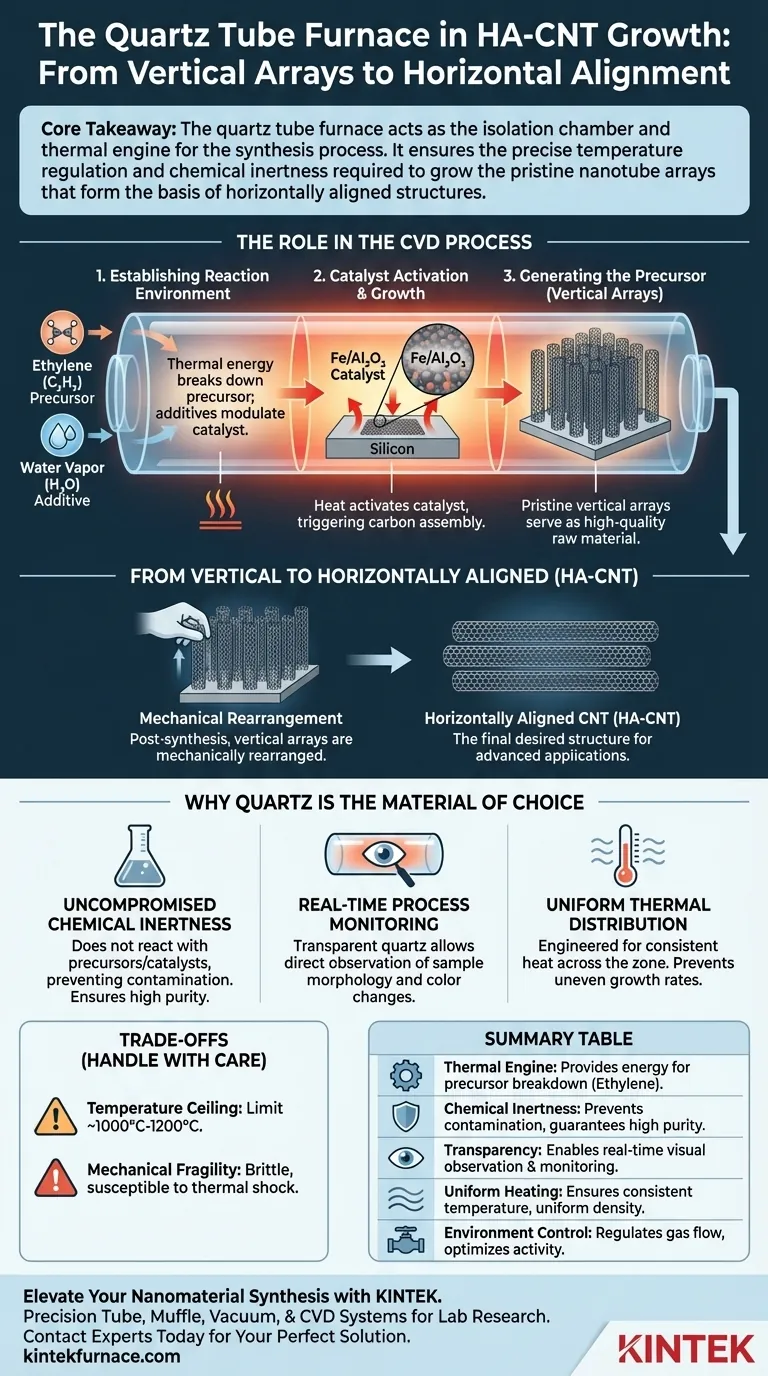
The primary function of a quartz tube furnace during the growth of carbon nanotubes is to create a controlled, high-temperature environment necessary for Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). Specifically, it facilitates the reaction of ethylene and water vapor to grow vertical carbon nanotubes on iron/alumina catalysts. These high-quality vertical arrays serve as the essential raw material that is subsequently mechanically rearranged into horizontally aligned carbon nanotubes (HA-CNT).
Core Takeaway The quartz tube furnace acts as the isolation chamber and thermal engine for the synthesis process. It ensures the precise temperature regulation and chemical inertness required to grow the pristine nanotube arrays that form the basis of horizontally aligned structures.
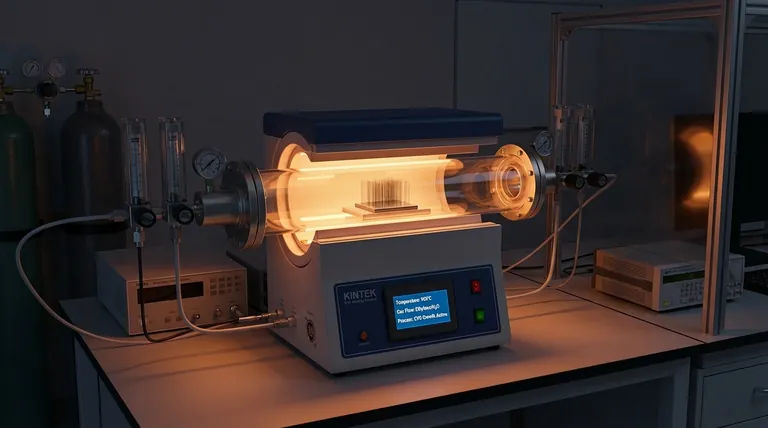

The Role of the Furnace in the CVD Process
Establishing the Reaction Environment
The furnace provides the thermal energy required to break down carbon precursor gases, such as ethylene.
