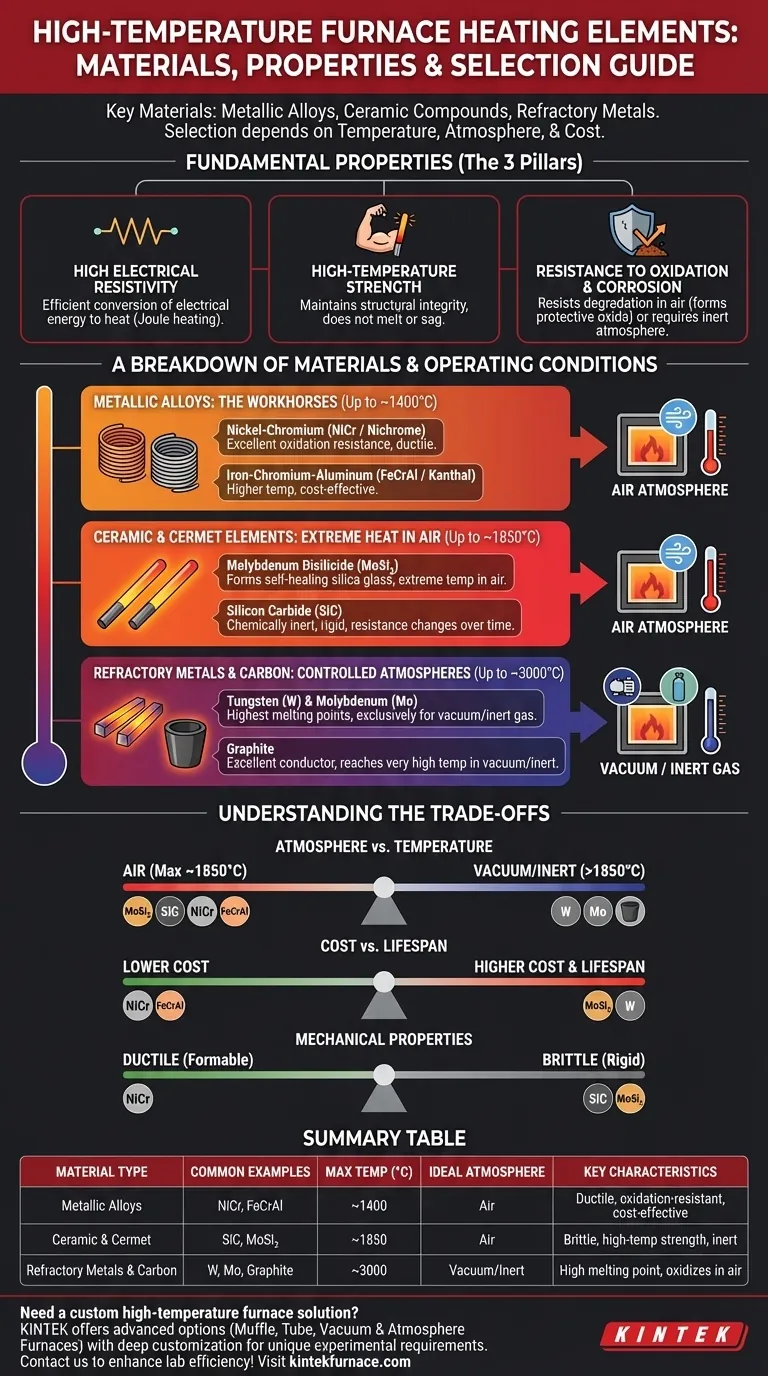
The most common materials for high-temperature furnace heating elements are specialized metallic alloys like nickel-chromium (Nichrome) and iron-chromium-aluminum (Kanthal), ceramic compounds like silicon carbide (SiC) and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂), and refractory metals like tungsten and molybdenum, which are reserved for vacuum or inert atmospheres. The final choice depends on the required operating temperature, the furnace atmosphere, and cost considerations.
The selection of a heating element is not about finding a single "best" material. It is a critical engineering decision that involves balancing the material's maximum temperature, its chemical resistance to the furnace environment, and its mechanical properties against the specific process requirements.
The Fundamental Properties of a Heating Element
To understand why certain materials are chosen, it's essential to understand the core principles governing their function. An effective heating element must excel in three key areas.
High Electrical Resistivity
An element generates heat by resisting the flow of electricity, a principle known as Joule heating. Materials with high electrical resistance, like Nichrome, efficiently convert electrical energy into thermal energy.
