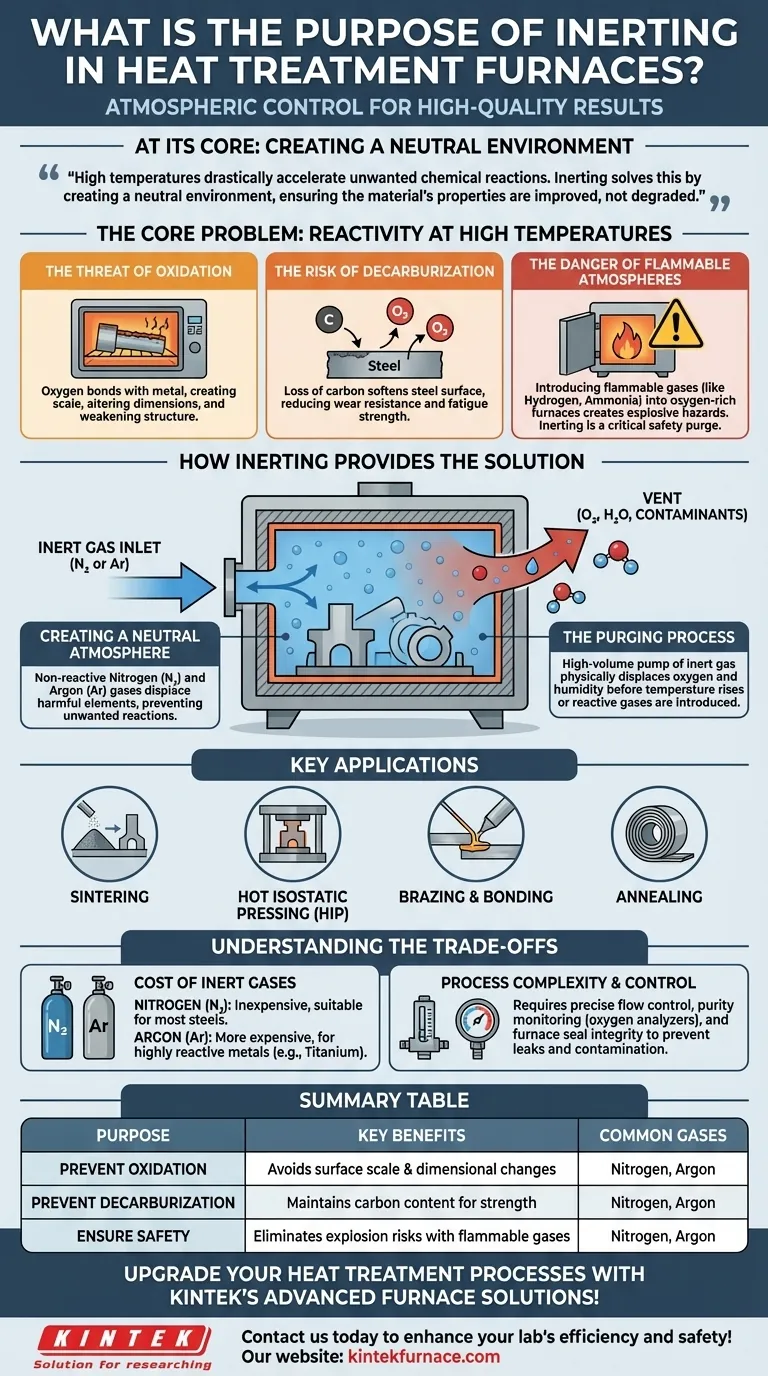
At its core, inerting a heat treatment furnace is a process of atmospheric control. It involves flooding the furnace chamber with a non-reactive gas, typically nitrogen or argon, to systematically purge and displace harmful elements like oxygen, water vapor, and flammable gases before and during the treatment cycle.
The fundamental challenge of heat treatment is that high temperatures drastically accelerate unwanted chemical reactions. Inerting solves this by creating a neutral environment, ensuring the material's properties are improved by the heat itself, not degraded by a reactive atmosphere.

The Core Problem: Reactivity at High Temperatures
Heat is the intended tool in a furnace, but it also acts as a powerful catalyst for destructive chemical reactions. Without a controlled atmosphere, the very process designed to strengthen a part can end up ruining it.
The Threat of Oxidation
At high temperatures, metals are highly susceptible to oxidation. Oxygen in the air will readily bond with the metal surface, creating scale or oxide layers.
