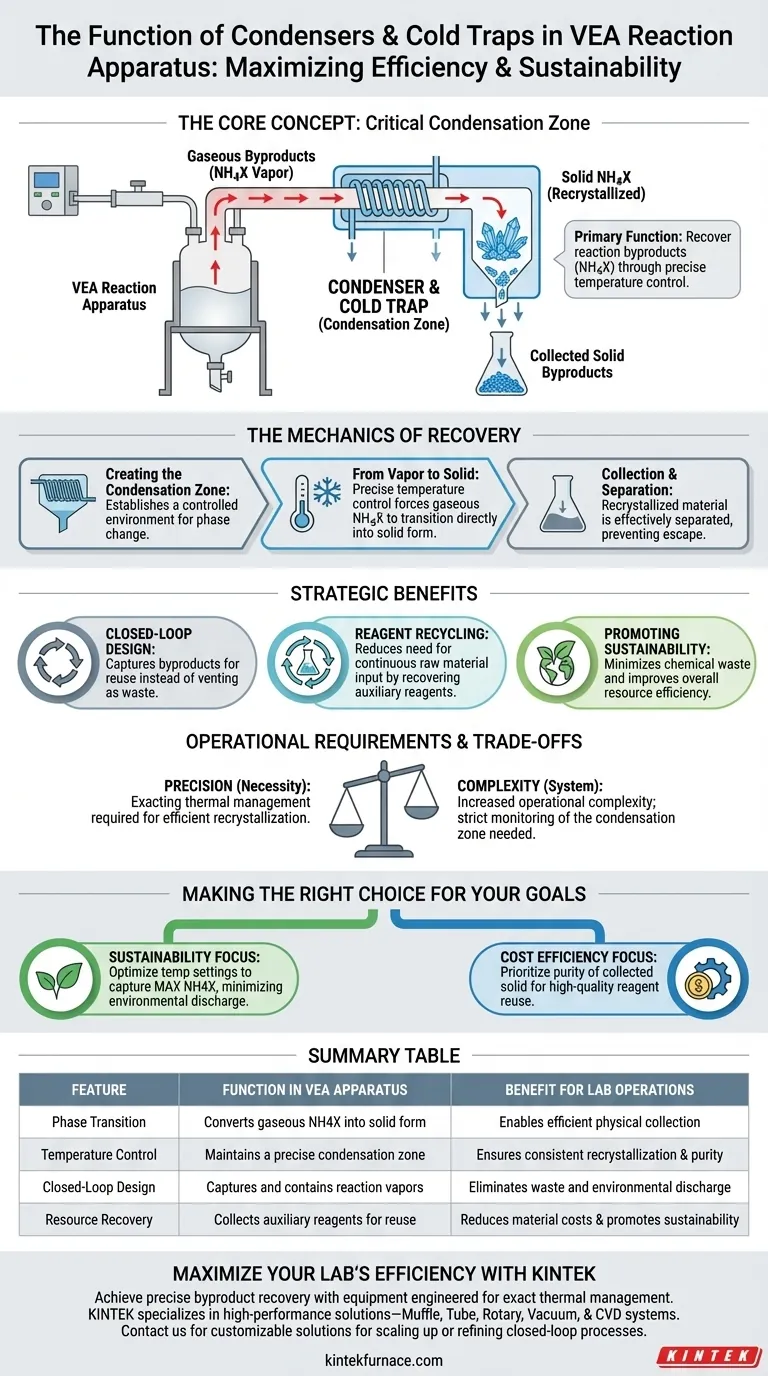
Condensers and cold traps serve as the critical condensation zone within a Vacuum Evaporation-Assisted (VEA) reaction apparatus. Their primary function is to recover reaction byproducts, specifically enabling the recrystallization and collection of excess ammonium halide (NH4X) through precise temperature control.
By converting gaseous byproducts back into solid form, these components create a closed-loop system. This not only maximizes efficiency but also enables the sustainable recycling of auxiliary reagents.
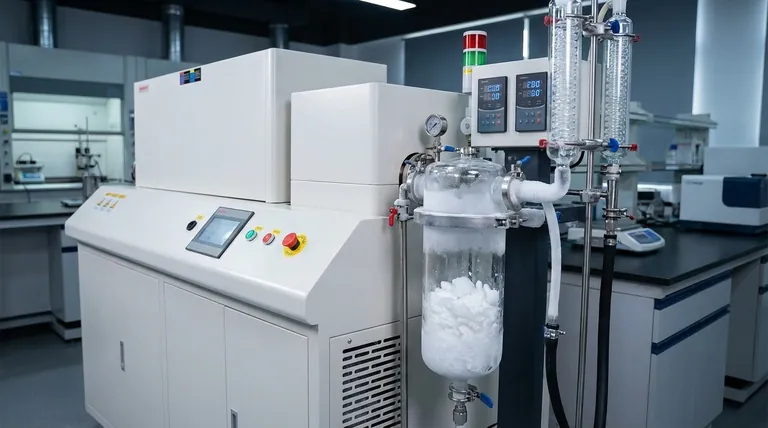

The Mechanics of Recovery
Creating the Condensation Zone
The central role of condensers and cold traps is to establish a controlled environment for phase change. They act as the designated condensation zone within the apparatus.
