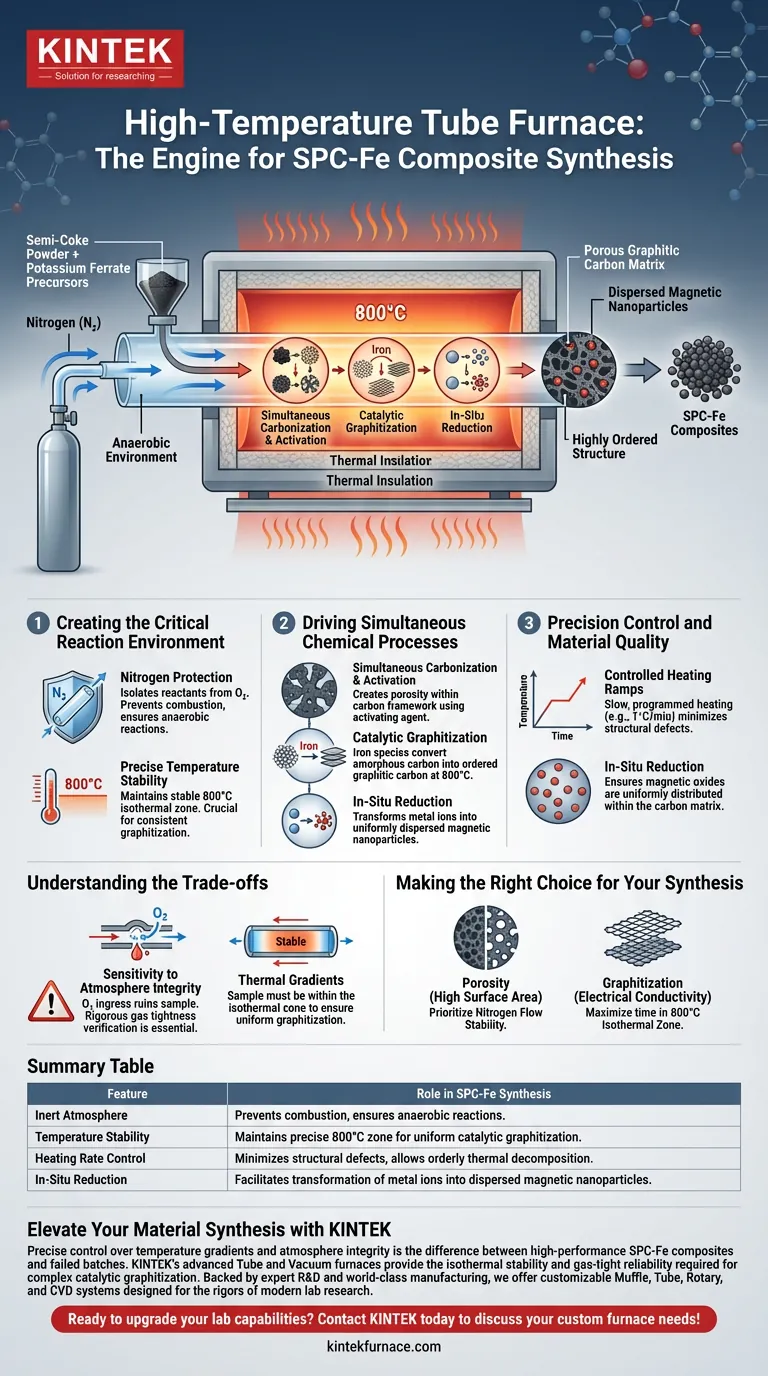
The high-temperature tube furnace serves as the critical reaction vessel that enables the synthesis of semi-coke based porous graphitic carbon–iron oxide (SPC-Fe) composites by establishing a controlled, anaerobic environment. Specifically, it maintains a stable reaction zone at 800°C under nitrogen protection, which allows semi-coke powder and potassium ferrate to undergo simultaneous carbonization, activation, and catalytic graphitization.
The tube furnace is not merely a heat source; it is a precision instrument that synchronizes thermal decomposition with chemical activation. By strictly controlling the atmosphere and temperature profile, it forces the precursors to evolve into a highly ordered, porous graphitic structure rather than simply burning away or degrading.
Creating the Critical Reaction Environment
Nitrogen Protection
The primary role of the tube furnace is to isolate the reactants from atmospheric oxygen.
By flushing the tube with nitrogen gas, the furnace creates a strictly anaerobic environment.
This prevents the semi-coke from combusting (burning to ash) and ensures that the chemical transformations are purely internal thermo-chemical reactions.
