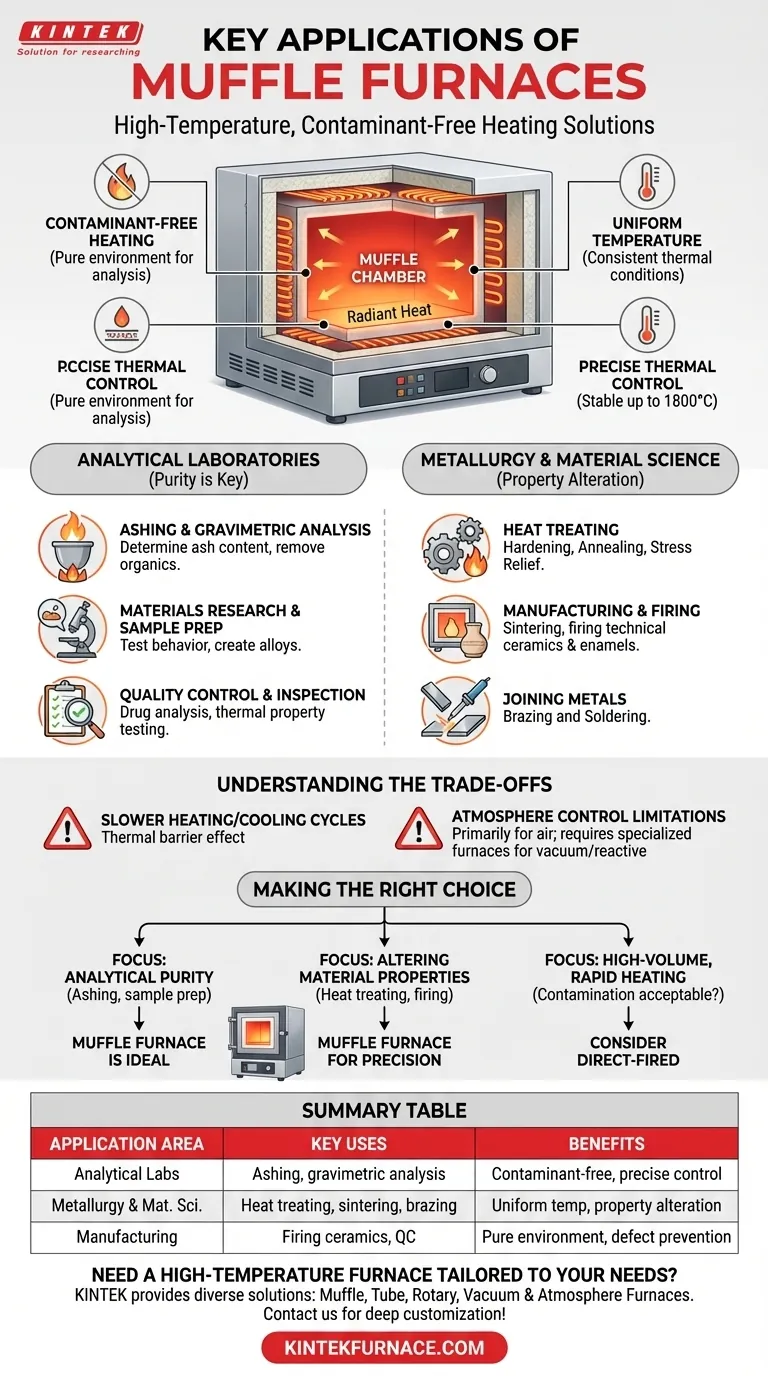
At its core, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven used for a wide range of applications across analytical laboratories, metallurgy, and specialized manufacturing. Its key applications include determining the ash content of a sample, heat-treating metals to alter their properties, and firing ceramics or enamel coatings in a pristine, controlled environment.
The defining feature of a muffle furnace is not just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its use of an isolated chamber—the "muffle"—to protect materials from fuel, combustion gases, and other contaminants. This ensures a uniformly heated and exceptionally pure processing environment.
