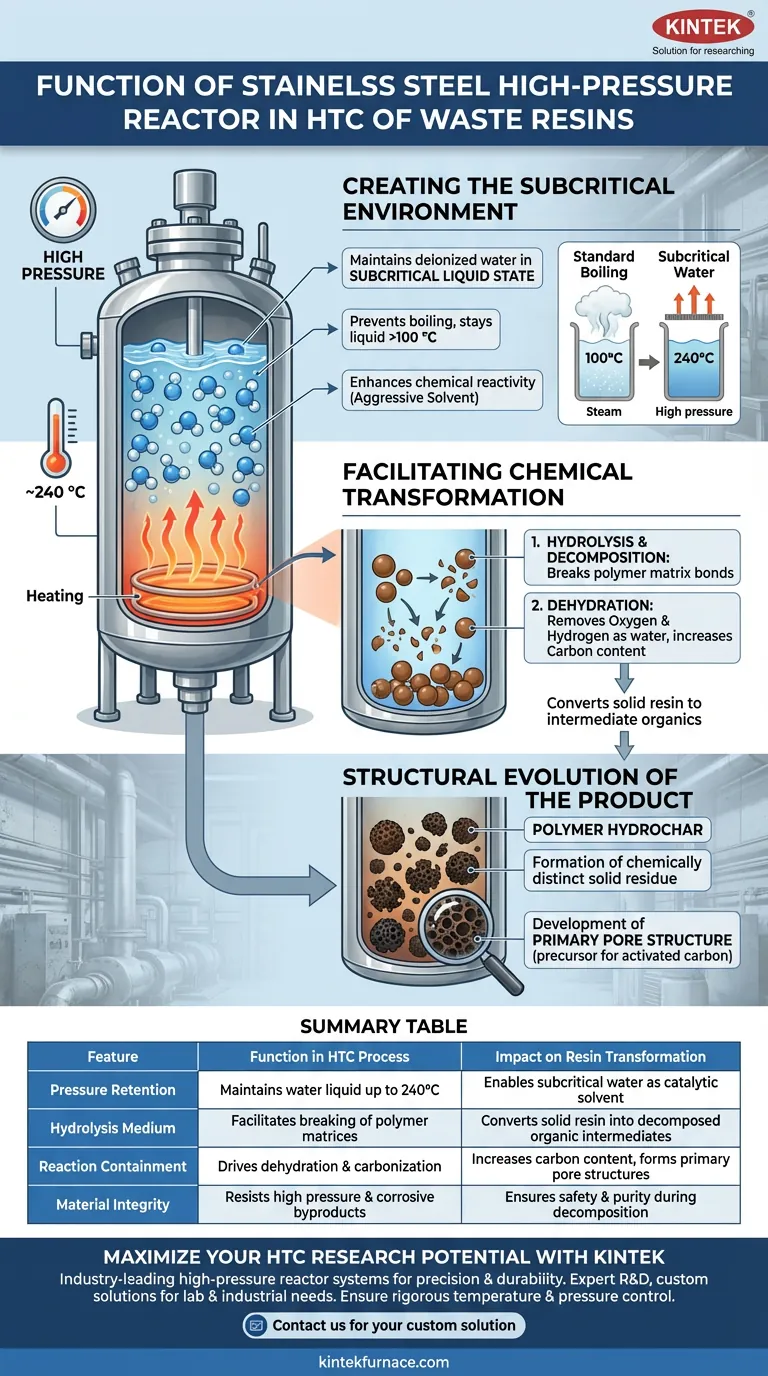
The function of a stainless steel high-pressure reactor is to generate a sealed environment that maintains deionized water in a subcritical liquid state. By sustaining high internal pressure, the reactor allows water to remain liquid at temperatures significantly above its boiling point—typically around 240 °C—which is the critical condition required to initiate the breakdown of waste ion-exchange resins.
The reactor serves as a containment vessel that forces water into a subcritical state, acting as a catalyst to decompose polymer structures and convert solid resins into porous polymer hydrochar through hydrolysis and dehydration.

Creating the Subcritical Environment
The primary role of the reactor is not merely to hold materials, but to fundamentally alter the physical properties of the solvent (water) used in the process.
Maintaining Liquid State at High Heat
Under normal atmospheric conditions, water vaporizes at 100 °C. The stainless steel reactor is designed to withstand the pressure generated when heating water to temperatures such as 240 °C.
By sealing the system, the reactor prevents boiling. This forces the deionized water to remain in a liquid phase, creating what is known as subcritical water.
