The core role of a vacuum melting furnace is to create a precisely controlled environment of high vacuum and high temperature. This unique combination manipulates the fundamental physical properties of magnesium, drastically lowering its boiling point so it can vaporize and separate from the less volatile impurities remaining in the slag.
A vacuum furnace doesn't just melt metal; it functions as a physical filter. By manipulating pressure and temperature, it makes magnesium uniquely volatile, allowing it to be distilled as a vapor while other contaminants are left behind as solids or liquids.
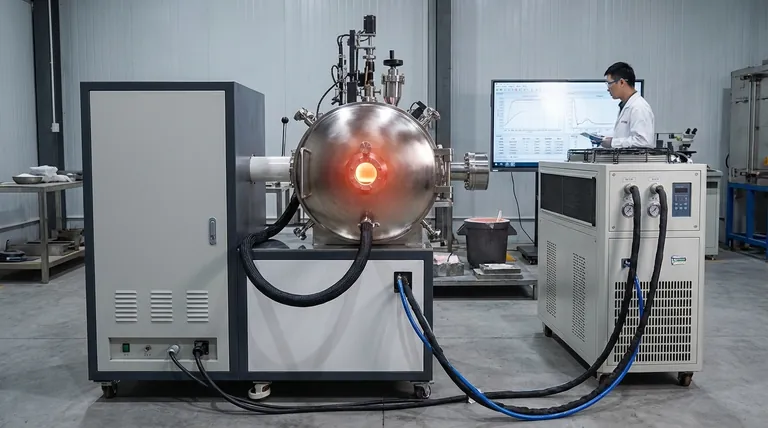

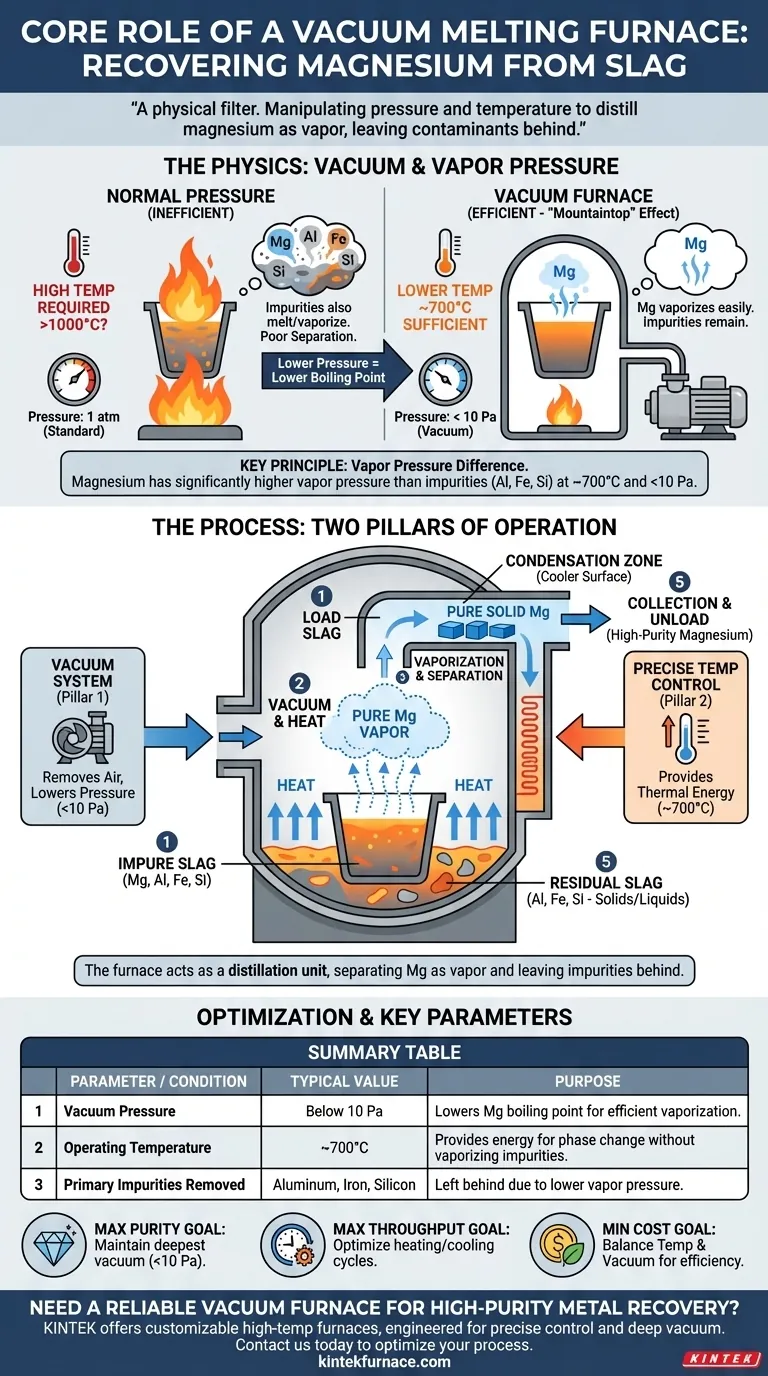
The Physics of Separation: Vacuum and Vapor Pressure
To understand the furnace's role, you must first understand the principle it exploits: the relationship between pressure and a substance's boiling point. This is the key to the entire recovery process.
