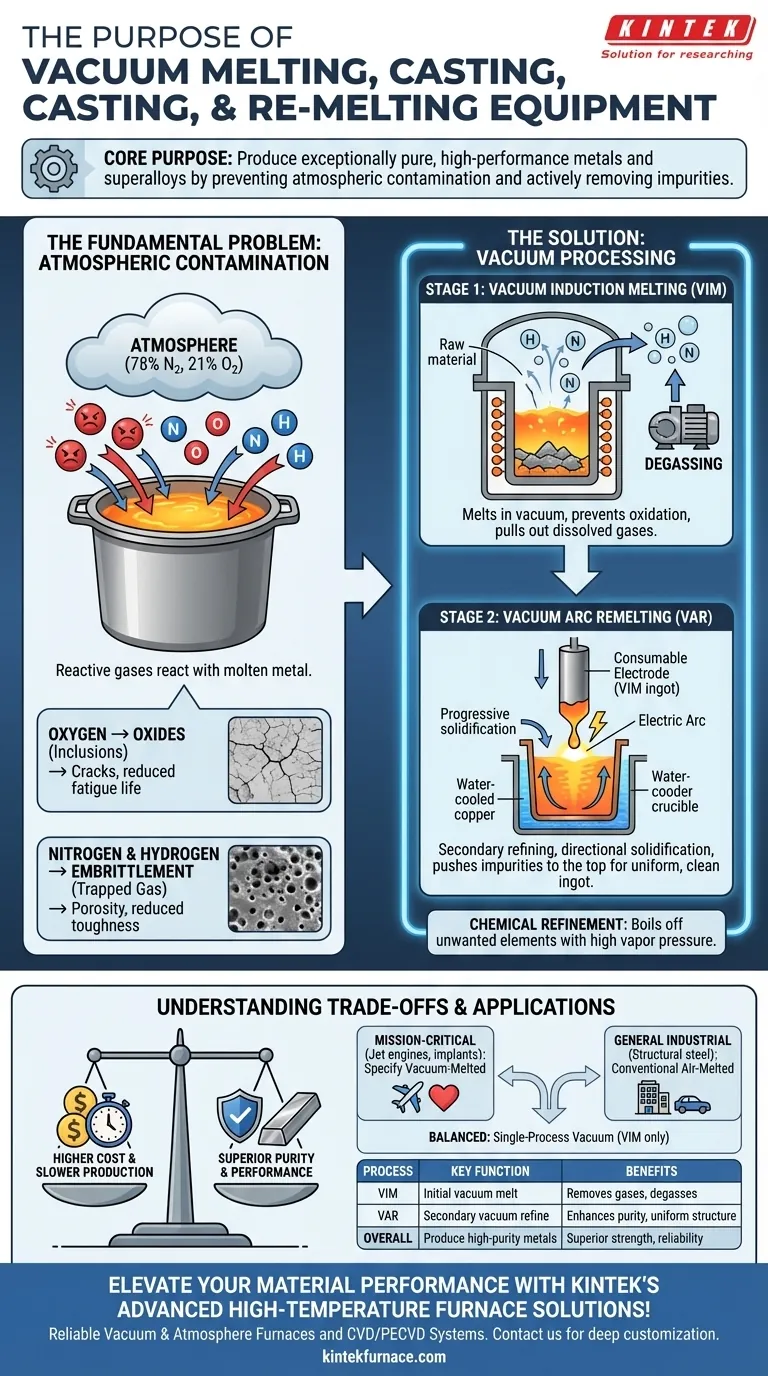
At its core, the purpose of vacuum melting, casting, and re-melting equipment is to produce exceptionally pure, high-performance metals and superalloys. By melting materials inside a vacuum, this process prevents contamination from the air and actively removes dissolved impurities, primarily reactive gases like oxygen and nitrogen, that degrade the final material's properties.
The fundamental advantage of vacuum processing is control. By removing the atmosphere, you eliminate an uncontrolled variable, preventing the formation of defects and allowing for the creation of alloys with superior strength, cleanliness, and reliability that are impossible to achieve with conventional air-melting techniques.
