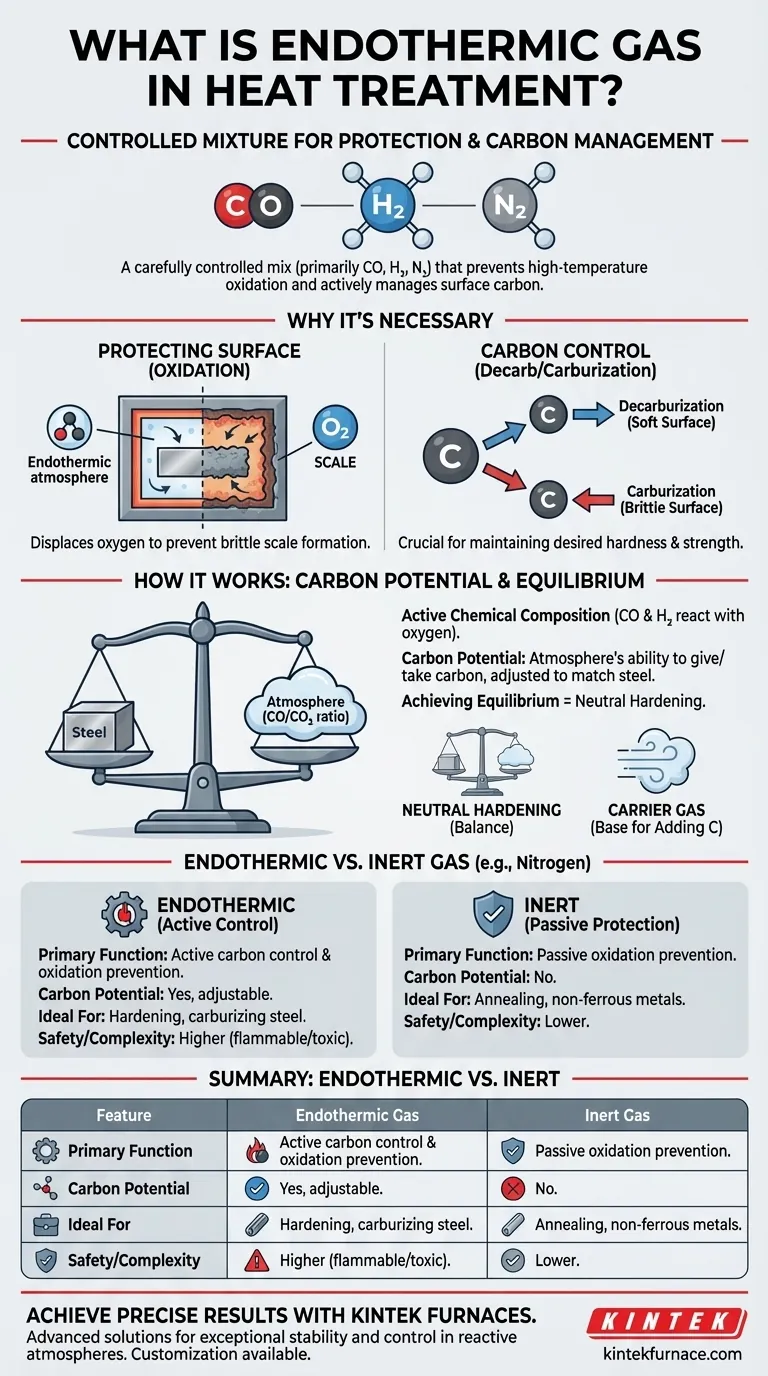
In short, endothermic gas is a carefully controlled mixture of combustible gases—primarily carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H₂), and nitrogen (N₂)—used during the heat treatment of steel. It serves as a protective atmosphere, preventing high-temperature oxidation (scaling), but its most critical function is to actively manage the carbon content on the surface of the steel part.
The core purpose of endothermic gas is not just to be a passive shield like an inert gas. It is an engineered, reactive atmosphere that establishes an equilibrium with the steel, allowing you to precisely control its surface carbon content and, therefore, its final mechanical properties.

Why a Special Atmosphere is Necessary
Protecting the Surface from Oxygen
At the high temperatures required for heat treatment, steel reacts readily with oxygen in the air. This reaction, known as oxidation, forms a layer of brittle scale on the part's surface.