Precise Temperature Stability
Synthesis of SPC-Fe composites requires a specific thermal energy threshold to trigger the necessary reactions.
The furnace maintains a stable high-temperature zone at 800°C.
This stability is non-negotiable; fluctuations in temperature can lead to incomplete activation or inconsistent graphitization across the sample batch.
Driving Simultaneous Chemical Processes
Simultaneous Carbonization and Activation
Inside the furnace, the semi-coke powder and potassium ferrate interact under high heat.
The furnace environment facilitates the carbonization of the semi-coke (increasing carbon content) while the potassium ferrate acts as an activating agent.
This simultaneous process creates the necessary porosity within the carbon framework.
Catalytic Graphitization
The furnace conditions enable the iron species present in the mixture to function as catalysts.
Under the 800°C heat, these iron species drive catalytic graphitization.
This converts amorphous (disordered) carbon into graphitic (ordered) carbon, significantly enhancing the material's electrical conductivity and structural stability.
Precision Control and Material Quality
Controlled Heating Ramps
While the target is 800°C, how you get there matters.
The tube furnace allows for programmed heating rates (e.g., 1°C per minute).
This slow, controlled ramp allows for the orderly thermal decomposition of the polymer backbone and minimizes structural defects caused by thermal shock.
In-Situ Reduction
The furnace environment supports the reduction of metal salts.
It facilitates the transformation of loaded metal ions into highly dispersed magnetic nanoparticles.
This dictates the final crystallinity of the magnetic oxides and ensures they are uniformly distributed within the carbon matrix.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sensitivity to Atmosphere Integrity
The effectiveness of the synthesis is entirely dependent on the integrity of the inert atmosphere.
If the nitrogen flow is interrupted or the tube seal leaks, oxygen ingress will immediately ruin the sample by oxidizing the carbon.
Operators must rigorously verify gas tightness before every high-temperature cycle.
Thermal Gradients
While the center of the tube is stable, the ends of the tube furnace are often cooler.
Placing the sample outside the isothermal zone (the region of uniform temperature) will result in heterogeneous products.
You must identify the exact length of the constant-temperature zone to ensure the entire batch undergoes the same degree of graphitization.
Making the Right Choice for Your Synthesis
To maximize the quality of your SPC-Fe composites, tailor the furnace operation to your specific requirements:
- If your primary focus is high surface area (Porosity): Prioritize the stability of the nitrogen flow to ensure the potassium ferrate activates the carbon without oxidative loss.
- If your primary focus is electrical conductivity (Graphitization): Ensure the sample remains in the center of the isothermal zone at 800°C for the full duration to maximize catalytic ordering.
The tube furnace is the defining tool that dictates the final crystalline and porous architecture of your composite material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in SPC-Fe Synthesis |
|---|---|
| Inert Atmosphere | Nitrogen flushing prevents combustion and ensures anaerobic chemical reactions. |
| Temperature Stability | Maintains a precise 800°C zone required for uniform catalytic graphitization. |
| Heating Rate Control | Programmed ramps minimize structural defects and allow orderly thermal decomposition. |
| In-Situ Reduction | Facilitates the transformation of metal ions into dispersed magnetic nanoparticles. |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise control over temperature gradients and atmosphere integrity is the difference between high-performance SPC-Fe composites and failed batches. KINTEK’s advanced Tube and Vacuum furnaces provide the isothermal stability and gas-tight reliability required for complex catalytic graphitization.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and CVD systems designed for the rigors of modern lab research. Don't settle for inconsistent results—leverage our engineering expertise to optimize your high-temperature processes.
Ready to upgrade your lab capabilities? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Preparation of Semi‐Coke‐Based Porous Graphitic Carbon–Iron Oxide Composites and Their Electrochemical Performance for Rhodamine B Degradation. DOI: 10.1155/er/9943954
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical single-temperature zone tube furnace facilitate the growth of high-quality PdSe2 single crystals?
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace ensure effective conversion during MOF selenization? Optimize Your Synthesis
- What is the difference between tube furnaces and muffle furnaces? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab Needs
- What is the role of mixing precursor with sulfur powder? Master Sulfidation in Tube Furnaces for Fe7S8@CT-NS
- What is the function of the five-zone heating layout in a multi-zone DTF? Master Thermal Precision in Combustion
- How are rotary tube furnaces applied in the chemical industry? Unlock Efficient Thermal Processing
- Why is a high-precision vacuum tube furnace essential for CVD graphene? Master Growth Control & Purity
- How does a tube furnace generate high temperatures for heat treatment? Discover Precision Heating Solutions



