This oxidation is not just a surface blemish; it can alter the dimensions of the part, compromise its structural integrity, and weaken its performance.
The Risk of Decarburization
For carbon-based steels, the presence of oxygen or water vapor at high temperatures can strip carbon atoms from the surface of the metal.
This loss of carbon, known as decarburization, softens the steel's surface, reducing its wear resistance and fatigue strength, directly undermining the goals of many heat treatment processes.
The Danger of Flammable Atmospheres
Many advanced heat treatments use reactive process gases (like hydrogen or ammonia) to achieve specific surface properties.
Introducing these flammable or combustible gases into an oxygen-rich furnace would create an explosive hazard. Inerting serves as a critical safety step to purge all oxygen before these reactive gases are introduced.
How Inerting Provides the Solution
By replacing the reactive ambient air with an inert gas, you effectively neutralize the environment inside the furnace, allowing the heat to do its work without interference.
Creating a Neutral Atmosphere
The most common inerting agents are nitrogen (N₂) and argon (Ar). These gases are chosen because they are non-reactive and will not interact with the metal parts, even at extreme temperatures.
They create a stable, neutral background that prevents the unwanted chemical reactions of oxidation and decarburization from occurring.
The Purging Process
The inerting process involves pumping a high volume of nitrogen or argon into the sealed furnace chamber. This physically displaces the oxygen, humidity, and any other contaminants, pushing them out through a vent.
This purge cycle ensures the internal atmosphere is clean and non-reactive before the temperature begins to rise or any active process gases are introduced.
Key Applications
This process is fundamental to achieving clean, high-quality parts in applications such as:
- Sintering: Fusing powdered materials (like those from additive manufacturing) into a solid, dense part.
- Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP): Using high pressure and temperature to eliminate porosity in castings or 3D-printed parts.
- Brazing and Bonding: Joining metals without melting them, requiring a perfectly clean surface free of oxides.
- Annealing: Softening metals to improve their ductility, where a bright, clean surface finish is required.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential, implementing an inerting strategy involves balancing cost, complexity, and material requirements. It is not a one-size-fits-all solution.
Cost of Inert Gases
Nitrogen is the workhorse of the industry. It is relatively inexpensive and suitable for the vast majority of heat treatment applications involving steels and other common alloys.
Argon is significantly more inert than nitrogen but is also more expensive. Its use is typically reserved for highly reactive metals like titanium, or in processes where even the slightest interaction with nitrogen cannot be tolerated.
Process Complexity and Control
Effective inerting is more than just opening a gas valve. It requires precise control of flow rates and a system for monitoring atmospheric purity (e.g., using an oxygen analyzer).
Leaks in the furnace seals can allow oxygen to re-enter, compromising the entire process. Maintaining furnace integrity and monitoring systems is critical for success and repeatability.
Not a Universal Requirement
Some processes, like carburizing or nitriding, intentionally use a reactive atmosphere to diffuse carbon or nitrogen into the steel's surface.
In these cases, inerting is still used for the initial safety purge, but it is then replaced by the active gas mixture. The inert atmosphere itself does not provide the desired chemical change.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your inerting strategy should be directly aligned with your material, your process, and your final component goals.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective treatment of common steels: Nitrogen is almost always the correct and most economical choice for preventing oxidation and decarburization.
- If your primary focus is treating highly reactive metals like titanium or specific superalloys: The superior inertness of argon is necessary to prevent material contamination and ensure optimal properties.
- If your primary focus is operational safety when using flammable process gases: A thorough inert gas purge is a non-negotiable first step to eliminate the risk of explosion.
Mastering the furnace atmosphere is fundamental to achieving consistent, high-quality results in modern manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Key Benefits | Common Gases Used |
|---|---|---|
| Prevent Oxidation | Avoids surface scale and dimensional changes | Nitrogen, Argon |
| Prevent Decarburization | Maintains carbon content for strength | Nitrogen, Argon |
| Ensure Safety | Eliminates explosion risks with flammable gases | Nitrogen, Argon |
| Applications | Sintering, HIP, Brazing, Annealing | Nitrogen, Argon |
Upgrade your heat treatment processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise fit for your unique experimental needs, helping you achieve consistent, high-quality results with reliable inerting. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and safety!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process



















