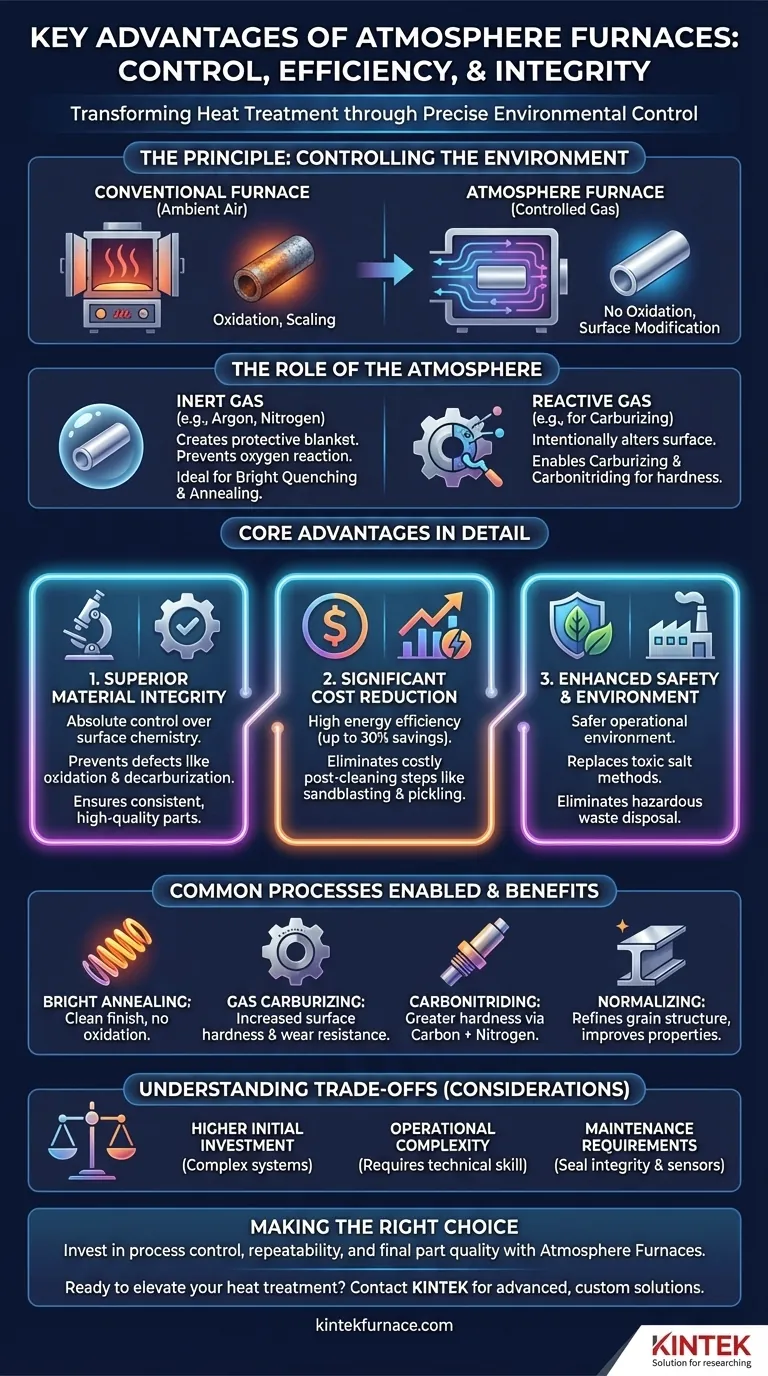
At their core, atmosphere furnaces deliver three distinct advantages: high energy efficiency, significant cost reduction, and superior control over material properties. By introducing a precisely controlled gas environment during heat treatment, these furnaces prevent undesirable chemical reactions like oxidation and enable specific surface modifications that are impossible in open-air systems.
An atmosphere furnace isn't just for heating; it's a tool for chemical engineering at high temperatures. Its primary value lies in creating a controlled, reactive or inert environment that protects the workpiece and actively modifies its surface chemistry for enhanced performance.

The Principle: Controlling the Environment
Beyond Simple Heating
A conventional furnace heats a material in ambient air. An atmosphere furnace goes a step further by first removing the air and then introducing a specific, artificially prepared gas mixture.