Enhancing Chemical Reactivity
In this subcritical state, water exhibits unique properties compared to ambient water. It acts as a more aggressive solvent and reaction medium.
The high-pressure environment ensures that the water penetrates the solid resin effectively, facilitating chemical reactions that would not occur under standard boiling conditions.
Facilitating Chemical Transformation
Once the subcritical environment is established, the reactor acts as the stage for the chemical metamorphosis of the waste resins.
Hydrolysis and Decomposition
The reactor environment triggers the decomposition of the stable polymer structures found in ion-exchange resins.
High-temperature liquid water drives hydrolysis, breaking the chemical bonds within the resin's polymer matrix.
Dehydration of Polymer Structures
Simultaneously, the reactor facilitates dehydration reactions. This process removes oxygen and hydrogen from the polymer structure in the form of water.
This step is vital for increasing the carbon content of the solid residue, transitioning it from a raw resin to a carbonaceous material.
Structural Evolution of the Product
The ultimate output of the reactor is a transformation of the physical form of the waste.
Formation of Polymer Hydrochar
The process successfully converts the solid waste resins into polymer hydrochar. This solid residue is chemically distinct from the original input material.
Development of Primary Pore Structure
Beyond simple chemical conversion, the reactor environment aids in developing a primary pore structure within the hydrochar.
This physical structuring provides the foundation for the material's future utility, potentially serving as a precursor for activated carbon or adsorption applications.
Understanding the Operational Requirements
While the reactor is the engine of this conversion, it imposes specific operational constraints that must be managed.
Pressure and Material Integrity
The "stainless steel" specification is not cosmetic; it is functional. The reactor must withstand significant internal pressure without deforming.
Furthermore, the decomposition of resins can release corrosive byproducts. The material construction ensures the reactor remains inert and does not degrade during the harsh hydrothermal process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The effectiveness of the Hydrothermal Carbonization (HTC) process depends heavily on how the reactor is utilized.
- If your primary focus is efficient decomposition: Ensure the reactor seal is perfect to maintain the pressure required for the subcritical state at 240 °C.
- If your primary focus is pore structure development: Regulate the temperature profile strictly, as the subcritical conditions directly influence the morphology of the resulting hydrochar.
By controlling pressure and temperature within this sealed vessel, you turn waste resin into a valuable carbon resource.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in HTC Process | Impact on Resin Transformation |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Retention | Maintains water in a liquid state up to 240°C | Enables subcritical water as a catalytic solvent |
| Hydrolysis Medium | Facilitates breaking of polymer matrices | Converts solid resin into decomposed organic intermediates |
| Reaction Containment | Drives dehydration and carbonization | Increases carbon content and forms primary pore structures |
| Material Integrity | Resists high pressure and corrosive byproducts | Ensures safety and purity during the decomposition phase |
Maximize Your HTC Research Potential with KINTEK
Ready to convert complex waste streams into valuable carbon resources? KINTEK provides industry-leading high-pressure reactor systems engineered for precision and durability. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as customizable stainless steel high-pressure reactors tailored to your unique lab-scale or industrial needs.
Our equipment ensures the rigorous temperature and pressure control required for successful hydrothermal carbonization and material synthesis.
Contact us today to find your custom solution and see how our advanced laboratory furnaces can enhance your process efficiency.
Visual Guide
References
- Reuse of Polymeric Resin for Production of Activated Hydrochar Applied in Removal of Bisphenol A and Diclofenac Synthetic Aqueous Solution. DOI: 10.3390/coatings15010027
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- Why are specific temperatures of 848 K, 898 K, and 948 K selected for the Thermal Oxidation of Ti-6Al-4V ELI alloy?
- Why is a constant temperature water bath or hot plate required for MXene post-treatment? Master Precise Delamination
- What is the purpose of setting an industrial drying oven to 70°C for sludge? Preserve Volatiles & Optimize Pre-treatment
- What are the benefits of ESR for carbonitride distribution in H13 steel? Enhance Your Material's Isotropic Properties
- How does a vacuum drying oven contribute to the study of the hydration degree in cement pastes? Essential Lab Insights
- Why is a vacuum drying oven necessary for activated carbon? Ensure Accurate BET and Pore Size Analysis
- What are the primary technical objectives of CoCrFeMnNi alloy annealing? Master Recrystallization & Phase Control
- What are the advantages of using a programmable high-temperature laboratory furnace for CSA cement? Precision Control



















