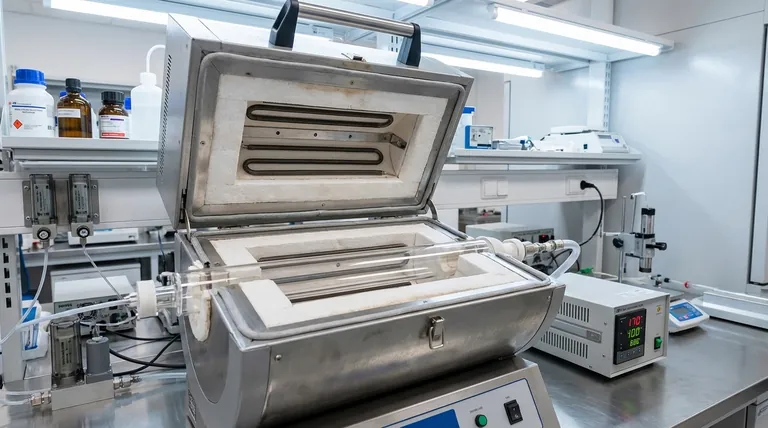
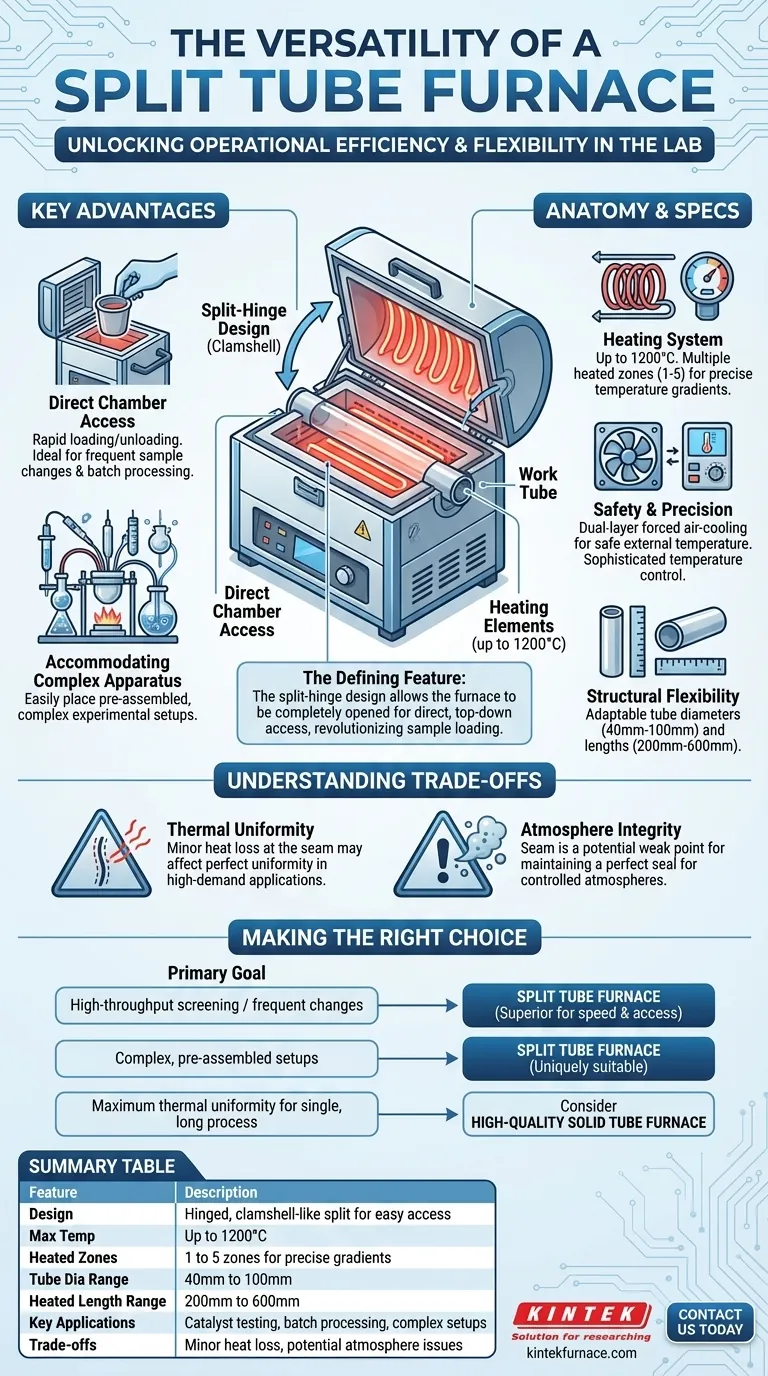
At its core, a split tube furnace is a laboratory heating device distinguished by a furnace body that is split lengthwise and connected by a hinge. This clamshell-like design allows the chamber to be opened completely, providing direct access to the interior. This simple yet critical feature is the source of its versatility, enabling easy placement of samples, accommodation of various tube sizes, and use with complex experimental apparatus.