This "atmosphere" is the key. It transforms the furnace from a simple oven into a highly controlled process chamber where both temperature and chemistry are managed with precision.
The Role of the Atmosphere
The gas composition is tailored to the desired outcome. An inert gas, like argon or nitrogen, is used to create a protective blanket. This prevents oxygen and moisture from reacting with the hot metal surface.
Alternatively, a reactive gas mixture is used to intentionally alter the surface of the part. This enables sophisticated metallurgical processes that change the material's fundamental properties.
Common Processes Enabled
This level of control unlocks a range of critical heat treatment applications. These include:
- Bright Quenching & Annealing: Heating and cooling parts without any surface oxidation, resulting in a clean, "bright" finish that requires no secondary cleaning.
- Gas Carburizing: Introducing carbon into the surface of steel to increase its hardness and wear resistance.
- Carbonitriding: Adding both carbon and nitrogen to the surface for even greater hardness.
- Normalizing: Refining the grain structure of a metal to improve its mechanical properties in a protected environment.
The Core Advantages in Detail
Advantage 1: Superior Material Integrity
The primary benefit is absolute control over the material's surface chemistry. This prevents common heat-treating defects like oxidation (scaling) and decarburization (loss of surface carbon).
The result is a higher quality, more consistent product. Parts emerge from the furnace with the exact surface properties intended, eliminating material waste and variability.
Advantage 2: Significant Cost Reduction
While the initial investment may be higher, atmosphere furnaces reduce operational costs in two key ways.
First, they are highly energy-efficient, with optimized heat retention leading to energy savings of up to 30% over older methods.
Second, by producing clean, finished parts, they eliminate the need for costly and labor-intensive secondary operations like sandblasting, pickling, or machining to remove scale.
Advantage 3: Enhanced Environmental and Operator Safety
Atmosphere furnaces provide a much safer and cleaner operational environment. They replace outdated heat treatment methods that relied on toxic materials like cyanide salts.
This eliminates the significant hazards of handling toxic substances and the environmental burden of disposing of contaminated waste salts and fixtures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Higher Initial Investment
Atmosphere furnaces are more complex than their conventional air-based counterparts. The systems required to control gas flow, ensure furnace seals are tight, and monitor the atmosphere add to the initial capital cost.
Operational Complexity
Operating an atmosphere furnace requires a higher level of technical skill. Personnel must manage gas supplies, understand the safety protocols for flammable or asphyxiant gases, and properly program the process controllers to achieve consistent results.
Maintenance Requirements
The integrity of the furnace is paramount. Gaskets, seals, and atmosphere control sensors require diligent and preventative maintenance to prevent leaks. A leak can compromise the process, ruin a batch of parts, and create safety hazards.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Choosing a furnace requires a clear understanding of your technical and business goals. The decision to invest in atmosphere control depends entirely on the required outcome.
- If your primary focus is surface finish and material integrity: Atmosphere control is non-negotiable for preventing oxidation and achieving bright, clean parts directly from the furnace.
- If you need to perform specific surface modifications: Processes like carburizing or nitriding fundamentally require a reactive gas atmosphere that only these furnaces can provide.
- If your process is simple and cost is the main driver: A conventional air furnace may be sufficient, provided surface oxidation and subsequent cleaning are acceptable for your application.
- If you are concerned with environmental regulations and safety: An atmosphere furnace eliminates the hazards and disposal costs associated with older, salt-based heat treatment methods.
Ultimately, choosing an atmosphere furnace is an investment in process control, repeatability, and final part quality.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Superior Material Integrity | Prevents oxidation and decarburization for consistent, high-quality parts |
| Significant Cost Reduction | Saves up to 30% in energy and eliminates secondary cleaning processes |
| Enhanced Safety | Replaces toxic methods, reducing environmental and operator hazards |
Ready to elevate your heat treatment processes? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Atmosphere Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your lab's efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure superior material outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of nitrogen in atmosphere furnaces? Unlock Enhanced Heat Treatment and Surface Hardening
- What is the relationship between temperature and the furnace atmosphere in material processing? Master the Critical Heat-Environment Balance
- Why is moisture control critical in inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Integrity
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity



















