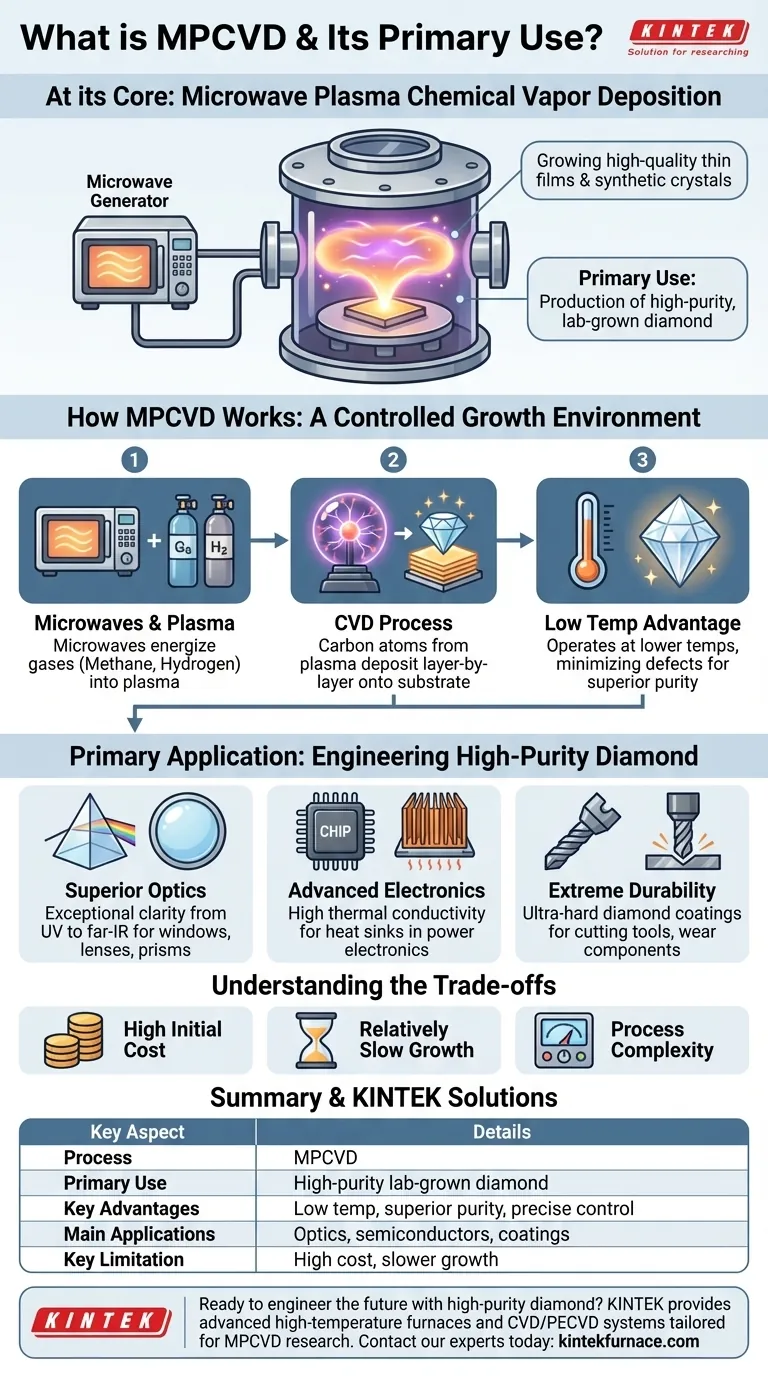
At its core, MPCVD stands for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition. It is an advanced process used to grow exceptionally high-quality thin films and synthetic crystals on a substrate. While it has applications in semiconductors, its most significant and defining use is the production of high-purity, lab-grown diamond for specialized industrial and technological purposes.
MPCVD is not just another coating technique; it is a precise, low-temperature method for engineering materials at the atomic level. Its true value lies in its ability to create exceptionally pure synthetic diamond, unlocking new capabilities in optics, electronics, and other high-performance fields.
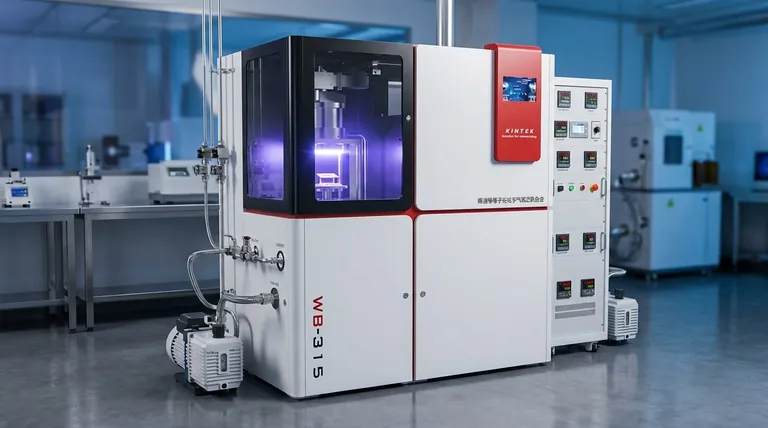

How MPCVD Works: A Controlled Growth Environment
MPCVD creates conditions that are ideal for growing crystalline structures, particularly diamond, without the extreme pressures and temperatures found in nature or other synthesis methods.
