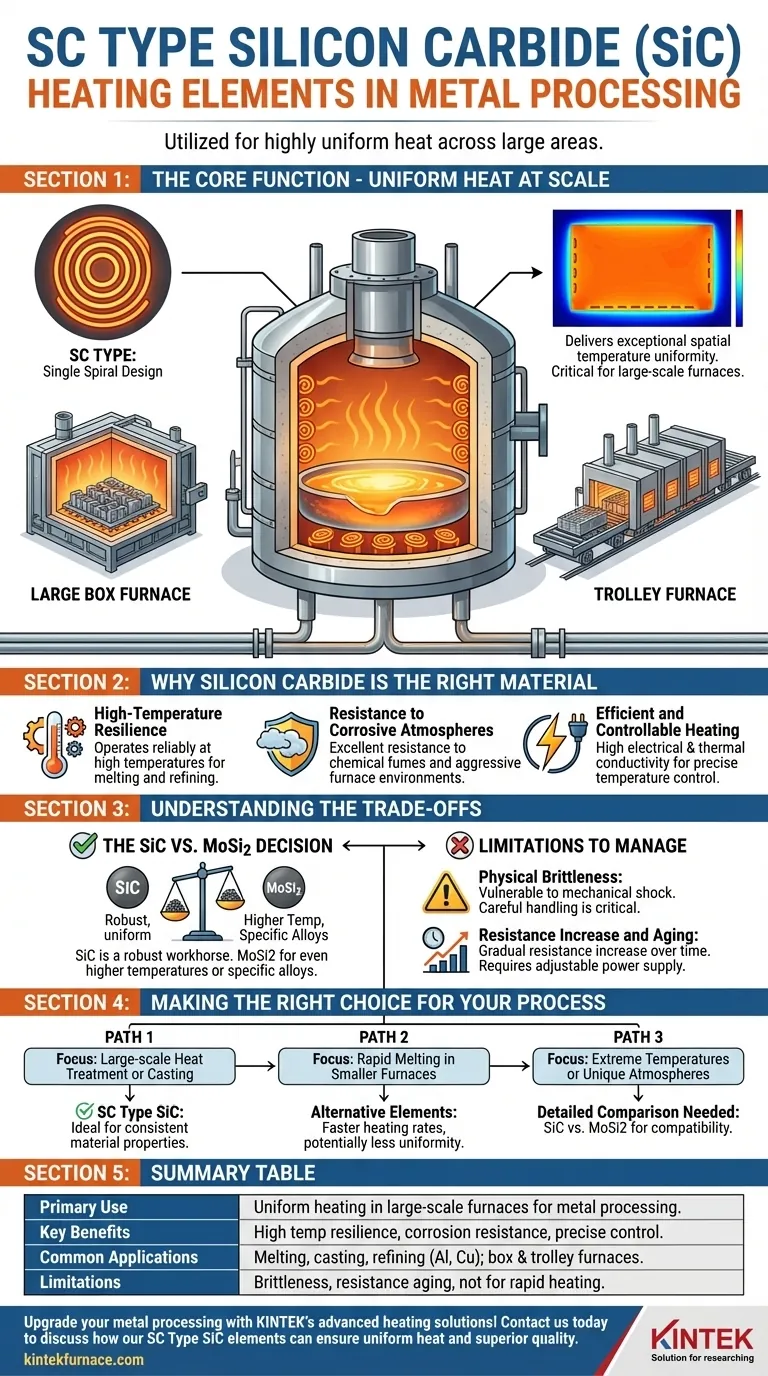
In metal processing, SC Type Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements are utilized for their ability to provide highly uniform heat across large areas. They are essential in furnaces used for melting, casting, and refining non-ferrous metals like aluminum and copper, where consistent temperature is critical for ensuring material quality and process stability.
The term "SC Type" refers to a Single Spiral configuration, a specific design engineered for one primary purpose: delivering exceptional spatial temperature uniformity. This makes it the ideal choice for large-scale furnaces where even heating is more critical than raw heating speed.

