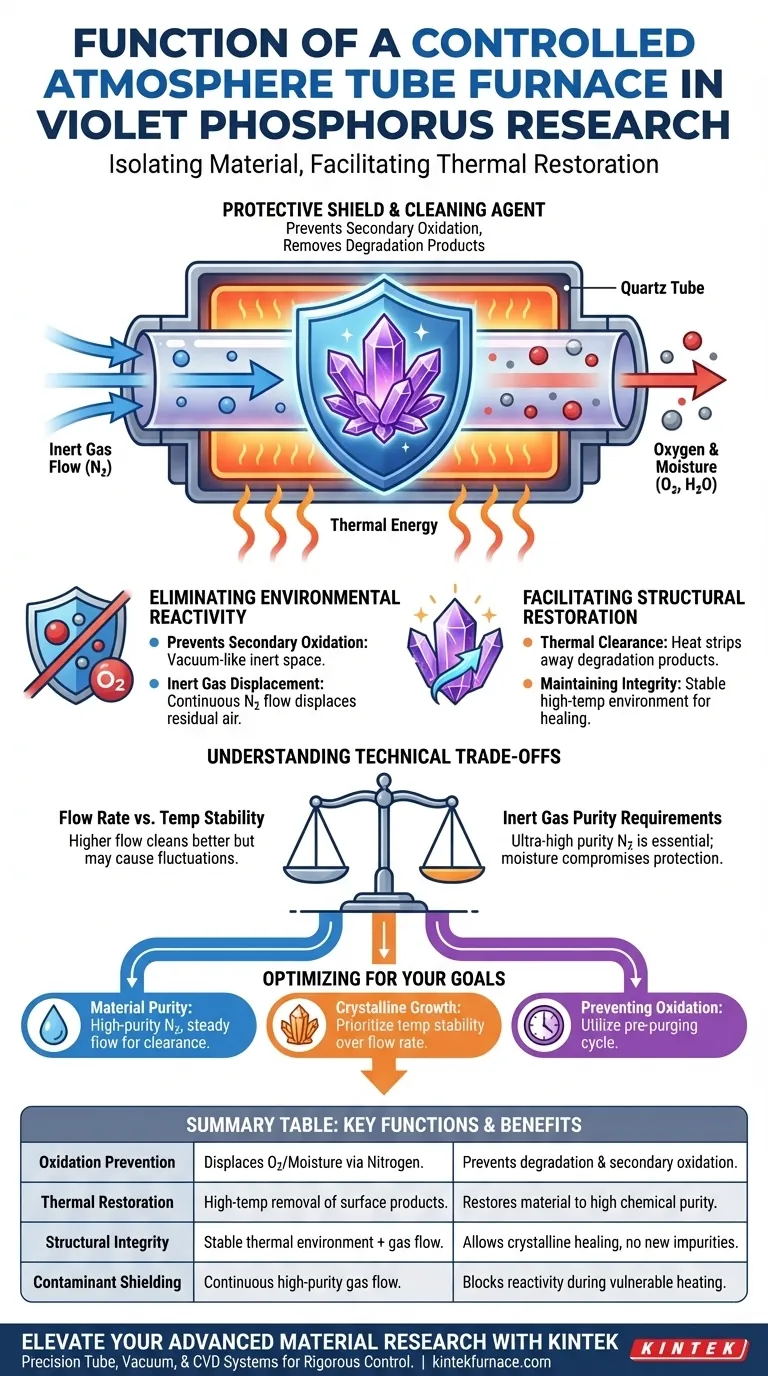
In Violet Phosphorus research, the primary function of a tube furnace's controlled atmosphere is to isolate the material from oxygen and moisture while facilitating thermal restoration. By maintaining a continuous flow of inert gas—typically Nitrogen—at high temperatures, the furnace prevents secondary oxidation and removes existing degradation products. This ensures the chemical structural integrity of the phosphorus remains intact during critical high-temperature processing.
The controlled atmosphere acts as both a protective shield and a cleaning agent, using thermal energy and inert gas flow to restore Violet Phosphorus without allowing environmental contaminants to compromise its delicate chemical structure.