The Role of Microwaves and Plasma
The process begins by introducing a precise mixture of gases, typically methane and hydrogen, into a vacuum chamber. Microwaves are then used to energize these gases, stripping electrons from their atoms and creating a glowing ball of charged gas known as plasma.
The Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) Process
Within this plasma, carbon atoms are freed from the methane molecules. These reactive carbon atoms then "deposit" onto a carefully prepared substrate, which is often a tiny, high-quality diamond seed crystal. Layer by layer, the carbon atoms arrange themselves into the crystal lattice, growing a larger diamond.
Why Low Temperature is a Key Advantage
Unlike other methods that require immense heat and pressure, MPCVD operates at relatively low temperatures. This prevents damage to the substrate and provides a highly controlled environment, which is critical for minimizing defects and achieving superior material purity.
The Primary Application: Engineering High-Purity Diamond
While MPCVD can create various films, its ability to produce diamond with specific, engineered properties has made it an indispensable technology.
Creating Diamond for Specific Needs
MPCVD can produce both polycrystalline diamond (PCD), which consists of many small crystals bonded together, and flawless single-crystal diamond. This versatility allows for the creation of materials tailored to different applications, from durable coatings to perfect optical lenses.
Unlocking Superior Optical Properties
MPCVD-grown diamonds exhibit exceptional optical clarity across a broad spectrum, from ultraviolet to far-infrared. Their high refractive index and low optical loss make them ideal for high-performance windows, lenses, and prisms, especially in harsh environments where other materials would fail.
Advancing Electronics and Cutting Tools
The unique properties of diamond—superior thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, and extreme hardness—make it a next-generation material. MPCVD is used to create diamond films for heat sinks in powerful electronics and to coat precision cutting tools, dramatically increasing their lifespan and performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is without its limitations. Being an advanced and precise method, MPCVD involves clear trade-offs compared to other material synthesis techniques.
High Initial Equipment Cost
MPCVD systems are complex and require significant capital investment. The need for vacuum chambers, microwave generators, and precise gas control systems makes the initial setup expensive.
Relatively Slow Growth Rates
Precision comes at the cost of speed. The layer-by-layer deposition process is methodical and can be much slower than bulk synthesis methods like High-Pressure High-Temperature (HPHT), making it less suitable for mass-producing lower-grade industrial diamonds.
Process Complexity
Operating an MPCVD reactor requires significant expertise. Maintaining a stable plasma and controlling gas purity, temperature, and pressure are critical variables that demand a high level of technical oversight to ensure a high-quality end product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Adopting MPCVD is a strategic decision driven by the need for material properties that are otherwise unattainable.
- If your primary focus is high-performance optics: MPCVD is the definitive method for creating diamond components with unmatched transparency and durability for lasers and sensors.
- If your primary focus is next-generation semiconductors: MPCVD provides the high-purity diamond substrates and films essential for managing heat in high-power electronic devices.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability: MPCVD is the premier choice for applying ultra-hard diamond coatings to cutting tools, medical implants, or wear-resistant components.
Ultimately, MPCVD empowers industries to engineer diamond as a technical material, moving beyond its natural limitations to solve modern engineering challenges.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Process | Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition |
| Primary Use | Synthesis of high-purity, lab-grown diamond |
| Key Advantages | Low-temperature operation, superior material purity, precise atomic-level control |
| Main Applications | High-performance optics, next-generation semiconductors, ultra-hard coatings |
| Key Limitation | High initial equipment cost and slower growth rates |
Ready to engineer the future with high-purity diamond?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing capabilities to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for cutting-edge applications like MPCVD. Our expertise in Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems, combined with strong deep customization capabilities, ensures your unique experimental requirements for diamond synthesis are met with precision.
Whether you are developing next-generation semiconductors, high-performance optical components, or ultra-durable coatings, our solutions are designed to deliver the material purity and control your research demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our MPCVD and furnace solutions can accelerate your innovative projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
- MPCVD Machine System Reactor Bell-jar Resonator for Lab and Diamond Growth
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What are some challenges associated with MPCVD? Overcome High Costs and Complexity for Diamond Synthesis
- Why is maintaining gas pipelines important in MPCVD equipment? Ensure Purity and Safety in Crystal Growth
- What is the basic principle of operation for the microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition system? Unlock High-Purity Material Growth
- Why is the temperature control system important in MPCVD equipment? Ensure Precise Diamond Growth and Process Stability
- How is CVD classified based on physical characteristics of vapor? Explore AACVD and DLICVD Methods



















