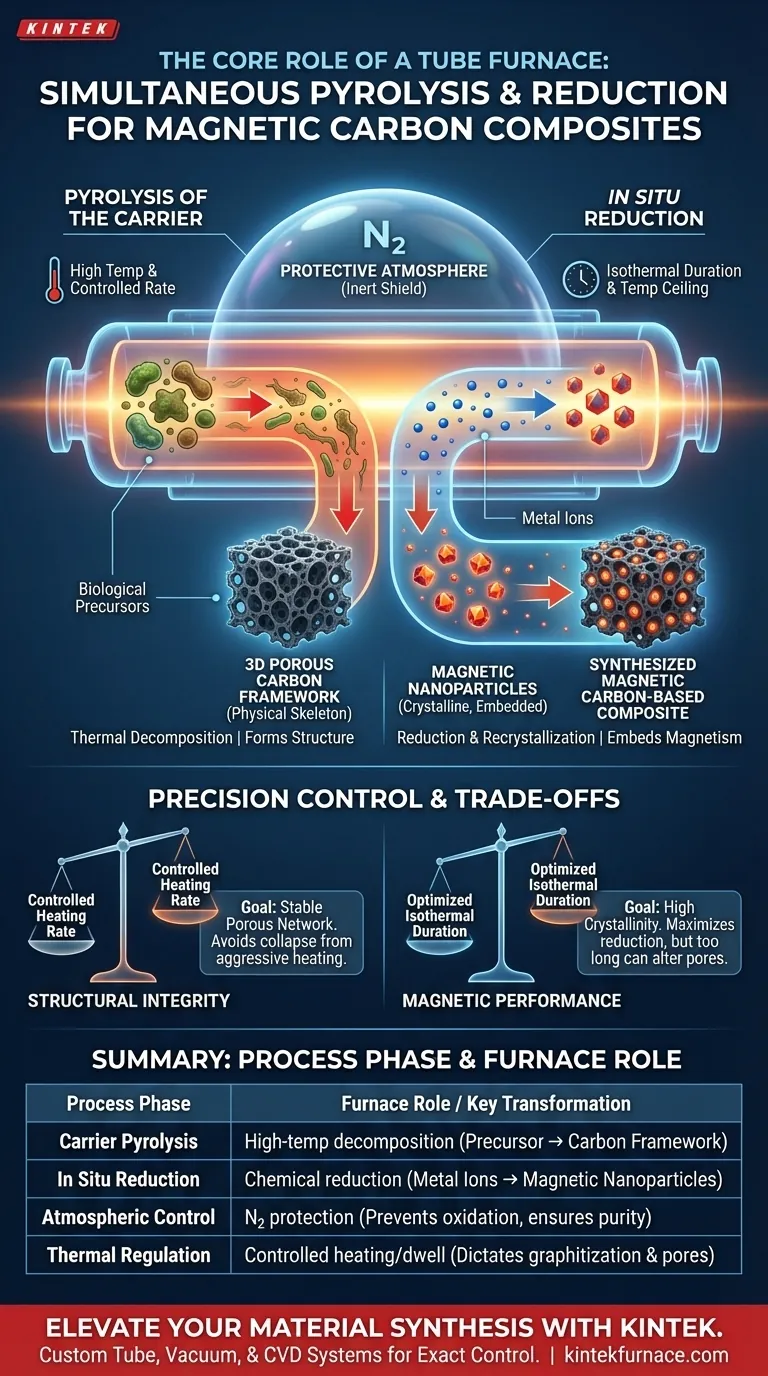
The core role of a tube furnace in this process is to provide a strictly controlled reaction environment that enables two distinct chemical transformations to occur simultaneously. It maintains a high-temperature, nitrogen-protected atmosphere that converts biological precursors into a porous carbon framework while concurrently reducing metal ions into crystalline magnetic nanoparticles.
By synchronizing pyrolysis and in situ reduction, the tube furnace dictates the material's fundamental properties, including the degree of graphitization, pore architecture, and the crystallinity of the magnetic components.

The Dual-Transformation Mechanism
The tube furnace does not simply heat the material; it orchestrates a complex, multi-stage evolution of the sample. This simultaneous processing is efficient but requires exact environmental conditions.
