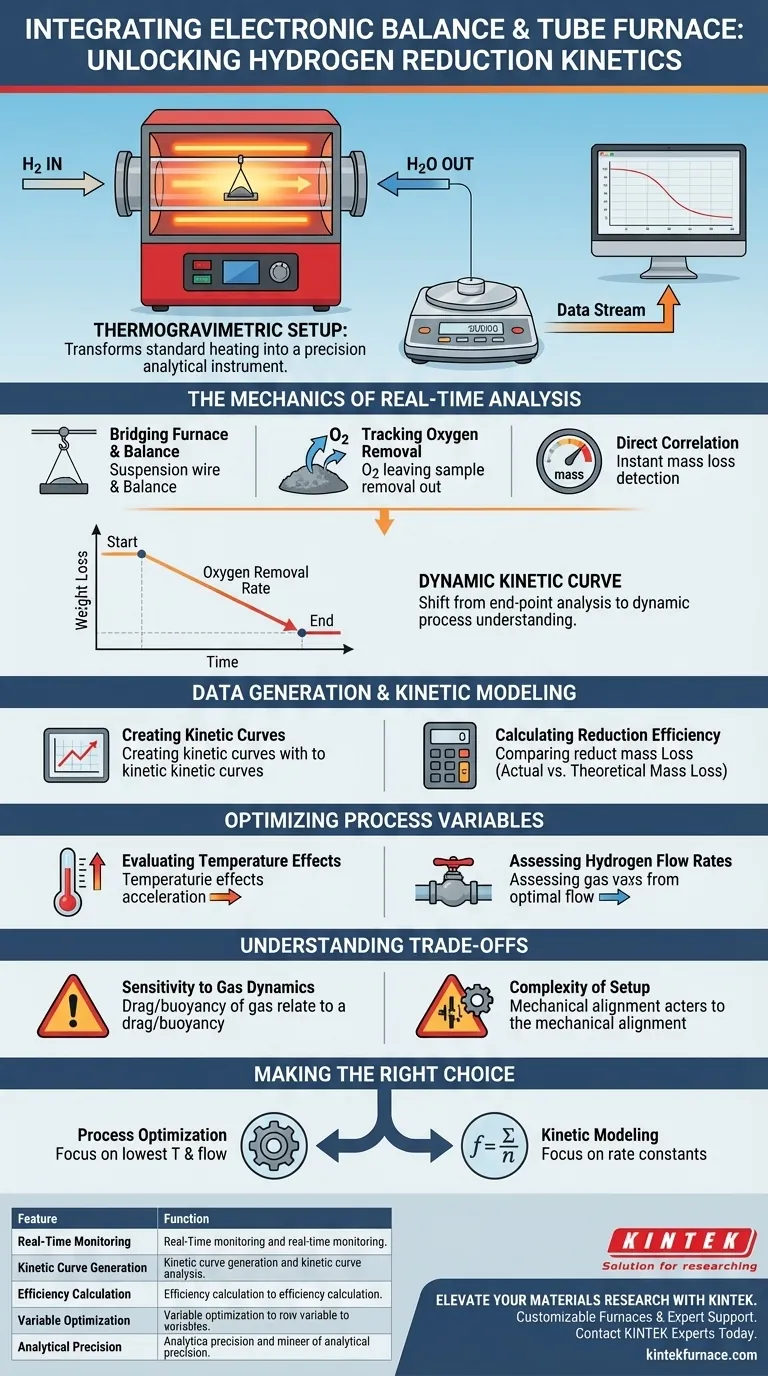
The integration of an electronic balance with a tube furnace fundamentally transforms a standard heating apparatus into a precision analytical instrument known as a thermogravimetric setup. By mechanically connecting the sample inside the heated zone to an external micro-balance, this system enables the continuous, real-time monitoring of weight variations throughout the hydrogen reduction experiment.
Core Insight This integration shifts the focus from simple end-point analysis to dynamic process understanding. It allows researchers to quantify the exact rate of oxygen removal as it occurs, facilitating the creation of precise kinetic curves and the calculation of reduction efficiency under varying thermal and flow conditions.

