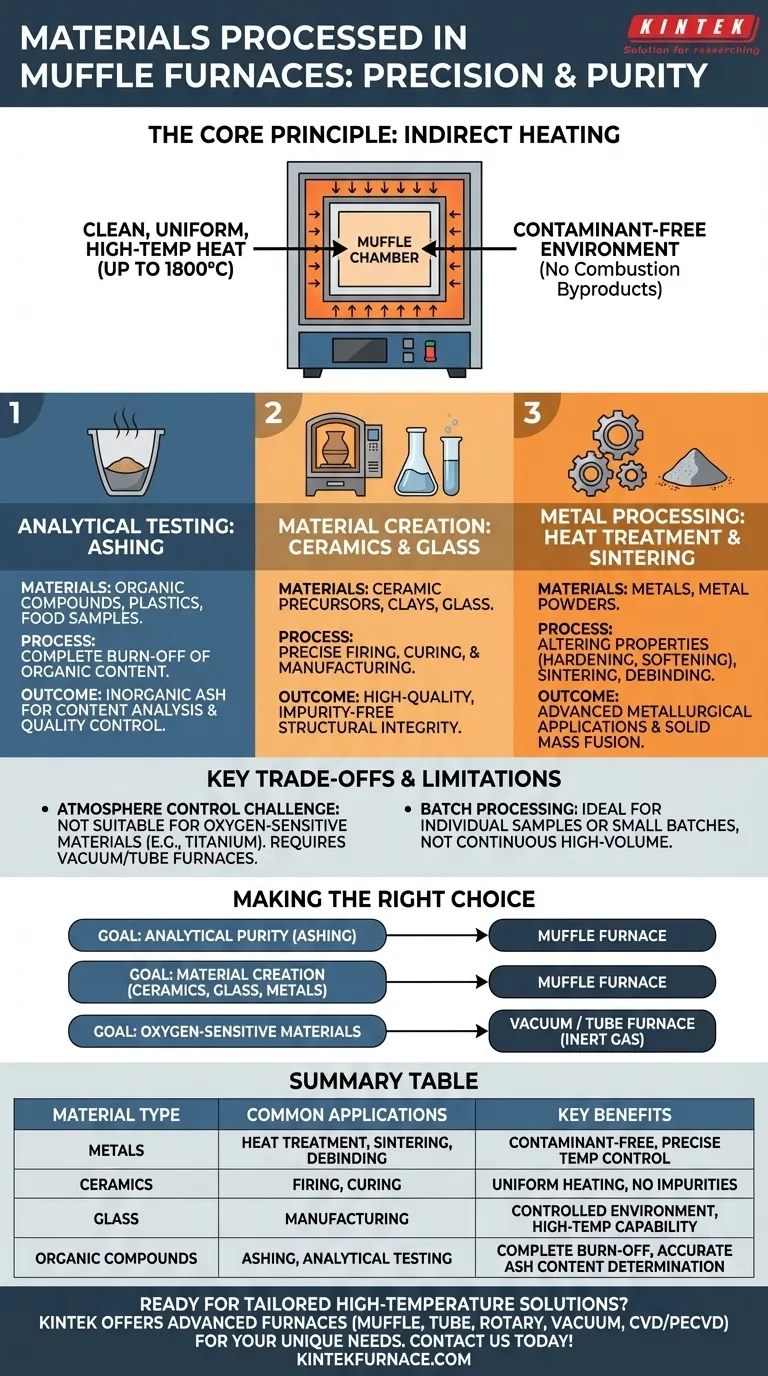
In short, muffle furnaces process a wide range of materials, including metals, ceramics, glass, and various organic or plastic compounds. Their primary function is not just heating, but doing so in a highly controlled environment, free from the byproducts of combustion, which makes them essential for both analytical testing and specialized manufacturing.
