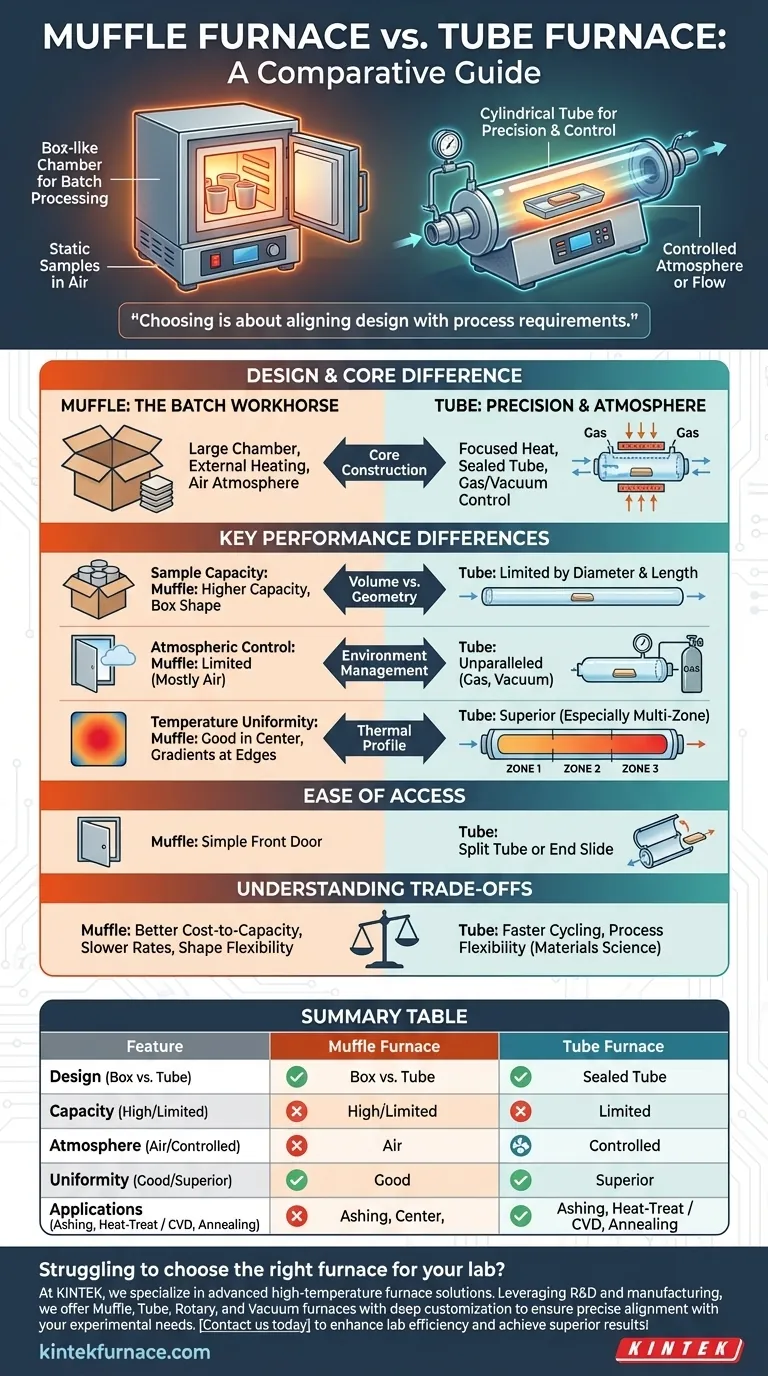
At their core, the primary difference between a tube furnace and a muffle furnace is their geometry and how they hold a sample. A muffle furnace is a box-like chamber designed for heating static samples in a contained space. In contrast, a tube furnace uses a cylindrical tube to heat samples, a design that is ideal for processes requiring a controlled atmosphere or uniform heating over a specific length.
Choosing between these furnaces is not about picking a "better" technology, but about aligning the furnace's fundamental design with your specific process requirements. Muffle furnaces excel at batch processing larger items, while tube furnaces offer superior control over the sample's atmosphere and thermal profile.

The Fundamental Design Distinction
To understand which furnace is right for you, we must first look at their core construction and the applications each design enables.