Eliminating Environmental Reactivity
Preventing Secondary Oxidation
Violet Phosphorus is highly sensitive to the presence of oxygen and moisture, which can lead to rapid material degradation. The controlled atmosphere creates a vacuum-like or inert space that physically blocks these reactive elements from reaching the sample.
The Role of Inert Gas Displacement
A continuous flow of Nitrogen or other inert gases serves to displace any residual air within the furnace tube. This displacement is vital because even trace amounts of oxygen at high temperatures can trigger unwanted chemical reactions that alter the phosphorus.
Facilitating Structural Restoration
Thermal Clearance of Degradation Products
The furnace utilizes thermal driving forces to strip away existing degradation products that may have formed on the material's surface. This "cleaning" process is essential for returning the Violet Phosphorus to a high state of purity.
Maintaining Chemical Structural Integrity
While heat is necessary for restoration, it also increases the material's vulnerability to the environment. The stable high-temperature environment provided by the furnace allows for structural healing while the inert gas flow ensures that no new impurities are introduced during this vulnerable phase.
Understanding Technical Trade-offs
Balancing Temperature and Flow Rates
A critical trade-off exists between the speed of gas flow and the stability of the temperature profile within the furnace. While higher flow rates ensure a cleaner atmosphere, they can sometimes cause temperature fluctuations that might stress the sensitive phosphorus crystals.
Inert Gas Purity Requirements
The effectiveness of the controlled atmosphere is entirely dependent on the purity of the source gas. If the Nitrogen supply contains even minute moisture content, the protective function of the furnace is compromised, potentially leading to the very oxidation the researcher is trying to avoid.
Optimizing the Environment for Your Research Goals
When configuring a laboratory tube furnace for Violet Phosphorus, your specific objectives will dictate the ideal atmospheric settings.
- If your primary focus is material purity: Ensure a high-purity Nitrogen source and a steady flow rate to maximize the clearance of degradation products.
- If your primary focus is structural crystalline growth: Prioritize temperature stability over high flow rates to maintain a consistent thermal environment for the phosphorus.
- If your primary focus is preventing immediate oxidation: Utilize a pre-purging cycle to ensure all oxygen is displaced before the heating elements are engaged.
The precision of a controlled atmosphere is the fundamental bridge between a degraded sample and a restored, high-integrity Violet Phosphorus crystal.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Description | Benefit to Violet Phosphorus |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidation Prevention | Displacement of O2 and moisture via inert gas (Nitrogen). | Prevents material degradation and secondary oxidation. |
| Thermal Restoration | High-temp removal of existing surface degradation products. | Restores material to a high state of chemical purity. |
| Structural Integrity | Stable thermal environment combined with protective gas flow. | Allows crystalline healing without introducing new impurities. |
| Contaminant Shielding | Continuous flow of high-purity source gas. | Blocks environmental reactivity during vulnerable heating phases. |
Elevate Your Advanced Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable when dealing with sensitive materials like Violet Phosphorus. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to deliver the rigorous atmospheric control and thermal stability your research demands.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to your specific gas purity and flow rate requirements, ensuring your samples remain protected from oxidation while achieving optimal crystalline growth.
Ready to optimize your thermal processing? Contact our specialists today to find the perfect furnace solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Xiangzhe Zhang, Shiqiao Qin. Photodegradation and van der Waals Passivation of Violet Phosphorus. DOI: 10.3390/nano14050422
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of using atmosphere furnaces? Boost Efficiency and Control in Heat Treatment
- What is the endothermic gas in heat treatment? Master Carbon Control for Superior Steel Hardening
- Why is an industrial calcination furnace required to process carbon-supported nickel catalysts at 600°C in nitrogen?
- Why are high-temperature vacuum or atmosphere furnaces used for annealing metal silicide? Unlock Peak Thermal Stability
- What is the purpose of inerting in heat treatment furnaces? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Safety
- What is the significance of the preheating step using a high-temperature furnace? Ensure Pellets Strength and Integrity
- Why is an Argon-Hydrogen gas mixture used in aerodynamic levitation? Achieve Pure Metal Melting and Precision Control
- What are the key considerations when using an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Ensure Safety and Precision for Your Lab



















