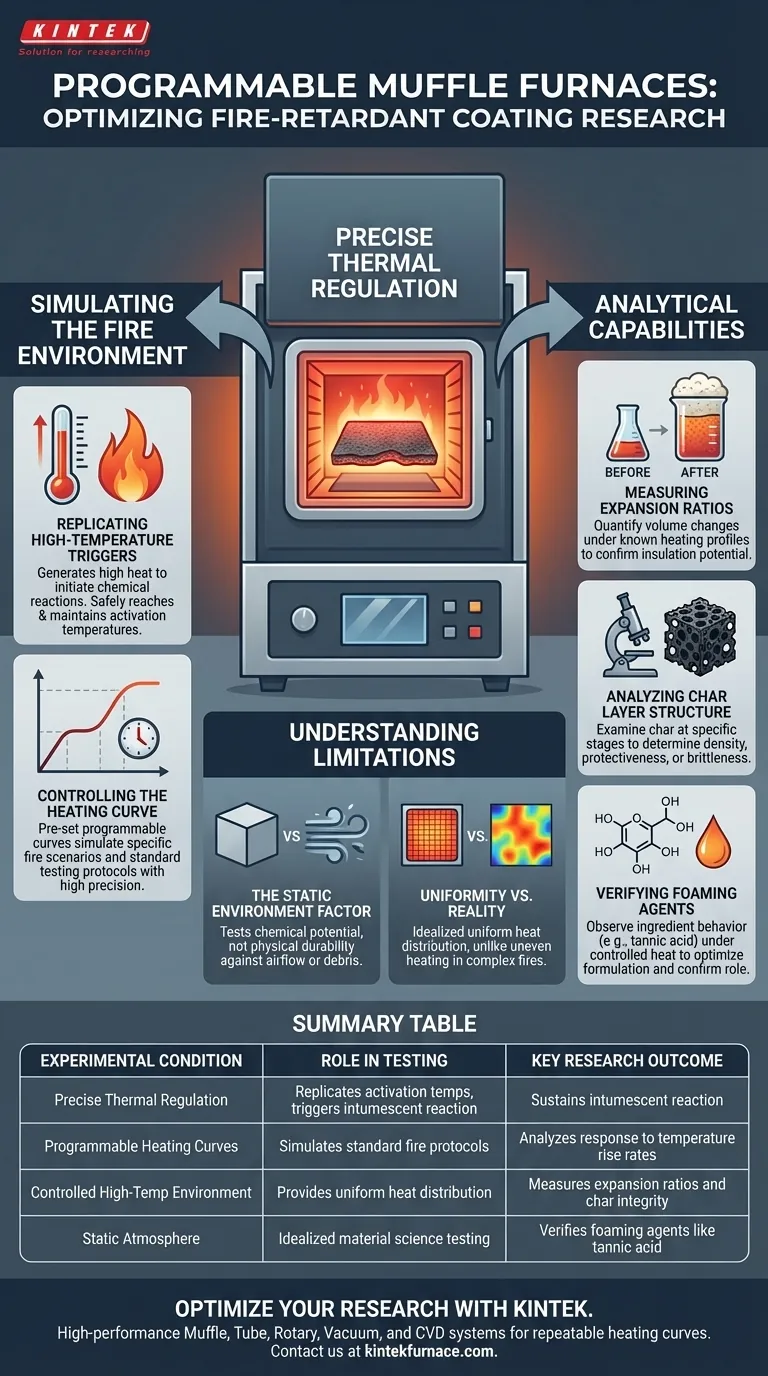
Precise thermal regulation is the defining capability of a programmable muffle furnace when observing fire-retardant coatings. It provides a strictly controlled, high-temperature environment that replicates the specific heating curves necessary to trigger and sustain the intumescent (expansion) reaction of the coating.
By governing the exact rate of temperature increase, researchers can quantitatively measure expansion ratios and analyze the structural integrity of the resulting char. This controlled simulation is essential for verifying the efficacy of specific foaming agents, such as tannic acid.
Simulating the Fire Environment
To understand how a coating will behave in a real fire, you must first observe it under consistent, repeatable thermal stress.
