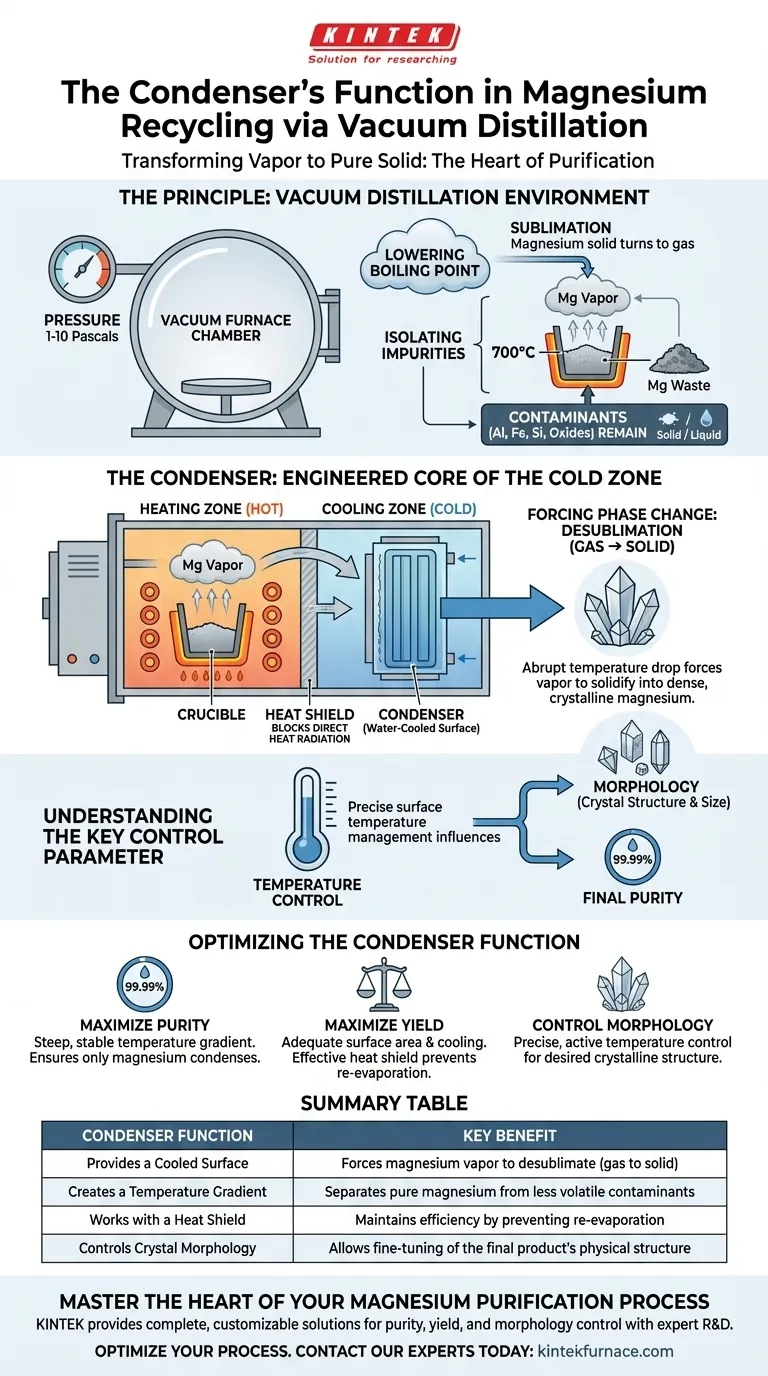
The primary function of the condenser in a vacuum distillation furnace is to provide a precisely controlled, cooled surface where purified magnesium vapor transforms back into a solid. It acts as the collection point, physically separating the high-purity magnesium from the less volatile contaminants left behind in the heating zone.
The condenser doesn't just passively collect magnesium; it actively leverages a steep temperature gradient within the vacuum to force a phase change. This physical separation is the very heart of the entire purification process.

The Principle: How Vacuum Distillation Works
To understand the condenser's role, you must first understand the environment in which it operates. A vacuum furnace creates a unique set of physical conditions designed for separation.
Lowering the Boiling Point
The furnace's vacuum system reduces the internal pressure dramatically, often to between 1 and 10 Pascals. This low-pressure environment significantly lowers the temperature at which magnesium turns from a solid directly into a gas (a process called sublimation).
Isolating the Impurities
While the furnace heats the magnesium waste to around 700°C, the magnesium vaporizes. However, common impurities like aluminum, iron, silicon, and various oxides have much higher boiling points and remain behind as a liquid or solid slag.
The Condenser's Role in a Two-Zone System
The furnace is essentially divided into a hot zone and a cold zone. The condenser is the engineered core of this cold zone, responsible for turning the purification theory into a physical reality.
Creating the Cold Surface
The condenser is an independently cooled component, often a water-cooled disc, positioned away from the primary heating elements. Its purpose is to be the coldest point within the furnace, creating a significant temperature gradient.
Forcing a Phase Change
As the hot, pure magnesium vapor migrates from the distillation area, it makes contact with the cold surface of the condenser. This abrupt drop in temperature forces the vapor to instantly transform from a gas back into a solid, a process known as desublimation.
This results in the deposition of dense, crystalline magnesium directly onto the condenser's surface, ready for harvesting.
The Critical Function of the Heat Shield
A component called a heat shield is almost always placed between the hot and cold zones. It blocks direct heat radiation from the crucible to the condenser.
This shield is essential for maintaining the steep temperature gradient, ensuring the condenser stays cool enough to be effective. It also prevents the newly deposited magnesium from being reheated and re-evaporated, which would drastically lower the system's overall yield and energy efficiency.
Understanding the Key Control Parameter
The condenser is not a passive component; its performance is actively managed to achieve specific outcomes.
The Impact of Temperature Control
The precise temperature of the condenser surface is the most critical control parameter. It directly influences the morphology (the physical structure and size of the crystals) and final purity of the collected magnesium.
By carefully managing this temperature, operators can fine-tune the final product to meet specific quality standards, completing the separation process with high precision.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Optimizing the condenser's function depends entirely on your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximizing purity: Maintain the steepest and most stable temperature gradient possible to ensure only the most volatile substance—magnesium—condenses.
- If your primary focus is maximizing yield: Ensure the condenser has adequate surface area and cooling capacity, and verify the heat shield is effectively preventing any re-evaporation of the deposited product.
- If your primary focus is controlling crystal morphology: Implement precise, active temperature control of the condenser surface, as this is the most influential factor on the final crystalline structure.
Ultimately, mastering magnesium purification requires viewing the condenser not as a simple collection plate, but as an active phase-change reactor.
Summary Table:
| Condenser Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Provides a Cooled Surface | Forces magnesium vapor to desublimate (gas to solid) |
| Creates a Temperature Gradient | Separates pure magnesium from less volatile contaminants |
| Works with a Heat Shield | Maintains efficiency by preventing re-evaporation |
| Controls Crystal Morphology | Allows fine-tuning of the final product's physical structure |
Master the Heart of Your Magnesium Purification Process
Is your magnesium recycling operation achieving the purity and yield you need? The condenser is the critical component that turns purification theory into high-value reality. At KINTEK, we don't just sell furnaces; we provide complete solutions backed by expert R&D and manufacturing.
Our Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum furnaces (including specialized CVD systems) are engineered for precision and reliability. We understand that every recycling goal is unique, which is why we offer fully customizable systems to meet your specific needs for purity, yield, and crystal morphology control.
Let's optimize your process. Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK vacuum distillation furnace can enhance your magnesium recycling efficiency and profitability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation



