From Vapor to Solid
Through precise temperature control, these components cool the reaction vapors. This cooling process forces the excess ammonium halide (NH4X) to transition from a gaseous state directly into a solid form.
Collection and Separation
Once the material is recrystallized, it is effectively separated from the vapor stream. This allows for the physical collection of the solid byproducts within the trap, preventing them from escaping the system.
Strategic Benefits of the System
Enabling a Closed-Loop Design
The integration of these components transforms the apparatus into a closed-loop system. Rather than venting byproducts as waste, the system captures them for reuse.
Facilitating Reagent Recycling
The primary advantage of this capture is the ability to recycle auxiliary reagents. By recovering the ammonium halide, the process reduces the need for continuous raw material input.
Promoting Sustainability
This recovery mechanism directly supports sustainable production practices. It minimizes chemical waste and improves the overall resource efficiency of the VEA process.
Operational Requirements and Trade-offs
The Necessity of Precision
While effective, this system relies heavily on precise temperature control. Without exacting thermal management, the ammonium halide may not recrystallize efficiently, leading to potential yield loss.
System Complexity
Implementing a closed-loop recovery system increases the operational complexity of the apparatus. Operators must monitor the condensation zone strictly to ensure the byproduct is collected as a solid rather than passing through as a vapor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goals
To maximize the benefits of condensers and cold traps in your VEA setup, align your operational parameters with your specific objectives.
- If your primary focus is Sustainability: Ensure your temperature settings are optimized to capture the maximum amount of NH4X to minimize environmental discharge.
- If your primary focus is Cost Efficiency: Prioritize the purity of the collected solid to ensure the recycled auxiliary reagents are of high enough quality for immediate reuse.
The effectiveness of a VEA apparatus ultimately hinges on its ability to turn waste back into resources through controlled condensation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in VEA Apparatus | Benefit for Lab Operations |
|---|---|---|
| Phase Transition | Converts gaseous NH4X byproducts into solid form | Enables efficient physical collection |
| Temperature Control | Maintains a precise condensation zone | Ensures consistent recrystallization and purity |
| Closed-Loop Design | Captures and contains reaction vapors | Eliminates waste and environmental discharge |
| Resource Recovery | Collects auxiliary reagents for reuse | Reduces material costs and promotes sustainability |
Maximize Your Lab’s Efficiency with KINTEK
Achieving precise byproduct recovery in Vacuum Evaporation-Assisted (VEA) reactions requires equipment engineered for exact thermal management. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance laboratory solutions—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all backed by expert R&D and customizable to your unique research needs.
Whether you are scaling up production or refining a closed-loop sustainable process, our high-temperature furnaces and reaction systems deliver the reliability your project demands. Contact us today to find the perfect solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Zhichao Zeng, Yaping Du. Vacuum evaporation-assisted reaction: sustainable solution for application of rare earth-based halide solid-state electrolytes. DOI: 10.1039/d5sc00003c
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 304 316 Stainless Steel High Vacuum Ball Stop Valve for Vacuum Systems
- Ultra High Vacuum Stainless Steel KF ISO CF Flange Pipe Straight Pipe Tee Cross Fitting
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a precise gas flow control and supply system necessary during the thermochemical conversion of rice husk biochar?
- What is the primary function of high-purity graphite crucibles? Ensure Superior Purity in Aluminum Alloy Melting
- How does the dispersion of ruthenium precursors on alumina carriers affect thermal processing in a lab furnace?
- Which industries can benefit from using the circulating water multifunctional vacuum pump? Discover Clean, Efficient Vacuum Solutions
- What role does a high-temperature ceramic crucible play in the pyrolysis synthesis of biochar? Ensure Pure Lab Results
- Why are laboratory precision stirrers and heating devices essential for synthesizing magnetic precursor solutions?
- How do graphite sleeves and ceramic crucibles function in induction furnaces? Key Roles in Material Synthesis
- What role do graphite molds play in graphite flake alignment? Engineered Precision for High Thermal Conductivity



