The Mechanics of Real-Time Analysis
Bridging the Furnace and the Balance
The core function of this setup is to bridge the gap between the high-temperature reaction environment and precise measurement tools. The sample is suspended within the tube furnace but remains physically connected to a sensitive micro-balance.
Tracking Oxygen Removal
In the context of hydrogen reduction, weight loss is the primary indicator of reaction progress. As hydrogen reacts with iron oxides, it removes oxygen in the form of water vapor.
Direct Correlation
The electronic balance detects this loss of mass instantly. This provides a direct, non-invasive method to measure exactly how much oxygen is being stripped from the sample at any given second.
Data Generation and Kinetic Modeling
Creating Dynamic Kinetic Curves
Rather than relying on "before and after" measurements, this system generates data points continuously. This allows you to plot dynamic reduction kinetic curves that visualize the speed and behavior of the reaction over time.
Calculating Reduction Efficiency
By comparing the actual weight loss against the theoretical oxygen content of the sample, researchers can calculate reduction efficiency with high precision. This metric defines the degree to which the iron oxide has been successfully converted to metallic iron.
Optimizing Process Variables
Evaluating Temperature Effects
The system allows for immediate assessment of how temperature changes impact reaction kinetics. You can pinpoint the exact temperature at which reduction begins and observe how reaction rates accelerate as heat increases.
Assessing Hydrogen Flow Rates
The setup is also used to test the impact of different hydrogen flow rates. Real-time data reveals the optimal flow required to maximize reduction speed without wasting excess gas.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sensitivity to Gas Dynamics
While highly precise, connecting a balance to a flow system introduces potential noise. The force of the hydrogen gas flowing over the sample can exert drag or buoyancy effects, potentially skewing weight readings if not properly calibrated.
Complexity of Setup
Integrating these two distinct systems requires careful mechanical alignment. Any physical contact between the suspension wire and the furnace walls can create friction, resulting in inaccurate kinetic data.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the value of an integrated furnace and balance system, align your analysis with your specific research objectives:
- If your primary focus is Process Optimization: Use the real-time data to identify the lowest temperature and flow rate that still achieve 100% reduction efficiency.
- If your primary focus is Kinetic Modeling: Focus on the slope of the weight-loss curve to determine the reaction rate constants and activation energy of the reduction process.
Success in hydrogen reduction relies not just on removing oxygen, but on understanding exactly how and when it leaves the material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Hydrogen Reduction |
|---|---|
| Real-Time Monitoring | Continuous tracking of weight loss as oxygen is removed. |
| Kinetic Curve Generation | Visualizes reaction speed and behavior over time. |
| Efficiency Calculation | Compares actual vs. theoretical mass loss for precise reduction data. |
| Variable Optimization | Evaluates impact of temperature and gas flow on reaction rates. |
| Analytical Precision | Transforms a standard furnace into a dynamic thermogravimetric tool. |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK
Precision in hydrogen reduction requires more than just heat; it requires the ability to monitor every milligram of change. KINTEK provides high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all engineered to support complex analytical integrations like thermogravimetric setups.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems are fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory needs. Whether you are optimizing reduction kinetics or developing new materials, our technical team is ready to help you design the perfect thermal solution.
Contact KINTEK Experts Today to discover how our customizable furnaces can enhance your lab’s efficiency and data accuracy!
Visual Guide
References
- Deddy C. Nababan, Sujeong Lee. Reduction of Iron Contained in Goethite-Rich Rare Earth Tailings by Hydrogen Gas. DOI: 10.1007/s11663-025-03826-y
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is it necessary to use a tube vacuum furnace with an argon atmosphere for sintering aluminum-based materials?
- What are the benefits of high yield and product concentration in a tube furnace? Boost Efficiency and Purity in Chemical Processes
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace contribute to the atmosphere-controlled sintering of Mn-Zn ferrites?
- Why is a Tube Resistance Furnace with Argon Necessary for TiO2 and Nickel Foam? Protect Substrate and Conductivity
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What are the space-saving benefits of a tube furnace? Maximize Lab Efficiency with Compact Design
- Why is environmental control in a high-temperature tube furnace necessary during NVP/C synthesis? Key to Success
- What conditions does a continuous flow fixed-bed quartz reactor provide? Master CO Oxidation Testing with Cobalt Oxide



















