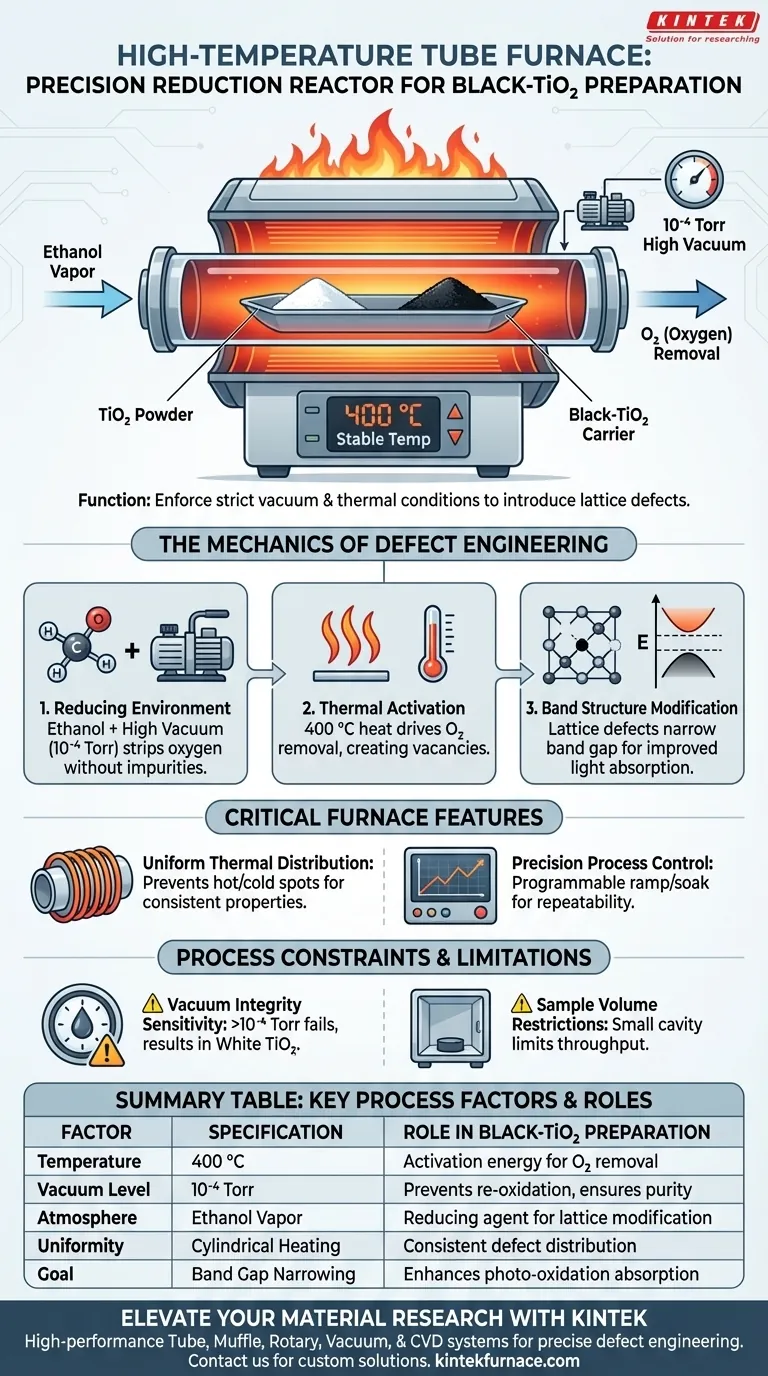
The high-temperature tube furnace serves as a precision reduction reactor specifically engineered to alter the chemical structure of titanium dioxide (TiO2). By maintaining a rigorous environment of 400 °C and high vacuum (10⁻⁴ Torr), it facilitates the thermal reduction of TiO2 powder using ethanol vapor, transforming the material into "Black-TiO2."
The furnace is not merely a heating element; it is a defect-engineering tool. Its primary function is to enforce the strict vacuum and thermal conditions required to introduce lattice defects, thereby modifying the TiO2 energy band structure and enhancing its photocatalytic capabilities.
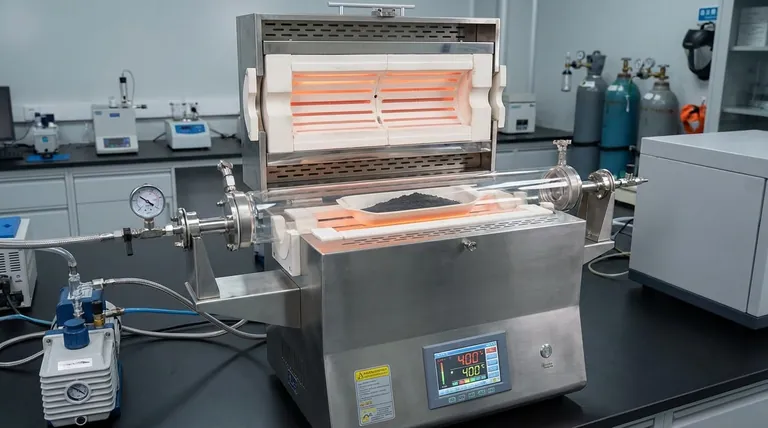

The Mechanics of Defect Engineering
Creating the Reducing Environment
The standard preparation of Black-TiO2 requires a specific chemical atmosphere that standard ovens cannot provide. The tube furnace enables the introduction of ethanol as a reducing agent while simultaneously maintaining a high vacuum of 10⁻⁴ Torr. This combination is essential to strip oxygen atoms from the TiO2 structure without introducing unwanted impurities.