High-Temperature Strength
The material must not melt, sag, or degrade at its operating temperature. A high melting point is a prerequisite, but the material must also maintain its structural integrity and shape over many thermal cycles.
Resistance to Oxidation and Corrosion
For furnaces operating in an air atmosphere, the element must resist oxidation. Materials like nickel-chromium form a protective oxide layer that prevents the element from burning out. For elements that oxidize easily, like tungsten, the furnace must operate in a vacuum or be filled with an inert gas.
A Breakdown of High-Temperature Materials
Heating element materials can be grouped into distinct categories based on their composition and ideal operating conditions.
Metallic Alloys: The Workhorses (Up to ~1400°C)
These alloys are the most common choice for a wide range of industrial and lab furnaces due to their ductility, reliability, and good performance in air.
Nickel-Chromium (NiCr) alloys, often known by the trade name Nichrome, are valued for their excellent resistance to oxidation and stable resistance at high temperatures. They are ductile and easy to form into coils.
Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl) alloys, known by trade names like Kanthal, can often reach slightly higher temperatures than NiCr alloys and are typically a more cost-effective solution.
Ceramic & Cermet Elements: For Extreme Heat in Air (Up to ~1850°C)
When temperatures exceed the limits of metallic alloys, ceramic-based elements are required. They offer superior performance at a higher cost and are more brittle.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) elements can operate at very high temperatures in air because they form a protective, self-healing layer of silica glass. They are a top choice for extreme-temperature air furnaces.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements are chemically inert and rigid, making them suitable for demanding environments. They do not sag at high temperatures but their resistance changes over time, requiring more sophisticated power control.
Refractory Metals & Carbon: For Controlled Atmospheres (Up to ~3000°C)
This class of materials boasts the highest melting points but has a critical weakness: they oxidize and fail almost instantly in the presence of oxygen at high temperatures.
Tungsten (W) and Molybdenum (Mo) are pure refractory metals used exclusively in vacuum or inert gas (like argon or nitrogen) furnaces. They enable the highest achievable process temperatures.
Graphite is an excellent conductor that can reach very high temperatures. Like refractory metals, it must be used in a vacuum or inert atmosphere to prevent it from rapidly burning away.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right material involves navigating a series of critical engineering trade-offs. There is no universally perfect option.
Atmosphere vs. Temperature
This is the most important relationship to understand. If your process requires an air atmosphere, you are limited to NiCr, FeCrAl, SiC, or MoSi₂ elements. To achieve temperatures above 1850°C, you must use a vacuum or inert atmosphere with a refractory metal or graphite element.
Cost vs. Lifespan
Generally, materials with higher temperature ratings, like MoSi₂ and Tungsten, are significantly more expensive than standard NiCr or FeCrAl alloys. However, specifying the correct material for the application prevents premature failure and costly downtime, justifying the initial investment.
Mechanical Properties: Ductility vs. Brittleness
Metallic alloys like Nichrome are ductile and can be easily formed into complex shapes. Ceramic elements like SiC and MoSi₂ are rigid and brittle, requiring more careful handling and support within the furnace structure to prevent fracture.
Selecting the Right Element for Your Application
Your choice must be driven by your primary operational goal. Base your decision on the required temperature and the furnace's internal atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating in air up to 1250°C: FeCrAl or NiCr alloys offer the best balance of cost, durability, and ease of use.
- If your primary focus is extreme-temperature processing in air (1300°C to 1850°C): Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) or Silicon Carbide (SiC) are the only viable options.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible temperatures (>1800°C): You must use a vacuum or inert gas furnace with Tungsten, Molybdenum, or Graphite elements.
Understanding these material capabilities and limitations is the key to designing and specifying a successful high-temperature system.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Examples | Max Temperature (°C) | Ideal Atmosphere | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic Alloys | Nichrome (NiCr), Kanthal (FeCrAl) | Up to ~1400 | Air | Ductile, oxidation-resistant, cost-effective |
| Ceramic & Cermet | Silicon Carbide (SiC), Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | Up to ~1850 | Air | Brittle, high-temperature strength, inert |
| Refractory Metals & Carbon | Tungsten, Molybdenum, Graphite | Up to ~3000 | Vacuum/Inert | High melting point, oxidizes in air |
Need a custom high-temperature furnace solution? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