The defining advantage of a split tube furnace isn't just high-temperature performance, but operational efficiency. Its hinged design transforms the process of sample loading from a restrictive, end-loading task into an open, flexible, and rapid operation, enabling more complex and frequent experimentation.

The Defining Feature: The Split-Hinge Design
The primary innovation of a split tube furnace is its physical structure. Unlike a traditional solid tube furnace, which is a monolithic cylinder, the split design fundamentally alters how a user interacts with the heating chamber.
Direct Chamber Access
The ability to open the furnace body provides direct, top-down access to the work tube. This eliminates the need to carefully slide delicate samples or complex reaction vessels into a long, "blind" tube from one end.
This design is ideal for applications requiring frequent sample changes, such as catalyst testing or batch processing, as it dramatically reduces the time and effort needed for setup and removal.
Accommodating Complex Apparatus
Many advanced experiments involve intricate setups with multiple probes, gas inlets, or unique reaction vessels. The open-access design allows for pre-assembled, complex apparatus to be placed directly into the furnace, something that is often impossible with a solid tube design.
Anatomy of a Modern Split Tube Furnace
While the hinge is its defining feature, the furnace's versatility is supported by a system of integrated components designed for precision and safety.
The Heating Chamber and Elements
The heat source is typically a high-quality heating coil capable of reaching maximum temperatures up to 1200°C. Many models offer multiple heated zones (from one to five), allowing researchers to create precise temperature gradients along the length of the tube for sophisticated thermal processing.
Temperature Control and Safety
Precision is achieved through sophisticated temperature controllers. A critical safety feature is dual-layer forced air-cooling, which maintains a low external case temperature, protecting both the operator and surrounding equipment even when the interior is at maximum heat.
Structural Flexibility
These furnaces are built to accommodate a range of work tube diameters, often from 40mm to 100mm, and heated lengths from 200mm to 600mm. This adaptability means a single furnace can be reconfigured for many different experimental scales and requirements.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No design is without compromises. The hinged body, while offering immense flexibility, introduces considerations not present in solid tube furnaces.
Thermal Uniformity
The seam where the two halves of the furnace meet can be a source of minor heat loss. While high-quality manufacturing minimizes this, achieving perfect thermal uniformity can be more challenging at the split than in a comparable solid tube furnace. For applications demanding the absolute highest uniformity, this is a factor to consider.
Atmosphere Integrity
For processes requiring a controlled atmosphere, the seam represents a potential weak point for maintaining a perfect seal. Effective sealing depends on the quality of the furnace's construction and any associated gaskets. Over time, these components may require maintenance to ensure atmospheric purity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate furnace requires aligning the equipment's strengths with your primary experimental goals.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput screening or frequent sample changes: The split tube furnace is the superior choice due to its rapid, open-access design.
- If your primary focus is working with complex, pre-assembled reaction vessels: The split tube's ability to accommodate intricate setups makes it uniquely suitable for this work.
- If your primary focus is maximum thermal uniformity for a single, long-duration process: A high-quality solid tube furnace may be a simpler and slightly more stable option, though modern split designs are highly competitive.
The split tube furnace empowers researchers by prioritizing operational flexibility and speed, making it an invaluable asset in dynamic research and development environments.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Design | Hinged, clamshell-like split for easy access |
| Max Temperature | Up to 1200°C |
| Heated Zones | 1 to 5 zones for precise gradients |
| Tube Diameter Range | 40mm to 100mm |
| Heated Length Range | 200mm to 600mm |
| Key Applications | Catalyst testing, batch processing, complex apparatus setups |
| Trade-offs | Minor heat loss at seam, potential for atmosphere integrity issues |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency with a versatile split tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs precisely. Contact us today to discuss how our split tube furnaces can streamline your research and boost productivity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















