High-strength, high-conductivity graphite molds serve as the functional core of the Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) process, acting simultaneously as the heating engine, the pressure vessel, and the shaping tool. They convert pulsed electric current into thermal energy to heat the sample while maintaining enough structural integrity to transmit massive unidirectional pressure. This dual action facilitates the full densification of Barium Titanate ceramics at temperatures significantly lower than those required by conventional sintering methods.
The graphite mold in SPS is not merely a passive container; it is an active component of the machine’s thermal and mechanical systems. By enabling the simultaneous application of heat and pressure, it allows for rapid consolidation that preserves the material's fine microstructure.

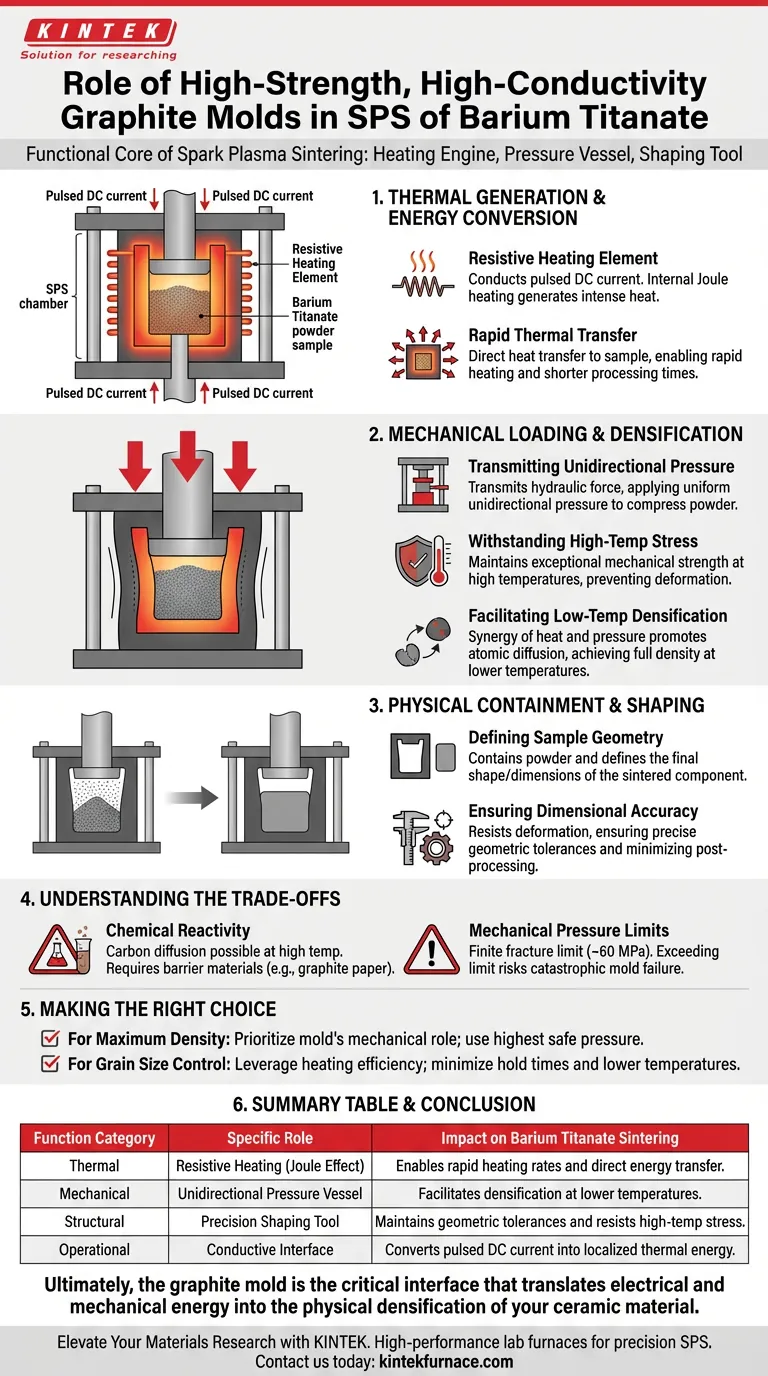
Thermal Generation and Energy Conversion
Acting as a Resistive Heating Element
The most distinct function of the graphite mold is its role as an electrical resistor. The mold conducts the pulsed direct current (DC) generated by the SPS system. Because graphite is conductive but possesses resistance, the passage of this current generates intense internal heat (Joule heating).
rapid Thermal Transfer
This mechanism allows thermal energy to be generated immediately surrounding the Barium Titanate powder. Unlike conventional furnaces that heat via external radiation, the graphite mold transfers heat directly to the sample, enabling rapid heating rates and shortening the overall processing time.