Thermal Activation at 400 °C
Heat acts as the catalyst for the reduction process. The furnace maintains a stable temperature of 400 °C, providing the necessary energy for the ethanol vapor to react with the TiO2 powder. This thermal energy drives the removal of oxygen, creating the desired vacancies (defects) within the crystal lattice.
Modification of Energy Band Structure
The ultimate function of this thermal processing is to alter the electronic properties of the carrier. By introducing defects into the TiO2 lattice, the furnace treatment modifies the energy band structure. This modification is critical for narrowing the band gap, allowing the material to absorb a broader spectrum of light for improved photo-oxidation.
Why a Tube Furnace is Critical
Uniform Thermal Distribution
The cylindrical design of the furnace, wrapped with heating coils, ensures that heat is applied evenly around the sample. This uniform thermal distribution prevents "hot spots" or "cold spots" that could lead to uneven reduction across the powder sample. Consistent heating is vital for ensuring that the entire batch of Black-TiO2 exhibits the same catalytic properties.
Precision Process Control
Advanced tube furnaces utilize thermocouples and control systems to regulate heat with high accuracy. This allows for programmable ramp rates and soak times, ensuring the sample reaches 400 °C gradually and stays there for the exact duration required. This repeatability is essential for verifying experimental data and scaling the production of the carrier.
Understanding Process Constraints and Limitations
Vacuum Integrity Sensitivity
The success of Black-TiO2 preparation is entirely dependent on the quality of the seal. Even a minor fluctuation in the vacuum pressure (above 10⁻⁴ Torr) can introduce atmospheric oxygen, neutralizing the reducing power of the ethanol. This results in standard white TiO2 rather than the defective, active Black-TiO2.
Sample Volume Restrictions
Tube furnaces typically feature a relatively small cavity designed for treating small samples. While excellent for research and precision, this creates a throughput bottleneck. Attempting to overload the tube can disrupt the airflow and thermal uniformity, leading to inconsistent defect formation within the lattice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the efficacy of your Black-TiO2 preparation, align your furnace settings with your specific research objectives:
- If your primary focus is maximizing catalytic activity: Prioritize vacuum stability; ensure your pump can maintain 10⁻⁴ Torr continuously to maximize the concentration of lattice defects.
- If your primary focus is experimental consistency: Utilize the furnace's programmable ramp rates to standardize the heating and cooling phases, eliminating variables between different batches.
By leveraging the tube furnace as a controlled environment for defect engineering rather than just a heat source, you unlock the synergistic potential of Black-TiO2 carriers in photo-oxidation processes.
Summary Table:
| Key Process Factor | Specification | Role in Black-TiO2 Preparation |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 400 °C | Provides activation energy for oxygen removal |
| Vacuum Level | 10⁻⁴ Torr | Prevents re-oxidation and ensures reduction purity |
| Atmosphere | Ethanol Vapor | Acts as the reducing agent for lattice modification |
| Uniformity | Cylindrical Heating | Ensures consistent defect distribution across powder |
| Goal | Band Gap Narrowing | Enhances light absorption for photo-oxidation |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precise defect engineering requires equipment that never wavers. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of advanced photocatalyst synthesis. Whether you are preparing Black-TiO2 carriers or exploring new crystal lattice modifications, our customizable lab high-temperature furnaces provide the vacuum integrity and thermal stability your research deserves.
Ready to achieve superior consistency in your lab? Contact KINTEK today for a customized solution
Visual Guide
References
- Julia Ong, J. C. Scaiano. Comparison of Composite Materials Designed to Optimize Heterogeneous Decatungstate Oxidative Photocatalysis. DOI: 10.3390/molecules30173597
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How does high-purity Nitrogen thermal annealing in a tube furnace facilitate the observation of Violet Phosphorus?
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace play in the carbonization process of moxa floss? Expert Guide to Biomass Synthesis
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for long-term heat treatment of FeTeSe crystals? Achieve High Crystallinity & Uniformity
- What materials are used for the chamber and insulation in three-zone split tube furnaces? Optimize Your High-Temp Processes
- What is the process for using a vacuum tube experimental furnace? Master Precise Control for Your Lab
- How is temperature regulation achieved in a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Master Precise Control for Your Lab
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace required for the post-treatment of composite anode materials in argon?
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature tube furnace in aerosol-assisted spray pyrolysis? | KINTEK



















