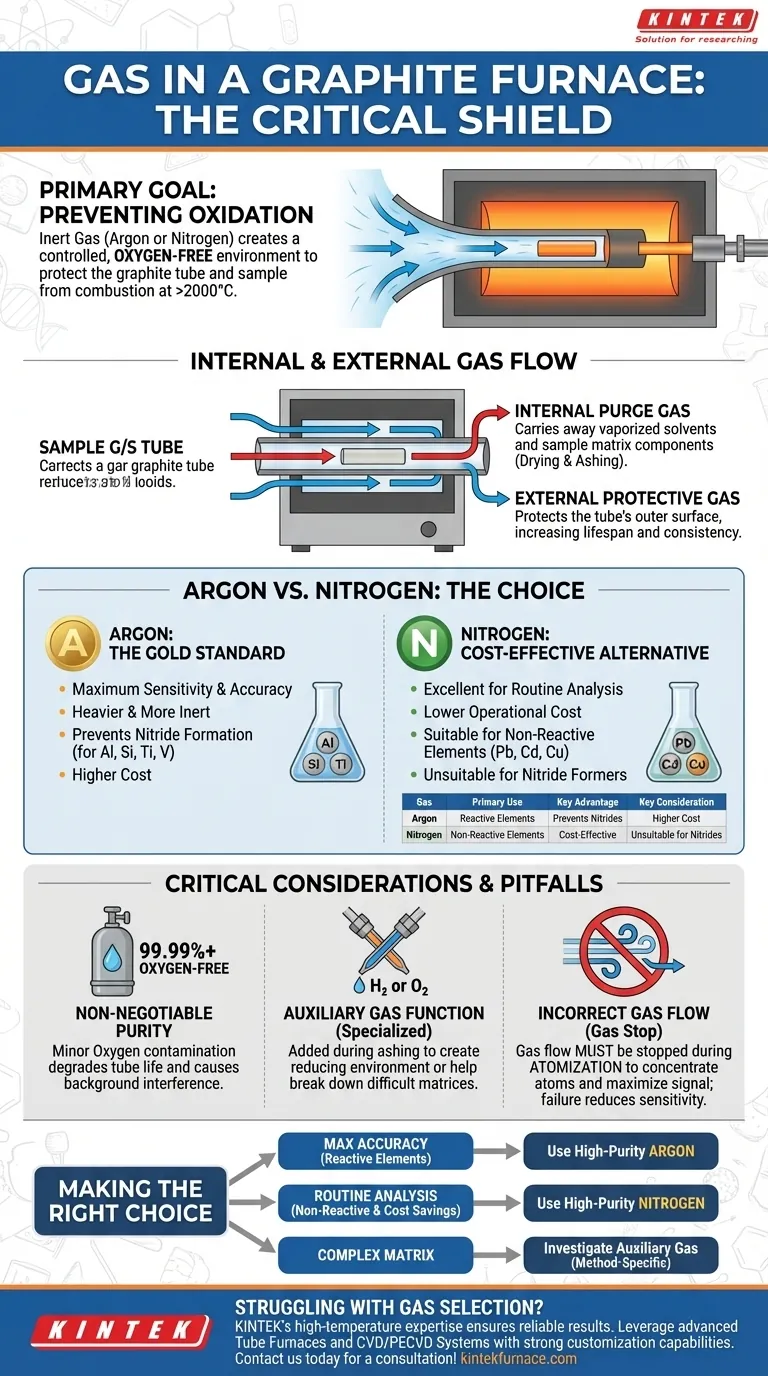
The primary gas used in a graphite furnace is a high-purity, oxygen-free inert gas. The two standard choices are argon and nitrogen. This gas is essential for creating a controlled, oxygen-free environment, which prevents the graphite tube and the sample from combusting at the extremely high temperatures required for analysis.
The core function of the gas in a graphite furnace is not to react, but to protect. It acts as an inert shield, purging oxygen to prevent the analytical components from being destroyed by oxidation, thereby ensuring the integrity of the measurement.

The Critical Role of Gas in a Graphite Furnace
To understand which gas to use, you must first understand its purpose. The gas system in a Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (GF-AAS) is fundamental to the entire technique.
