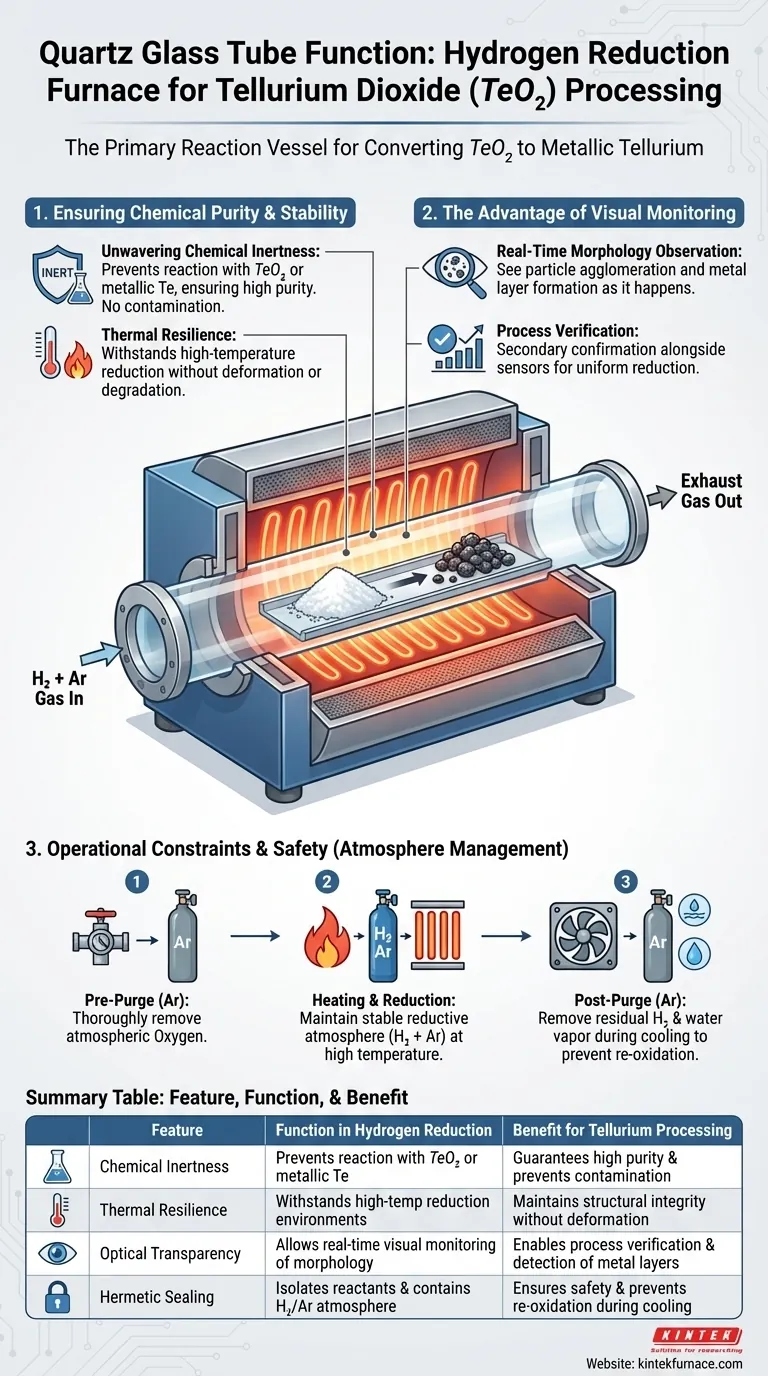
The quartz glass tube acts as the primary reaction vessel within the hydrogen reduction furnace setup. It provides a hermetically sealed, chemically inert environment necessary to convert tellurium dioxide ($TeO_{2}$) into metallic tellurium without introducing contaminants. Furthermore, its unique material properties allow it to withstand the rigorous thermal demands of the reduction process while offering optical transparency for real-time monitoring.
The quartz tube serves a dual purpose: it guarantees the purity of the metallic tellurium by preventing chemical cross-contamination, and its transparency enables real-time visual inspection of material changes during the critical reduction phase.

Ensuring Chemical Purity and Stability
The primary function of the quartz tube is to isolate the reactants from the outside environment and the heating elements of the furnace.
Unwavering Chemical Inertness
The most critical attribute of quartz glass in this application is its excellent chemical stability.
