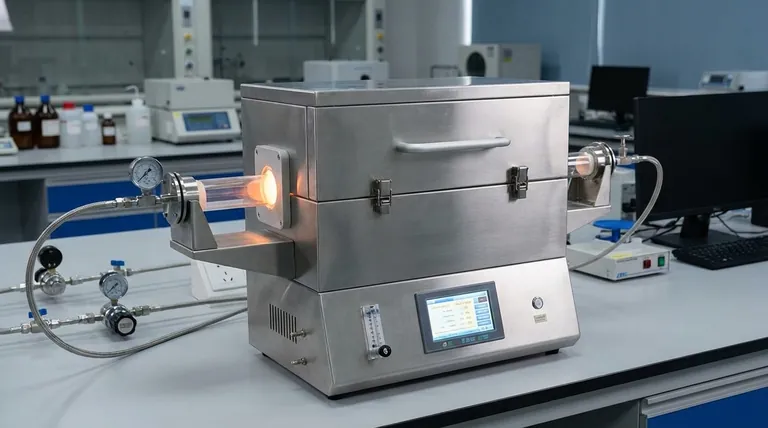
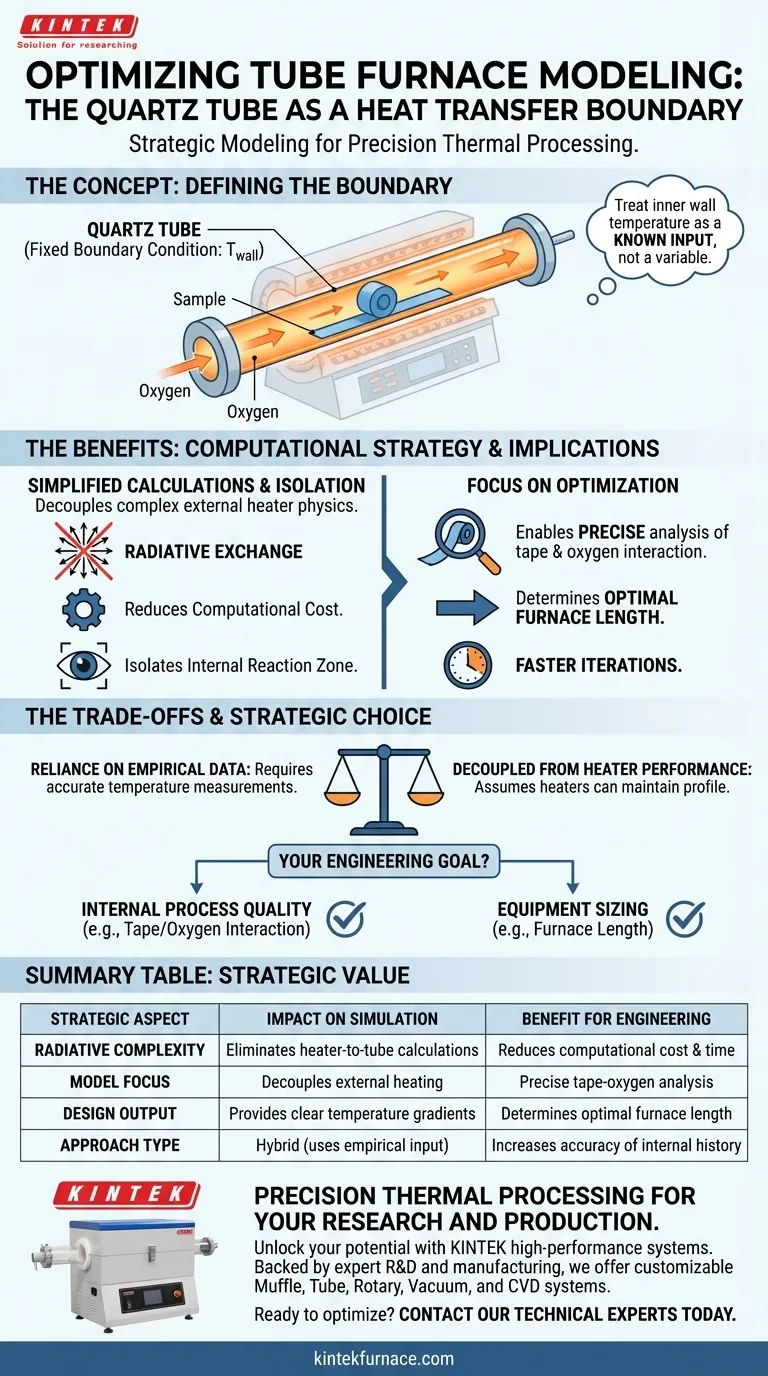
Defining the quartz tube as a heat transfer boundary condition is a strategic modeling decision that isolates the internal process from external variables. By treating the inner wall’s temperature distribution as a known input rather than a variable to be solved, you decouple the complex physics of the external heating elements from the internal reaction zone. This significantly simplifies the mathematical model by eliminating the need to calculate the radiative exchange between the heaters and the tube.