The Core Function: Uniform Heat at Scale
The primary value of the SC Type element in metallurgy is not just its ability to get hot, but its ability to create a stable, homogenous thermal environment. This is a direct result of its specific design.
What "SC Type" Signifies: The Single Spiral Design
The "SC" designation is shorthand for Single Spiral. This refers to the physical construction of the heating element.
This spiral configuration is optimized to radiate heat evenly over a large surface area, minimizing the temperature variance that can occur between different points in a large furnace.
The Importance of Spatial Temperature Uniformity
In metal processing, inconsistent temperatures can lead to significant quality issues, such as uneven grain structure, internal stresses in castings, or incomplete refining.
SC Type elements are placed along the bottom or sides of large furnaces to create a vast, consistent heating zone. This ensures the entire metal batch experiences the same thermal conditions, leading to predictable and high-quality results.
Typical Furnace Applications
Due to their uniform heating characteristics, SC Type elements are most commonly found in large-scale industrial furnaces.
This includes large box furnaces for heat treating large components and trolley furnaces where products are moved through extensive, precisely controlled heating zones.
Why Silicon Carbide is the Right Material
The choice of silicon carbide as the base material is just as important as the SC Type's spiral design. The material's inherent properties make it uniquely suited for the harsh environment of metal processing.
High-Temperature Resilience
SiC elements can operate reliably at the high temperatures required to melt and refine metals, providing the necessary energy for these demanding processes without degrading quickly.
Resistance to Corrosive Atmospheres
Melting and refining metals can release fumes and create chemically aggressive atmospheres inside a furnace. The ceramic nature of silicon carbide provides excellent resistance to this corrosion, ensuring a longer service life compared to many metallic elements.
Efficient and Controllable Heating
SiC offers a combination of high electrical conductivity and good thermal conductivity. This allows it to efficiently convert electrical power into heat and distribute it effectively, enabling precise temperature control.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, SC Type SiC elements are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to proper application.
The SiC vs. MoSi2 Decision
Silicon carbide is one of the two most common high-temperature elements, alongside Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2). While SiC is a robust workhorse, MoSi2 elements can often reach even higher temperatures and may be required for specific high-temperature alloys or processes. The best choice depends on the specific temperature and atmospheric requirements of your application.
Physical Brittleness
Like all ceramic materials, SiC heating elements are brittle. They are susceptible to damage from mechanical shock or impact. Careful handling during furnace installation and maintenance is absolutely critical to prevent fracture.
Resistance Increase and Aging
Over their operational life, SiC elements experience a gradual increase in electrical resistance. This "aging" is a natural process that must be managed. The power supply system for the furnace must be capable of adjusting its output voltage to compensate for this change and maintain consistent power delivery.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct heating element strategy requires aligning the element's strengths with your specific metallurgical goal.
- If your primary focus is large-scale heat treatment or casting: SC Type's superior temperature uniformity makes it an ideal choice for ensuring consistent material properties across large batches.
- If your primary focus is rapid melting in smaller furnaces: A different element configuration or type might provide faster heating rates, though potentially at the cost of some uniformity.
- If your process involves extreme temperatures or unique atmospheres: You must conduct a detailed comparison between Silicon Carbide and Molybdenum Disilicide elements to ensure material compatibility and longevity.
Ultimately, understanding the direct link between an element's physical design and its thermal performance is the key to engineering a reliable and efficient heating process.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Uniform heating in large-scale furnaces for metal processing |
| Key Benefits | High temperature resilience, corrosion resistance, precise control |
| Common Applications | Melting, casting, refining of aluminum, copper; box and trolley furnaces |
| Limitations | Brittleness, resistance aging, not ideal for rapid heating |
Upgrade your metal processing with KINTEK's advanced heating solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all supported by deep customization to precisely meet your experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our SC Type SiC elements can ensure uniform heat and superior quality in your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights



