Muffle Furnace: The Batch Processing Workhorse
A muffle furnace, often used interchangeably with the term "box furnace," features a chamber made of high-temperature insulation that forms a "muffle" around the sample.
The heating elements are typically positioned outside this chamber, heating the sample primarily through radiation and convection. Its large, open-box design is optimized for holding one or more static samples, such as crucibles, trays, or whole components.
This makes it the standard choice for general-purpose lab work like ashing, sintering, binder burnout, or heat-treating parts in air.
Tube Furnace: Precision and Atmospheric Control
A tube furnace's design is centered on a long, cylindrical process tube, typically made of ceramic, quartz, or a metal alloy.
The heating elements surround this tube, providing focused heat. The key advantage here is the ability to seal both ends of the tube. This allows you to create a tightly controlled environment by either pulling a vacuum or flowing a specific process gas (like argon, nitrogen, or hydrogen) over the sample.
This capability is essential for applications like chemical vapor deposition (CVD), purification, annealing in an inert atmosphere, or growing crystals.
Key Performance and Application Differences
The design of each furnace leads to critical differences in performance, capacity, and the types of processes they can handle effectively.
Sample Capacity and Form Factor
Muffle furnaces generally offer more internal capacity for the same price compared to tube furnaces. Their box shape can accommodate a wide variety of sample sizes and shapes, as long as they fit through the door.
Tube furnaces are inherently limited by the diameter and heated length of the process tube. This constrains the physical size of the sample but is ideal for processing wires, rods, or powders spread out in a sample boat.
Atmospheric Control
This is the most significant differentiator. Tube furnaces provide unparalleled atmospheric control. By sealing the ends with flanges, you can precisely manage the gas environment, which is impossible to do with the simple door of a standard muffle furnace.
While some specialized muffle furnaces can be modified for inert gas, they rarely achieve the purity and control of a dedicated tube furnace system.
Temperature Uniformity
For applications requiring a highly consistent temperature over a specific length, a multi-zone tube furnace is superior. These models use two or three independent heating zones that can be programmed to create an exceptionally flat thermal profile along the central portion of the tube.
A muffle furnace's temperature is most uniform in the center of the chamber, but it naturally has gradients closer to the door and walls.
Ease of Access
A muffle furnace offers simple access through a front-loading door. A split tube furnace offers similar convenience, hinging open to allow the entire process tube to be placed or removed easily. This is particularly useful for tubes with complex external connections.
A solid tube furnace requires sliding the sample and the process tube in from one end, which can be less convenient.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right furnace requires weighing their inherent advantages against their limitations for your specific budget and application.
The Cost-to-Capacity Ratio
For general heating tasks, a muffle furnace provides the most heating volume for your investment. If you simply need to heat a large object or many samples in air, a muffle furnace is the more economical choice.
Heating and Cooling Rates
Due to their larger thermal mass and thick insulation, muffle furnaces are often slower to heat up and cool down.
Tube furnaces, especially smaller models, have a lower thermal mass and can often cycle through temperatures more quickly, increasing throughput for certain processes.
Process Flexibility
A muffle furnace offers flexibility in the shape of the sample you can heat. Its large chamber is forgiving.
A tube furnace offers flexibility in the process itself. The ability to control atmosphere, introduce reactive gases, or use a vacuum opens up a much wider range of materials science and chemistry applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the primary goal of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is batch processing, ashing, or heat-treating multiple or large parts in air: A muffle furnace is the most direct and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is precise atmospheric control, CVD, or processing samples under a gas flow: A tube furnace is the necessary tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum temperature uniformity over a specific length: A multi-zone tube furnace is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab heating with the best volume-to-cost ratio: A muffle furnace will provide the most value.
Ultimately, selecting the correct furnace is a matter of matching the equipment's inherent design to the precise demands of your scientific or industrial process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Box-like chamber | Cylindrical tube |
| Sample Capacity | High for batch processing | Limited by tube diameter and length |
| Atmospheric Control | Limited, typically air | Excellent, with vacuum or gas flow |
| Temperature Uniformity | Good in center, gradients at edges | Superior with multi-zone options |
| Common Applications | Ashing, sintering, heat-treating in air | CVD, annealing, purification in controlled atmospheres |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique requirements. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure precise alignment with your experimental needs, whether for batch processing or controlled atmosphere applications. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















