is also often more efficient, as heat is generated directly within the material rather than being transferred from an external flame, reducing energy loss.
Common Applications of Rotary Kilns
The versatility of rotary kilns makes them essential in a wide range of industries.
Material Transformation
Kilns are widely used for processes like calcination, a key step in producing cement where limestone is heated to create lime and carbon dioxide. Other uses include heat setting and inducing various phase changes in materials.
Waste Management and Recovery
In a critical environmental application, cement kilns are used to incinerate hazardous waste and municipal garbage.
This process not only neutralizes harmful substances but also harnesses the energy from the waste, using it as a supplemental fuel source to reduce the consumption of coal or gas.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate kiln technology depends on balancing environmental regulations, operational costs, and process requirements.
- If your primary focus is minimizing environmental impact and maximizing process control: Electromagnetic induction kilns are the superior choice, offering emission-free operation and highly precise heating.
- If your primary focus is leveraging existing fuel infrastructure or processing waste-to-energy streams: Traditional combustion kilns remain a proven and effective technology, especially when adapted for resource recovery.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln's simple principle of combining heat and motion provides a powerful and adaptable platform for industrial material processing.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Traditional Combustion Kiln | Electromagnetic Induction Kiln |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Direct fuel combustion (gas, coal) | Electromagnetic induction currents |
| Environmental Impact | Produces emissions (CO2, particulates) | Zero direct emissions |
| Energy Source | Fossil Fuels | Electricity (potentially renewable) |
| Key Advantage | Proven technology, waste-to-energy capable | Superior process control, high efficiency |
Ready to Optimize Your Thermal Processing?
Whether you need the robust performance of a traditional combustion kiln or the clean, precise control of an electromagnetic induction system, KINTEK has the solution. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, CVD systems, and other lab high-temp furnaces, all customizable for your unique material processing needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior results with the right rotary kiln technology for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions



