The Primary Goal: Preventing Oxidation
At the temperatures used for atomization (often exceeding 2000°C), the carbon of the graphite tube would instantly burn away if exposed to oxygen in the air.
The flow of inert gas purges the furnace of all ambient air, creating an environment where the graphite tube can be heated without being destroyed. This also protects the sample itself from unwanted oxidative reactions.
Internal Gas Flow (The Purge Gas)
A controlled flow of inert gas is directed through the inside of the graphite tube during the initial drying and ashing stages of a temperature program.
This internal flow serves to carry away vaporized solvents and combusted sample matrix components, effectively cleaning the analysis zone before the final, high-temperature atomization step.
External Gas Flow (The Protective Gas)
Simultaneously, a separate flow of the same inert gas is passed over the outside of the graphite tube.
This external sheath of gas is what protects the tube's outer surface from atmospheric oxygen, drastically increasing its operational lifespan and ensuring consistent heating performance.
Choosing Between Argon and Nitrogen
While both argon and nitrogen are inert, the choice between them is not arbitrary and depends on the specific analytical goal.
Argon: The Gold Standard for Sensitivity
Argon is the universally preferred gas for most graphite furnace applications. It is heavier and more chemically inert than nitrogen, especially at very high temperatures.
For certain elements like aluminum, silicon, titanium, and vanadium, nitrogen can react at high temperatures to form stable nitrides. This chemical reaction traps the analyte, preventing it from being atomized and leading to suppressed, inaccurate results. Argon does not have this issue.
Nitrogen: The Cost-Effective Alternative
High-purity nitrogen is significantly less expensive than argon and serves as an excellent alternative for many routine analyses.
For elements that do not form stable nitrides (such as lead, cadmium, or copper), nitrogen provides the necessary inert atmosphere at a lower operational cost without compromising analytical results.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Selecting the right gas is only part of the equation. Purity and proper use are just as critical.
The Non-Negotiable Need for Purity
Using a "high-purity" (typically 99.99% or better) and "oxygen-free" grade of gas is essential.
Even minor oxygen contamination in the gas supply will rapidly degrade the graphite tube, shortening its life and causing poor analytical reproducibility. It can also cause significant chemical background interferences.
The Function of an Auxiliary Gas
Some advanced methods may call for an "auxiliary" or "reactive" gas to be mixed in small, controlled amounts with the inert gas stream, usually during the ashing step.
Common examples include hydrogen, which creates a reducing environment, or a small percentage of oxygen, which can help break down a difficult organic matrix. This is a specialized technique for matrix modification and is not part of the standard furnace operation.
Incorrect Gas Flow and Pressure
The gas flow must be stopped or significantly reduced just before and during the atomization step. This ensures the atomized cloud of the target element remains concentrated in the light path for as long as possible, maximizing the absorption signal.
Failure to properly control this "gas stop" phase will result in the atoms being swept out of the furnace too quickly, leading to drastically reduced sensitivity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Your analytical requirements should dictate your gas selection and setup.
- If your primary focus is maximum accuracy and analyzing reactive elements (like Al, Si, Ti): Use high-purity argon, as it prevents signal loss from nitride formation at high temperatures.
- If your primary focus is routine analysis of non-reactive elements and cost savings: Use high-purity nitrogen, as it is a perfectly suitable and more economical choice for many common applications.
- If you are struggling with a complex sample matrix: Investigate method-specific uses of an auxiliary gas during the ashing step to aid in matrix removal.
Ultimately, the correct gas choice creates the stable, controlled environment that is the foundation of a successful graphite furnace analysis.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Primary Use Case | Key Advantage | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Argon | High-sensitivity analysis of reactive elements (e.g., Al, Si, Ti) | Prevents nitride formation; ensures maximum accuracy | Higher cost compared to nitrogen |
| Nitrogen | Routine analysis of non-reactive elements (e.g., Pb, Cd, Cu) | Cost-effective for many applications | Unsuitable for elements that form stable nitrides |
Struggling with gas selection or background interference in your furnace analysis? KINTEK's expertise in high-temperature furnace solutions is your key to reliable results. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced Tube Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems, complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique analytical requirements. Let our experts help you optimize your process—contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