Pyrolysis of the Carrier
The furnace subjects biological precursors to high heat, causing thermal decomposition.
This process breaks down the organic material, converting it into a three-dimensional hierarchical porous carbon carrier.
This carbon structure serves as the physical skeleton for the final composite material.
In Situ Reduction
While the carbon carrier forms, the furnace acts on the metal ions loaded within the precursor.
The high-temperature environment facilitates the reduction and recrystallization of these ions.
This results in the formation of magnetic nanoparticles that are embedded directly within the carbon matrix.
The Criticality of Precision Control
The difference between a functional magnetic composite and a failed sample lies in the furnace's ability to regulate specific variables.
Atmospheric Protection
The furnace maintains a nitrogen ($N_2$) protective atmosphere throughout the process.
This inert environment is non-negotiable; it prevents the oxidation of the carbon carrier and protects the precursors from degradation.
Without this shield, the materials would simply burn or degrade rather than forming the desired structures.
Thermal Regulation
The furnace allows for precise programming of the heating rate and isothermal duration.
These thermal profiles directly determine the final degree of graphitization (how ordered the carbon is).
They also dictate the final pore structure and the crystallinity of the resulting magnetic oxides.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the tube furnace enables simultaneous processing, it introduces specific sensitivities that must be managed.
Sensitivity to Heating Rates
If the heating rate is too aggressive, you risk compromising the structural integrity of the porous carbon carrier.
Conversely, a rate that is too slow may result in inefficient energy use or incomplete graphitization.
Balancing Crystallinity and Porosity
Extended isothermal durations (dwelling time) can improve the crystallinity of the magnetic nanoparticles.
However, excessive heat exposure may alter the pore structure negatively, potentially reducing the surface area of the carbon carrier.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your synthesis process, you must tune the tube furnace parameters to match your specific material requirements.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Prioritize a controlled heating rate to ensure the biological precursors form a stable, hierarchical porous carbon network without collapsing.
- If your primary focus is Magnetic Performance: Focus on optimizing the isothermal duration and temperature ceiling to maximize the reduction and crystallinity of the magnetic nanoparticles.
The tube furnace is not just a heat source; it is the architect of your material’s final microstructure and magnetic capability.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Furnace Role | Key Transformation |
|---|---|---|
| Carrier Pyrolysis | High-temp decomposition | Biological precursor → Porous carbon framework |
| In Situ Reduction | Chemical reduction & recrystallization | Metal ions → Magnetic nanoparticles |
| Atmospheric Control | Nitrogen ($N_2$) protection | Prevents oxidation and ensures material purity |
| Thermal Regulation | Controlled heating & isothermal dwell | Dictates graphitization and pore architecture |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between a successful composite and a failed experiment. At KINTEK, we understand that your research depends on exact thermal and atmospheric control. Our advanced Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems are designed to provide the stable nitrogen environments and programmable heating rates essential for simultaneous pyrolysis and in situ reduction.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Expert R&D: Backed by industry-leading manufacturing.
- Customizable Solutions: Tailored high-temperature furnaces for your unique lab requirements.
- Proven Results: Optimized for high crystallinity and structural integrity in magnetic carbon-based materials.
Ready to achieve superior material properties? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace needs with our engineering team.
Visual Guide
References
- Yu Gao, Tifeng Jiao. Three-Dimensional Porous Artemia Cyst Shell Biochar-Supported Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Efficient Removal of Chromium from Wastewater. DOI: 10.3390/molecules30081743
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a tube furnace in CVD COF synthesis? Achieve Precision 2D Film Growth
- What role do furnace chamber working conditions play in selecting a vertical tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Process Success
- What is the function of a stainless steel tubular horizontal reactor? Optimize Plastic Waste Catalytic Pyrolysis
- What is the function of the high-purity quartz tube in CVT for ZrTe5? Ensure High Purity and Vacuum Integrity
- What functions does a support frame provide in tube furnace modernization? Gain Stability and Experimental Flexibility
- Why is a high-precision tube furnace necessary for YIG thin films? Unlock Superior Magnetic Performance
- What is the role of a vertical tube resistance furnace in WEEE and copper co-smelting? Precision Smelting Solutions
- What is the function of a high-temperature tube furnace in pp-fiber production? Master Precise Carbonization Control



