A protective atmosphere, like endothermic gas, displaces the oxygen inside the furnace, completely preventing this destructive scaling and preserving the part's surface finish.
The Deeper Problem: Carbon Control
Simply preventing oxidation is not enough for most steels. The carbon content within the steel is what primarily determines its hardness and strength.
At high temperatures, the carbon atoms within the steel become mobile. If the surrounding atmosphere is not precisely controlled, carbon can either leave the steel (decarburization), creating a soft surface, or be added to it (carburization), creating a brittle one.
How Endothermic Gas Solves the Problem
Its Active Chemical Composition
Endothermic gas is typically generated by reacting a hydrocarbon fuel, like natural gas, with a limited amount of air. This creates a gas rich in carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H₂), with the remainder being primarily nitrogen (N₂).
The CO and H₂ components are "reducing" agents, meaning they readily react with any stray oxygen. More importantly, the carbon monoxide provides a source of carbon to the atmosphere itself.
The Principle of Carbon Potential
The true power of endothermic gas lies in the concept of carbon potential. This is a measure of the atmosphere's ability to either give carbon to or take carbon from the steel at a specific temperature.
By carefully monitoring and adjusting the gas composition (specifically the ratio of CO to CO₂), an operator can set the atmosphere's carbon potential to perfectly match the carbon content of the steel being treated. This creates a state of equilibrium where no net carbon transfer occurs.
"Neutral Hardening" vs. Carrier Gas
When the carbon potential of the gas matches the steel, the process is called neutral hardening. The steel is heated and cooled to achieve its desired hardness without altering its surface chemistry.
Endothermic gas can also be used as a carrier gas. In this case, it's the base atmosphere to which other gases (like more natural gas for carburizing) are added to intentionally increase the steel's surface carbon in a controlled manner.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Critical Need for Control
Endothermic gas is not a "set it and forget it" solution. Its effectiveness depends entirely on constant monitoring and precise control, typically using an oxygen probe or infrared gas analyzer.
If the carbon potential is too low, decarburization will occur, defeating the purpose of the heat treatment. If it's too high, unwanted carburization or soot formation can ruin the parts.
Safety and Infrastructure
The primary components, CO and H₂, are toxic and flammable, respectively. Operating an endothermic atmosphere requires a well-maintained furnace, proper ventilation, and robust safety protocols. It also requires an on-site endothermic gas generator, which represents a significant equipment investment.
Endothermic vs. Inert Gas
Inert gases like nitrogen (N₂) and argon (Ar) are much simpler. They provide excellent oxidation protection and are completely non-reactive. However, they cannot actively manage carbon content and can even contribute to decarburization if not perfectly pure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Choosing the correct furnace atmosphere is fundamental to achieving the desired metallurgical outcome.
- If your primary focus is simple annealing or treating non-ferrous metals: An inert gas like nitrogen is often the safest, simplest, and most effective choice.
- If your primary focus is hardening, carburizing, or carbonitriding medium-to-high carbon steels: Endothermic gas is the industry standard because it provides the active control over carbon potential necessary to protect the integrity of the steel.
Ultimately, mastering the use of a furnace atmosphere is as critical as controlling the temperature itself for successful heat treatment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Endothermic Gas | Inert Gas (e.g., Nitrogen) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Active carbon control & oxidation prevention | Passive oxidation prevention |
| Carbon Potential | Yes, adjustable | No |
| Ideal For | Hardening, carburizing steel | Annealing, non-ferrous metals |
| Safety/Complexity | Higher (flammable/toxic) | Lower |
Achieve precise, repeatable results in your steel heat treatment processes. Endothermic gas is critical for hardening and carburizing, but its effectiveness depends on precise furnace control and a reliable atmosphere. KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces, including our Vacuum & Atmosphere and Tube Furnaces, are engineered for exceptional stability and control, providing the ideal environment for managing reactive atmospheres. Our strong in-house customization capabilities allow us to tailor a furnace solution to your specific gas and thermal requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you master carbon potential and enhance your lab's capabilities. Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments



