Replicating High-Temperature Triggers
The primary function of the furnace is to generate the high-temperature environment required to initiate the chemical reaction. Intumescent coatings are designed to remain inert until they reach a specific activation temperature. The muffle furnace allows researchers to reach and maintain these critical temperatures safely.
Controlling the Heating Curve
The "programmable" aspect of the furnace is the most critical variable. Instead of simply blasting the sample with heat, the furnace follows a pre-set heating curve. This ensures that the temperature rises at a specific rate, allowing researchers to simulate different fire scenarios or standard testing protocols with high precision.
Analytical Capabilities
Beyond simply heating the material, the experimental conditions provided by the furnace facilitate deep quantitative analysis.
Measuring Expansion Ratios
One of the key metrics for fire-retardant performance is the expansion ratio. By subjecting the coating to a known heating profile, researchers can measure the volume of the coating before and after the test. This data confirms whether the coating expands sufficiently to provide the necessary insulation.
Analyzing Char Layer Structure
The effectiveness of a coating relies on the quality of the "char" (the carbonaceous foam) it produces. The furnace allows researchers to stop the heating process at specific temperatures to examine the char layer structure. This helps determine if the char is dense and protective or brittle and porous.
Verifying Foaming Agents
The conditions in the furnace are specifically used to verify the performance of ingredients like tannic acid. By observing how these agents behave under controlled heat, researchers can confirm their role in the foaming process and optimize the chemical formulation.
Understanding the Limitations
While programmable muffle furnaces are powerful tools for material science, they provide an idealized environment that differs from field conditions.
The Static Environment Factor
A muffle furnace typically provides a static atmosphere. Real-world fires involve turbulent airflow, varying oxygen levels, and physical debris impact. The furnace tests the chemical potential of the material, not its physical durability against wind or structural shifting.
Uniformity vs. Reality
The furnace is designed to provide uniform heat distribution. While this is excellent for scientific reproducibility and comparing different formulations, it does not simulate the uneven heating or "cold spots" that might occur in a complex structural fire.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
When utilizing a programmable muffle furnace, tailor your experimental design to your specific analytical goals.
- If your primary focus is formulation screening: Use the furnace to run rapid, identical heating curves to compare the expansion ratios of different foaming agents (like tannic acid) side-by-side.
- If your primary focus is mechanism study: Program the furnace to hold at incremental temperatures to extract samples, allowing you to observe the evolution of the char layer structure at different stages of the reaction.
The programmable muffle furnace transforms fire testing from a chaotic event into a measurable, reproducible science.
Summary Table:
| Experimental Condition | Role in Fire-Retardant Testing | Key Research Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Precise Thermal Regulation | Replicates specific activation temperatures | Triggers and sustains intumescent reaction |
| Programmable Heating Curves | Simulates standard fire testing protocols | Analyzes response to specific temperature rise rates |
| Controlled High-Temp Environment | Provides uniform heat distribution | Measures expansion ratios and char integrity |
| Static Atmosphere | Idealized material science testing | Verifies foaming agents like tannic acid |
Optimize Your Fire-Retardant Research with KINTEK
Precision is paramount when analyzing the chemical potential and char structure of your coatings. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all of which are fully customizable for your unique lab high-temp needs.
Whether you are verifying new foaming agents or refining expansion ratios, our programmable furnaces deliver the repeatable heating curves your research demands.
Ready to elevate your material testing? Contact us today to find the perfect furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- James Covello, Gary E. Wnek. Tannic acid's role as both char former and blowing agent in epoxy‐based intumescent fire retardants. DOI: 10.1002/pls2.10118
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What types of materials are commonly processed in muffle furnaces? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Metals, Ceramics, and More
- What are some key applications of muffle furnaces? Unlock Precision and Purity in High-Temp Processes
- What are the main applications of a muffle furnace? Unlock Precision Heating for Material Transformations
- How is a muffle furnace utilized during the secondary thermal decomposition of ZnCl2-impregnated biochar?
- What is the general structure of a muffle furnace? Discover Its Precision Engineering
- Why is precise temperature control in a muffle furnace essential during the secondary calcination of acid-etched catalysts?
- What are the common applications of the box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment for Your Lab
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace in birnessite preparation? Optimize High-Temp Calcination Control



