It does not react with the tellurium dioxide starting material or the resulting metallic tellurium. This inertness is vital for preventing the introduction of impurities, ensuring the final product maintains high purity.
Thermal Resilience
The reduction of tellurium dioxide requires a controlled high-temperature environment.
Quartz glass is specifically selected for its ability to withstand these high-temperature reduction environments without deforming or degrading. This ensures the structural integrity of the reaction vessel throughout the heating and dwelling phases.
The Advantage of Visual Monitoring
Unlike opaque ceramic or metal tubes, quartz glass offers a significant operational advantage: transparency.
Real-Time Morphology Observation
The transparency of the quartz allows operators to visually monitor the progress of the reaction inside the tube.
You can directly observe changes in material morphology, such as particle agglomeration. It also allows you to detect the formation of metal layers as the reduction proceeds, providing immediate feedback on the process status.
Process Verification
Visual access acts as a secondary verification method alongside temperature and gas flow sensors.
Seeing the physical transformation helps confirm that the reduction is occurring uniformly across the sample.
Operational Constraints and Safety
While the quartz tube handles the thermal and chemical loads, the integrity of the process relies on how the tube environment is managed.
Managing the Atmosphere
The tube must contain a stable reductive atmosphere, typically a mixture of hydrogen and argon.
To prevent explosions caused by mixing hydrogen with atmospheric oxygen, the tube must be thoroughly purged with high-purity argon before the heating process begins.
Preventing Re-oxidation
The function of the tube extends into the cooling phase.
It is critical to purge the tube again after the process to remove residual hydrogen and generated water vapor. This prevents the newly formed metallic tellurium from re-oxidizing and ensures the final microstructure meets catalytic activity requirements.
Maximizing Process Success
To ensure you are getting the most out of your reduction setup, consider your primary objectives.
- If your primary focus is High Purity: Ensure the quartz tube is free of micro-fractures and rely on its chemical inertness to prevent cross-contamination between the vessel and the $TeO_{2}$.
- If your primary focus is Process Optimization: Leverage the transparency of the tube to visually correlate temperature settings with physical changes in the material, such as agglomeration.
By maintaining a rigorous purging protocol and utilizing the optical clarity of the quartz, you ensure both the safety of the operation and the quality of the final metallic tellurium.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Hydrogen Reduction | Benefit for Tellurium Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents reaction with $TeO_{2}$ or metallic tellurium | Guarantees high purity and prevents contamination |
| Thermal Resilience | Withstands high-temperature reduction environments | Maintains structural integrity without deformation |
| Optical Transparency | Allows real-time visual monitoring of morphology | Enables process verification and detection of metal layers |
| Hermetic Sealing | Isolates reactants and contains hydrogen/argon atmosphere | Ensures safety and prevents re-oxidation during cooling |
Elevate Your Material Processing with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable in hydrogen reduction and high-purity material synthesis. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all of which are fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory or industrial needs.
Whether you are processing tellurium dioxide or developing advanced semiconductors, our lab high-temp furnaces provide the thermal stability and atmospheric control required for success. Don't compromise on purity. Contact KINTEK today to discover how our expert heating solutions can optimize your research and production workflows.
Visual Guide
References
- Hanwen Chung, Bernd Friedrich. Hydrogen Reduction of Tellurium Oxide in a Rotary Kiln, Initial Approaches for a Sustainable Process. DOI: 10.3390/cryst15050478
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the technical requirements for an industrial tube furnace for selective chlorination? Reach 1873 K with Precision
- Why is a Horizontal Tube Furnace used for the torrefaction of Refuse Derived Fuel (RDF)? Boost Fuel Efficiency Now
- Why is it critical to precisely control the heating rate at 3°C/min for Ni/NiO@GF electrodes? Achieve Structural Integrity
- What is the primary function of a horizontal tube furnace in simulating the oxidation behavior of hot-rolled steel?
- How does a three-zone furnace improve process control? Achieve Precise Temperature Uniformity and Gradients
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in the synthesis of Sr3Al2O6? Achieve 1300°C Phase Purity
- What are the specifications for large volume single zone tube furnaces? Find Your Ideal High-Temp Solution
- What is the primary function of high-vacuum quartz tube sealing in Mo2S3 synthesis? Ensure Phase Purity and Precision



