Core Takeaway: treating the quartz tube's inner wall temperature as a fixed boundary condition drastically reduces computational complexity. This allows you to bypass external radiation calculations and focus entirely on the critical heat transfer between the tape and the flowing oxygen, enabling precise optimization of the furnace length.

The Computational Strategy
Simplifying Radiative Calculations
Radiative heat transfer is computationally expensive due to its non-linear nature and geometric complexity.
In a full furnace model, you would typically calculate how heating elements radiate energy to the quartz tube. However, by measuring the actual temperature distribution of the quartz tube's inner wall and applying it as a boundary condition, you bypass these complex calculations entirely.
Isolating the Reaction Zone
The quartz tube acts as the "central vessel" that mediates heat exchange.
By defining its inner surface as the boundary, you shift the focus of the simulation. The model no longer cares how the tube gets hot; it only cares about how the tube transfers that heat to the internal components. This creates a focused analysis of the environment surrounding the sample tape.
Implications for Design Optimization
Focusing on Tape and Oxygen Interaction
Once the boundary is set, the model can dedicate its resources to the internal physics.
You can explicitly analyze the heat transfer behavior between the sample tape and the flowing oxygen. This reveals how temperature gradients develop within the gas flow and how effectively heat is delivered to the tape surface.
Optimizing Furnace Length
The ultimate practical benefit of this modeling approach is geometric optimization.
By understanding the specific heat transfer rates between the tube wall, the oxygen, and the tape, you can determine exactly how long the tape must remain in the hot zone. This directly informs the necessary design length of the furnace to ensure proper thermal processing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Reliance on Empirical Data
This method is not a "pure" simulation; it is a hybrid approach.
It requires accurate, pre-measured temperature distributions of the quartz tube’s inner wall. If your input measurements are inaccurate or low-resolution, the simulation results will be equally flawed.
Decoupling from Heater Performance
This approach assumes the heating elements can maintain the defined wall temperature.
Because you are simplifying the external radiation, this model cannot predict if the heating elements are actually capable of sustaining the required temperature profile under a heavy thermal load. It assumes the boundary condition is absolute.
Making the Strategic Modeling Choice
When deciding how to structure your thermal simulation, consider your specific engineering goals:
- If your primary focus is internal process quality: Use this boundary condition to analyze the precise thermal history of the tape and its interaction with the flowing oxygen.
- If your primary focus is equipment sizing: Leverage the simplified calculation speed to iterate quickly on the optimal furnace length required for your process.
By correctly defining this boundary condition, you transform the quartz tube from a variable into a constant, turning a complex physics problem into a manageable design tool.
Summary Table:
| Strategic Aspect | Impact on Simulation | Benefit for Engineering |
|---|---|---|
| Radiative Complexity | Eliminates non-linear heater-to-tube calculations | Reduces computational cost and time |
| Model Focus | Decouples external heating from internal reaction | Enables precise analysis of tape-oxygen interaction |
| Design Output | Provides clear temperature gradients | Determines optimal furnace length for processing |
| Approach Type | Hybrid (uses empirical input data) | Increases accuracy of internal thermal history |
Precision Thermal Processing for Your Research and Production
Unlock the full potential of your thermal experiments with KINTEK. Whether you are modeling complex heat transfer or scaling up production, our high-performance systems provide the consistency your data demands.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of laboratory equipment including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. All our high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique boundary conditions and processing requirements.
Ready to optimize your thermal results? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect customizable furnace solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
References
- Zili Zhang, Qiuliang Wang. A Tube Furnace Design for the Oxygen Annealing of a REBCO Superconducting Joint. DOI: 10.3390/ma18133053
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in the preparation of cellulose-based carbon nanofibers?
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the synthesis of Ni17W3/MoO3-x/WO3-x catalysts during annealing?
- What is a 70mm tube furnace and what is its primary use? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- Why are sealed quartz tubes required for Au-Seeded TiO2 nanowires? Ensure Vapor-Phase Stability and VLS Growth
- How does air annealing in a tube furnace enhance the performance of TiO2 nanorods? Boost Crystallinity and Conductivity
- How does the temperature controller function in a 70mm tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thermal Control for Your Lab
- What kind of experimental environment does a high vacuum tube furnace provide for high-performance ceramic preparation?
- What happens to quartz tubes in a tube furnace at temperatures above 1000°C? Understanding Devitrification and Material Limits



