The core value of a muffle furnace lies in its design: it heats materials indirectly within a sealed chamber, or "muffle." This separation from the heating elements prevents contamination, making it the definitive tool for applications demanding purity and precision, such as determining the ash content of a sample or creating high-quality ceramics.

What Defines a Muffle Furnace's Purpose?
To understand the materials processed in a muffle furnace, you must first understand its fundamental principle: providing clean, uniform, high-temperature heat.
The Principle of Indirect Heating
A muffle furnace isolates the material being processed from the actual source of heat. In modern electric models, heating elements surround an inner chamber.
This design means the material is heated through conduction, convection, and blackbody radiation, not by an open flame.
A Contaminant-Free Environment
Because there is no combustion involved in the heating process, no fuel byproducts (like soot or gases) can interact with and contaminate the sample.
This purity is critical for scientific analysis and for manufacturing materials where chemical composition must be strictly controlled.
High-Temperature Capabilities
Modern muffle furnaces can reach temperatures as high as 1,800°C (3,272°F). This capability unlocks sophisticated metallurgical and material science applications that require extreme heat.
Core Applications and Materials Processed
The combination of high heat and a clean environment makes the muffle furnace indispensable across several key industrial and laboratory domains.
Analytical Testing: Ashing
Materials: Organic compounds, plastics, food samples, and other combustible materials.
Ashing is one of the most common uses for a muffle furnace. The process involves heating a sample at high temperatures to completely burn away all organic content, leaving only the inorganic, non-combustible residue, or ash. This is used to determine the ash content percentage for quality control and analysis.
Material Creation: Ceramics and Glass
Materials: Ceramic precursors (clays, powders) and glass.
The uniform, contaminant-free heating is ideal for firing ceramics and manufacturing glass. It allows for precise control over the curing and hardening process without introducing impurities that could compromise the structural integrity or appearance of the final product.
Metal Processing: Heat Treatment and Sintering
Materials: Metals and metal powders.
In metallurgy, muffle furnaces are used for heat-treating processes that alter a metal's physical and mechanical properties. This can include hardening or softening.
They are also used for advanced applications like sintering, where powdered metal is heated to fuse into a solid mass, and debinding, a critical step in metal injection molding to remove binder materials before final sintering.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While versatile, a muffle furnace is not a universal solution. Its primary limitation is its default operating atmosphere.
The Challenge of Atmosphere Control
A standard muffle furnace operates with air inside the chamber. This oxygen-rich environment is perfect for oxidative processes like ashing.
However, it is completely unsuitable for processing reactive metals (like titanium) or materials that must be protected from oxidation. These applications require specialized vacuum or tube furnaces that can maintain an inert gas atmosphere.
Best Suited for Batch Processing
Muffle furnaces are typically designed as self-contained boxes, making them ideal for processing individual samples or small-to-medium batches of material.
They are generally not designed for continuous, high-volume production lines, which often require tunnel or conveyor-style furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal processing tool depends entirely on your material and your objective.
- If your primary focus is analytical purity: Use a muffle furnace for applications like ashing, where a clean burn-off is essential for accurate results.
- If your primary focus is material creation: A muffle furnace is the standard for firing ceramics, forming glass, and heat-treating most common metals.
- If your primary focus is processing oxygen-sensitive materials: A muffle furnace is unsuitable; you must use a vacuum furnace or a tube furnace with an inert gas supply.
Ultimately, understanding the principle of indirect heating is the key to knowing when a muffle furnace is the right tool for your high-temperature application.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Metals | Heat treatment, sintering, debinding | Contaminant-free heating, precise temperature control |
| Ceramics | Firing, curing | Uniform heating, no impurities |
| Glass | Manufacturing | Controlled environment, high-temperature capability |
| Organic Compounds | Ashing, analytical testing | Complete burn-off, accurate ash content determination |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with tailored high-temperature solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization ensures they meet your unique experimental needs—whether for metals, ceramics, or analytical testing. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can drive precision and efficiency in your work!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