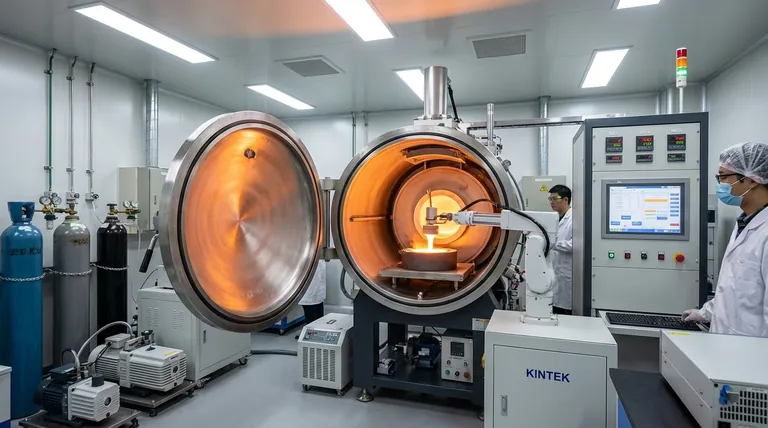

The Fundamental Problem: Atmospheric Contamination
In conventional metallurgy, metal is melted in the open air or under a simple protective slag. While effective for many applications, this exposes the molten metal to the atmosphere, which is approximately 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen.
How Air Degrades Molten Metal
Molten metals are highly reactive. At high temperatures, they readily react with the gases present in the air, introducing impurities directly into the material's microstructure as it solidifies.
The Role of Oxygen: Creating Oxides
Oxygen is the primary enemy of metal cleanliness. It reacts with the molten metal and its alloying elements to form non-metallic inclusions (oxides). These microscopic ceramic particles act as stress concentrators, becoming initiation points for cracks and significantly reducing the material's fatigue life and ductility.
The Role of Nitrogen and Hydrogen: Embrittlement
Nitrogen and hydrogen gases can dissolve into the molten metal. As the metal cools and solidifies, the solubility of these gases decreases, causing them to be trapped within the metallic structure. This can lead to porosity and internal defects, causing embrittlement and reducing the material's overall toughness.
How Vacuum Processing Provides the Solution
Vacuum melting technologies directly solve the problem of atmospheric contamination by removing the air from the equation. The process is often performed in two main stages: a primary melt followed by a secondary remelt for further refinement.
Stage 1: Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM)
The initial charge of raw material is melted in an induction furnace housed inside a vacuum-sealed chamber. The vacuum prevents oxidation from occurring and, as the metal becomes liquid, the low-pressure environment helps pull dissolved gases like hydrogen and nitrogen out of the melt. This is known as degassing.
Stage 2: Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR)
For the most demanding applications, the ingot created by VIM undergoes a secondary refining process. In VAR, the VIM ingot is used as a large consumable electrode. A powerful electric arc is struck between this electrode and a base plate inside a water-cooled copper crucible, all under vacuum. The metal melts drop by drop, solidifying directionally and progressively, pushing remaining impurities to the top and resulting in an exceptionally clean and uniform final ingot.
The Principle of Chemical Refinement
Beyond just removing gases, the vacuum environment can also be used to refine the metal by boiling off other unwanted elements with high vapor pressures. This allows for precise control over the final chemical composition of the alloy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While vacuum melting produces superior materials, it is not a universal solution. The decision to use it involves significant technical and economic considerations.
Significant Cost Increase
Vacuum furnaces and the associated high-vacuum pumping systems are complex and expensive to build, operate, and maintain. This makes vacuum-melted alloys significantly more costly than their air-melted counterparts.
Slower Production Rates
Achieving and maintaining a high vacuum is a time-consuming process. The cycle times for vacuum melting and remelting are much longer than for conventional processes, limiting production throughput.
Loss of Volatile Alloying Elements
The same high-vacuum, high-temperature environment that removes impurities can also boil away desirable alloying elements with high vapor pressure (e.g., manganese, chromium). This requires careful process control and alloy design to manage.
When to Specify Vacuum-Melted Alloys
Choosing whether to use a vacuum-melted material depends entirely on the performance requirements and budget of your application.
- If your primary focus is mission-critical performance and safety: Specify vacuum-melted alloys for applications like jet engine turbine disks, structural aerospace components, medical implants, or power generation turbines where material failure is not an option.
- If your primary focus is general industrial use: For applications like structural steel, automotive bodies, or consumer goods, conventional air-melted metals provide the necessary performance at a much lower cost.
- If your primary focus is balancing cost with enhanced performance: Consider specifying a single-process vacuum treatment (VIM only) or other refining processes that offer a step-up from air-melt without the full cost of a VIM/VAR duplex process.
Ultimately, understanding the role of vacuum processing empowers you to select the right material with a clear justification for its cost and capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Function | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) | Initial melting under vacuum | Removes gases, prevents oxidation, degasses impurities |
| Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR) | Secondary refining under vacuum | Enhances purity, directional solidification, uniform structure |
| Overall Purpose | Produce high-purity metals | Superior strength, cleanliness, reliability for critical applications |
Elevate your material performance with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable equipment like Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, helping you achieve superior purity and performance in metals and alloys. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your critical applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity



