Mechanical Loading and Densification
Transmitting Unidirectional Pressure
To achieve high density, the Barium Titanate powder must be compressed during heating. The graphite mold serves as the transmission medium for the system's hydraulic force. It applies uniform, unidirectional pressure directly to the sample, physically forcing particles together.
Withstanding High-Temperature Stress
Graphite is unique because it maintains exceptional mechanical strength even at the high temperatures required for sintering ceramics. This allows the mold to withstand significant axial pressure without deforming or failing, ensuring the sample is compressed effectively throughout the thermal cycle.
Facilitating Low-Temperature Densification
The combination of the mold’s ability to generate heat and transmit pressure creates a synergistic effect. This environment promotes atomic diffusion and helps the powder overcome kinetic barriers, allowing Barium Titanate to achieve full density at lower temperatures than would be possible with pressureless sintering.
Physical Containment and Shaping
Defining Sample Geometry
At a fundamental level, the mold acts as the forming tool. It contains the loose ceramic powder and defines the final shape and dimensions of the sintered Barium Titanate component.
Ensuring Dimensional Accuracy
Because high-strength graphite resists deformation under load, it ensures that the final ceramic product maintains precise geometric tolerances, minimizing the need for extensive post-processing or machining.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While graphite molds are essential to SPS, they introduce specific constraints that must be managed to ensure success.
Chemical Reactivity and Contamination
At elevated temperatures, carbon from the graphite mold can diffuse into the ceramic sample or react with it. While not explicitly detailed in the primary reference for Barium Titanate, standard SPS practice often requires the use of barrier materials (like graphite paper or boron nitride coatings) to prevent surface contamination or adhesion.
Mechanical Pressure Limits
Although high-strength graphite is robust, it has a finite fracture limit (typically around 60 MPa for standard high-strength grades). Exceeding this pressure to force densification can result in catastrophic mold failure, meaning there is a hard ceiling on the mechanical force available to aid sintering.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When designing your SPS experiments for Barium Titanate, consider how the mold functions align with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Maximum Density: Prioritize the mold's mechanical role by utilizing the highest safe pressure the graphite grade can withstand to aid compaction.
- If your primary focus is Grain Size Control: Leverage the mold's heating efficiency to minimize hold times and lower sintering temperatures, preventing grain growth.
Ultimately, the graphite mold is the critical interface that translates electrical and mechanical energy into the physical densification of your ceramic material.
Summary Table:
| Function Category | Specific Role | Impact on Barium Titanate Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal | Resistive Heating (Joule Effect) | Enables rapid heating rates and direct energy transfer. |
| Mechanical | Unidirectional Pressure Vessel | Facilitates densification at lower temperatures. |
| Structural | Precision Shaping Tool | Maintains geometric tolerances and resists high-temp stress. |
| Operational | Conductive Interface | Converts pulsed DC current into localized thermal energy. |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK
Precision in Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) begins with superior hardware. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-performance lab high-temp furnaces—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all customizable to meet your unique Barium Titanate sintering needs. Whether you require advanced temperature control or robust structural integrity for high-pressure applications, our engineering team is ready to assist.
Ready to optimize your lab's efficiency? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace requirements.
Visual Guide
References
- Effect of Beam Power on Intermetallic Compound Formation of Electron Beam-Welded Cu and Al6082-T6 Dissimilar Joints. DOI: 10.3390/eng6010006
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is power requirement determined for heaters? Calculate Energy Needs for Efficient Heating
- What precautions should be taken when handling MoSi2 heating elements? Ensure Longevity and Safety in High-Temp Applications
- What materials are used for heating elements in high-temperature furnaces? Optimize Your Furnace Performance
- How does a graphite heater work? Achieving Extreme Temperatures Beyond 2000°C
- How are SC Type Silicon Carbide Heating Elements utilized in metal processing? Achieve Uniform Heat for Quality Metals
- How do ceramic heating elements function? Achieve Superior, Safe, and Efficient Heat
- Why are high-purity graphite electrodes necessary for Joule heating? Ensure Precise Mesoporous Carbon Engineering
- What are Positive Thermal Coefficient (PTC) materials? Self-Regulating Heaters for Ultimate Safety & Efficiency



















