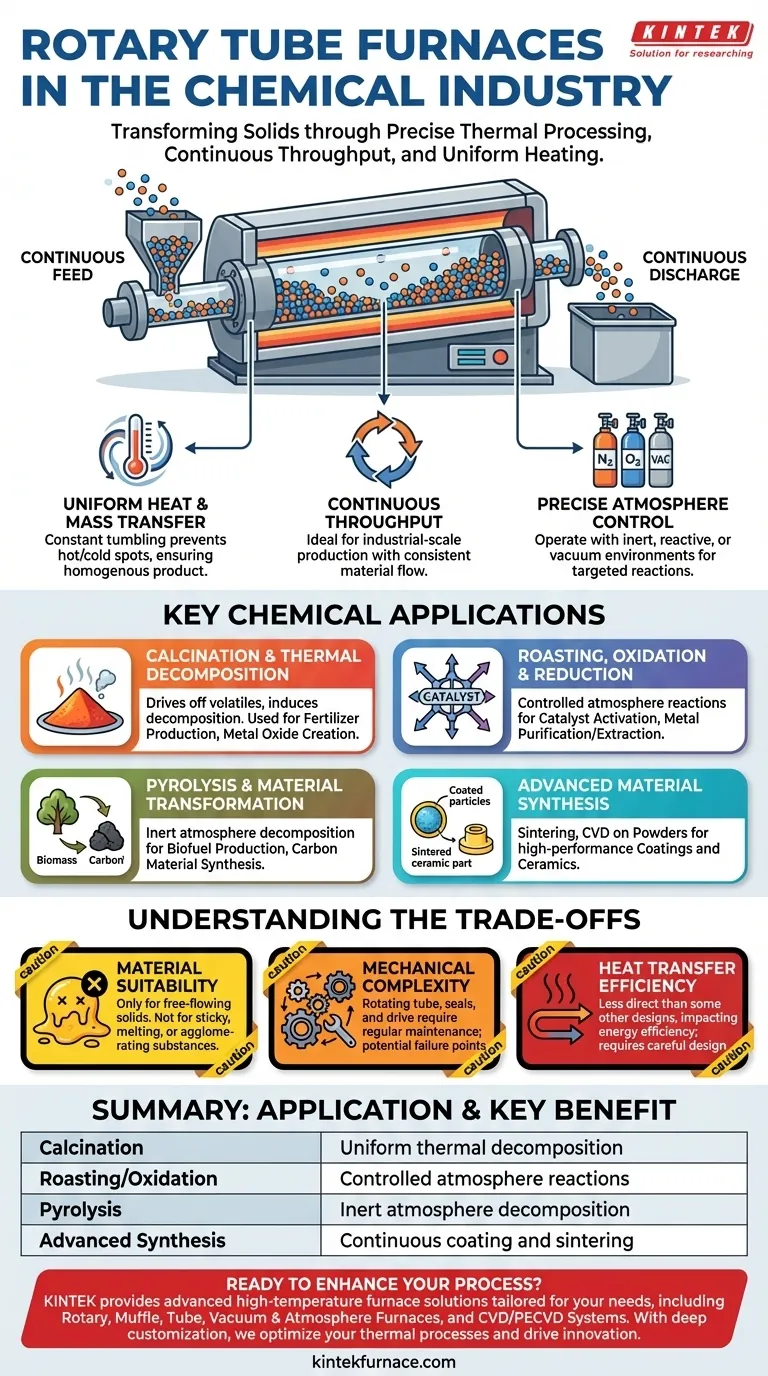
In the chemical industry, rotary tube furnaces are primarily used to induce chemical transformations in solid, granular, or powdered materials through precise thermal processing. They excel at processes requiring continuous throughput and uniform heating, such as calcination for fertilizer production, oxidation for catalyst preparation, and pyrolysis for material decomposition.
The true value of a rotary tube furnace is its ability to continuously tumble and mix materials as they are heated. This dynamic movement ensures every particle is uniformly exposed to the desired temperature and atmospheric conditions, which is critical for consistent, large-scale chemical processing.

The Core Principle: Why a Rotary Furnace?
A rotary tube furnace's design directly addresses a fundamental challenge in industrial chemistry: how to uniformly heat large quantities of solid materials. Its rotating chamber acts like a highly controlled, high-temperature mixer.