The Challenge at Normal Pressure
At standard atmospheric pressure, you would need to heat slag to extremely high temperatures to boil magnesium. This approach is inefficient and would likely melt or vaporize other unwanted elements, resulting in a poor-quality final product.
How Vacuum Changes the Game
A vacuum pump removes air and other gases from the furnace, dramatically lowering the internal pressure. This low-pressure environment makes it much easier for magnesium atoms to escape from the liquid or solid slag and enter a gaseous state.
Think of it like boiling water on a high mountain. Because the air pressure is lower, water boils at a temperature below 100°C. The vacuum furnace creates an "extreme mountaintop" environment for magnesium.
Exploiting Vapor Pressure Differences
Every element has a natural tendency to vaporize, known as its vapor pressure. Magnesium has a significantly higher vapor pressure than common impurities like aluminum, iron, and silicon.
The furnace creates conditions—specifically a pressure below 10 Pa and a temperature around 700°C—where magnesium's vapor pressure is high enough for it to rapidly evaporate, while the impurities' vapor pressures remain negligible.
The Two Pillars of Furnace Operation
The furnace's success relies on its ability to perfectly manage two independent but complementary systems.
Pillar 1: The High-Vacuum System
The primary job of the vacuum system is to create and maintain the low-pressure environment. By removing air, it clears the path for magnesium vapor to leave the slag and travel to a cooler collection area where it can condense back into a pure solid.
Pillar 2: The Precise Temperature Control
Heat provides the thermal energy required for the phase change from solid/liquid to gas. The temperature must be carefully controlled.
It needs to be hot enough to facilitate magnesium vaporization but cool enough to prevent the impurities from also boiling off. This precise thermal management ensures the separation is clean and effective.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
While highly effective, this process is not without its operational challenges and limitations. Understanding them is critical for any practical application.
Energy Consumption
Maintaining a deep vacuum while simultaneously heating material to 700°C is extremely energy-intensive. This represents a significant portion of the operational cost and is a primary factor in the process's overall economic viability.
Process Integrity
The entire system depends on the furnace being perfectly sealed. Any air leaks compromise the vacuum, raising the boiling point of magnesium and drastically reducing the efficiency and purity of the separation.
Batch Processing Limitations
Unlike some continuous industrial processes, vacuum furnaces typically operate in batches. The need to load the slag, draw a vacuum, run the heating cycle, cool down, and then remove the purified magnesium and residual slag creates a cyclical workflow that impacts overall throughput.
Applying This to Your Goal
The furnace's operation can be optimized based on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing purity: Maintaining the deepest possible vacuum (well below 10 Pa) is your most critical variable, as this creates the largest separation in boiling points between magnesium and contaminants.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: Optimizing the heating and cooling cycle times is key, but this cannot be done at the expense of achieving the target temperature and vacuum levels.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational cost: The goal is to find the perfect balance between temperature and vacuum—using just enough of each to achieve the desired separation without wasting energy.
Ultimately, the vacuum furnace provides an elegant solution by transforming a complex chemical separation problem into a straightforward physical one.
Summary Table:
| Key Process Parameter | Typical Value / Condition | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Pressure | Below 10 Pa | Lowers magnesium's boiling point for efficient vaporization. |
| Operating Temperature | ~700°C | Provides thermal energy for phase change without vaporizing impurities. |
| Primary Impurities Removed | Aluminum, Iron, Silicon | Left behind as solids/liquids due to lower vapor pressure. |
| Recovery Mechanism | Distillation & Condensation | Magnesium vapor travels to a cooler surface and condenses into pure solid form. |
Need a Reliable Vacuum Furnace for High-Purity Metal Recovery?
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, CVD systems, and other lab high-temp furnaces, all customizable for unique needs. Our vacuum furnaces are engineered to deliver the precise temperature control and deep vacuum required for efficient and pure magnesium recovery from slag.
Contact us today to discuss how a KINTEK vacuum furnace can optimize your metal recovery process, enhance purity, and improve your operational efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification



