By maintaining specific flow rates of additives like water vapor, the system modulates the activity of the catalyst, ensuring the continuous growth of carbon structures rather than amorphous carbon soot.
Catalyst Activation and Growth
Inside the tube, the heat activates the catalyst material—typically iron/alumina coated on silicon substrates.
This thermal activation is the trigger that allows the carbon atoms from the gas to assemble into tubular structures.
Generating the Precursor for Alignment
According to standard methodologies, the furnace often grows the nanotubes in a vertical orientation first.
These vertical arrays are the "high-quality raw materials." The horizontal alignment is achieved by mechanically rearranging these pristine vertical tubes after the furnace process is complete.
Why Quartz is the Material of Choice
Uncompromised Chemical Inertness
The success of HA-CNT growth depends on the purity of the carbon structure.
Quartz is chemically inert, meaning it does not react with the precursor gases or the sensitive catalyst materials. This prevents impurities from the tube walls from contaminating the nanotubes.
Real-Time Process Monitoring
Unlike ceramic or metal furnaces, quartz is transparent.
This allows researchers to perform real-time observation of the process. You can visually monitor changes in sample morphology and color during pyrolysis, providing immediate feedback on the reaction status.
Uniform Thermal Distribution
Quartz tube furnaces are engineered to provide uniform heating across the heating zone.
Even temperature distribution is critical; thermal gradients could lead to uneven growth rates or varying nanotube diameters across the substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Ceilings
While quartz has high heat resistance, it typically has a working limit around 1000°C to 1200°C.
If your specific synthesis protocol requires ultra-high temperatures (e.g., for graphitizing certain defects), quartz may soften or devitrify, necessitating a switch to alumina tubes.
Mechanical Fragility
Despite its thermal robustness, quartz remains a glass-like material.
It is brittle and susceptible to thermal shock if cooled too rapidly. Careful handling is required during loading and unloading to prevent fracture, unlike more robust metal reactors.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your equipment for HA-CNT growth, consider the following approach:
- If your primary focus is process optimization: Leverage the transparency of the quartz tube to visually monitor the onset of pyrolysis and adjust gas flows in real-time.
- If your primary focus is sample purity: Ensure the tube is regularly cleaned to maintain its chemical inertness, as contamination can poison the iron catalysts.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency: Utilize quartz over specialized ceramics, as it offers the best balance of performance and price for standard CVD applications up to 1000°C.
The quartz tube furnace is not just a heater; it is the transparent vessel that ensures the chemical fidelity of your nanotube precursors.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in HA-CNT Synthesis | Benefit to Research |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Engine | Provides energy for precursor breakdown (Ethylene) | Ensures stable CVD reaction kinetics |
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents contamination from tube walls | Guarantees high-purity nanotube structures |
| Transparency | Enables real-time visual observation | Facilitates instant monitoring of pyrolysis |
| Uniform Heating | Maintains consistent temperature across catalyst | Ensures uniform nanotube diameter and density |
| Environment Control | Regulates gas flow (Water Vapor/Ethylene) | Optimizes catalyst activity and prevents soot |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is the foundation of high-quality HA-CNT growth. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems specifically engineered to meet the rigorous demands of advanced lab research. Whether you need standard quartz configurations or fully customizable high-temperature furnaces, our expert R&D and manufacturing teams ensure your equipment delivers the thermal uniformity and chemical purity your projects require.
Ready to optimize your CVD process?
Contact KINTEK Experts Today to find the perfect furnace solution for your unique laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Jae‐Moon Jeong, Seong Su Kim. Aligned Carbon Nanotube Polymer Nanocomposite Bipolar Plates Technology for Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries. DOI: 10.1002/eem2.70030
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What critical experimental conditions does a tube furnace provide for carbonizing PI-COFs? Master Thermal Precision
- What is the technical significance of the high-temperature environment provided by a tube furnace in the synthesis of Fe3O4@Fe-AC?
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace contribute to the preparation of highly porous carbon sheets from cellulose?
- What role does the integration of an electronic balance and a tube furnace play in hydrogen reduction experiments?
- What is the significance of defining the quartz tube as a heat transfer boundary? Optimize Your Furnace Modeling
- Why is a sealed vacuum quartz tube required for synthesis of 1T-SnS2 via CVT? Ensure Pure Crystal Growth
- What critical environmental controls does a tubular furnace provide for CMS membranes? Optimize Pore Engineering
- What role does a tube pyrolysis reactor play in sludge and chloride co-pyrolysis? Enhanced Heavy Metal Removal



