Uniform Heat and Mass Transfer
The constant tumbling of the material bed ensures that particles from the center are continuously brought to the surface. This action prevents localized hot or cold spots, leading to a homogenous product. This is essential for reactions where temperature consistency dictates the final product's quality and purity.
Continuous Throughput
Unlike a static batch furnace, a rotary furnace can be fed material continuously at one end and discharge the finished product at the other. This makes it ideal for industrial-scale production lines where a consistent flow of material is necessary.
Precise Atmosphere Control
These furnaces can operate with controlled atmospheres, such as inert gases (nitrogen, argon), reactive gases (oxygen), or under a vacuum. This allows chemists to drive specific reactions, like preventing unwanted oxidation during pyrolysis or intentionally inducing oxidation during roasting.
Key Chemical Applications Breakdown
The combination of continuous mixing, uniform heating, and atmospheric control makes rotary furnaces indispensable for several key chemical processes.
Calcination and Thermal Decomposition
Calcination is a process that uses heat to drive off volatile substances (like water or carbon dioxide) and induce thermal decomposition. Rotary furnaces are the standard for this.
A prime example is in fertilizer manufacturing, where they are used to produce substances like diammonium phosphate. The furnace drives off water and facilitates the reaction at a specific temperature. Similarly, they are used to convert metal hydroxides or carbonates into their respective oxides.
Roasting, Oxidation, and Reduction
Roasting involves heating a solid material in the presence of air or another reactive gas. This is a common method for purification or to prepare a material for a subsequent step.
In chemical synthesis, this is used for catalyst activation or to perform oxidation, which removes electrons and changes a material's chemical state. Conversely, by using a reducing atmosphere (like hydrogen), they can perform reduction to extract metals from ores or compounds.
Pyrolysis and Material Transformation
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures in an inert atmosphere. This process "cracks" complex organic materials into simpler, more valuable substances without combustion.
Rotary furnaces are used to convert biomass into biofuels or to create specialized carbon products. The controlled environment prevents the material from simply burning, allowing for a targeted chemical transformation.
Advanced Material Synthesis
In more advanced applications, rotary furnaces are used for creating high-performance materials. This includes sintering powders to create dense, strong ceramics or metallurgical parts.
They are also employed for processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), where precursor gases react and deposit a thin film onto the surface of powder particles tumbling inside the tube. This method is used to create sophisticated coatings that can improve a material's wear resistance or catalytic activity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the rotary tube furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to proper application.
Material Suitability
These furnaces are designed exclusively for free-flowing granular or powdered solids. They are not suitable for liquids, materials that become sticky, or substances that melt and agglomerate at the processing temperature, as this would halt the tumbling action.
Mechanical Complexity
The rotating tube, seals, and drive mechanism introduce mechanical complexity compared to a static furnace. The seals that maintain the controlled atmosphere at the inlet and outlet are critical components that require regular maintenance and can be points of failure.
Heat Transfer Efficiency
While the tumbling action is excellent for solids, the overall heat transfer from the external heating elements to the bulk material can be less direct than in some other furnace designs. This can impact energy efficiency and require careful design to achieve target temperatures in the core of the material bed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the right thermal equipment depends entirely on your material, desired scale, and the specific chemical transformation you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is bulk production of a chemical powder or mineral: The continuous throughput and uniform heating of a rotary furnace make it the most efficient and logical choice.
- If your primary focus is creating high-performance coated powders or catalysts: A rotary furnace with advanced atmosphere control is ideal for ensuring every particle is uniformly treated.
- If your primary focus is small-batch R&D or processing materials that melt: A static batch furnace may offer simpler operation and more direct temperature control for your specific sample.
- If your primary focus is thermally treating a small number of large, solid objects: A chamber or box furnace would be a more appropriate tool for the task.
Ultimately, the rotary tube furnace is the industry workhorse for any chemical process that demands uniform heat treatment of continuous-flowing solid particles.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Calcination | Uniform thermal decomposition | Fertilizer production, metal oxide creation |
| Roasting/Oxidation | Controlled atmosphere reactions | Catalyst activation, metal purification |
| Pyrolysis | Inert atmosphere decomposition | Biofuel production, carbon material synthesis |
| Advanced Synthesis | Continuous coating and sintering | CVD on powders, ceramic part manufacturing |
Ready to enhance your chemical processing with precision and efficiency? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for your needs. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is designed for industries requiring uniform heating and continuous throughput. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure our solutions precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processes and drive your innovations forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing



