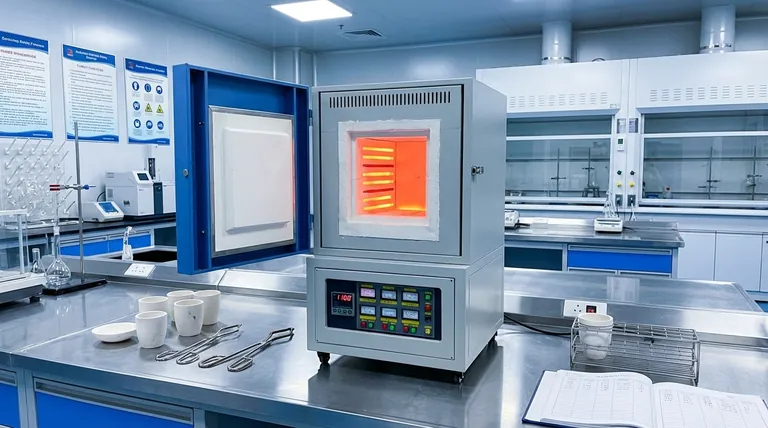

The Principle: Why a "Muffle" Is Critical
A muffle furnace's versatility comes from one core design element: the muffle. This is a sealed inner chamber that separates the material being heated from the furnace's heating elements.
Contaminant-Free Heating
Modern electric muffle furnaces heat the muffle chamber through conduction, convection, and radiation. Because the material never comes into contact with the heating source or combustion byproducts, its chemical purity is preserved, which is critical for scientific analysis and high-spec manufacturing.
Uniform Temperature Environment
The muffle radiates heat evenly from all sides, creating a highly uniform temperature zone. This consistency ensures that an entire sample or workpiece is processed under the exact same thermal conditions, preventing inconsistencies and defects.
Precise Thermal Control
This design allows for extremely precise and stable temperature control, often up to 1800°C (3272°F). This level of control is essential for sophisticated metallurgical processes and repeatable laboratory testing.
Key Applications in Analytical Laboratories
The clean heating environment of a muffle furnace makes it an indispensable tool for analysis and research where sample purity is non-negotiable.
Ashing and Gravimetric Analysis
This is one of the most common applications. A sample is heated to a high temperature to burn off all organic substances, leaving only the inorganic "ash." This process is used in food science, coal quality analysis, and environmental testing to determine the non-combustible content of a material.
Materials Research and Sample Preparation
Researchers use muffle furnaces to test material behavior at high temperatures, create novel alloys, or prepare samples for further analysis. This includes applications in the pharmaceutical, chemical, and nuclear industries.
Quality Control and Inspection
In manufacturing, muffle furnaces are used to test the thermal properties of components or to conduct inspections, such as drug analysis and water quality testing, that require a controlled heating step.
Core Uses in Metallurgy and Material Science
The ability to precisely control high temperatures makes muffle furnaces essential for modifying the physical and mechanical properties of materials.
Heat Treating: Hardening, Annealing, and Stress Relief
Metals are subjected to controlled heating and cooling cycles to change their properties. Processes like hardening (to increase strength), annealing (to soften and increase ductility), and stress relief (to remove internal stresses from fabrication) rely on the furnace's uniform heat.
Manufacturing and Firing Processes
Muffle furnaces are central to creating parts and coatings. This includes sintering, where powdered material is heated to create a solid mass (used in metal injection molding), and firing technical ceramics and enamel coatings, which require a clean environment to prevent discoloration and defects.
Joining Metals: Brazing and Soldering
Brazing and soldering are processes used to join two pieces of metal using a filler material. A muffle furnace provides the consistent, widespread heat needed to melt the filler metal and create a strong, clean joint across the entire workpiece.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, a muffle furnace is not always the perfect tool for every high-temperature task. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Slower Heating and Cooling Cycles
The muffle that provides protection also acts as a thermal barrier. This means muffle furnaces often heat up and cool down more slowly than direct-fired furnaces, which can impact throughput in high-volume production environments.
Atmosphere Control
While many muffle furnaces can operate with a controlled atmosphere (e.g., using inert gas), they are primarily designed for use in air. For processes requiring a hard vacuum or highly reactive atmospheres, a dedicated vacuum or atmosphere furnace may be more efficient.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a muffle furnace depends entirely on whether its core benefit—a pure, uniform heating environment—is essential for your task.
- If your primary focus is analytical purity: A muffle furnace is the ideal choice for applications like ashing, materials analysis, or sample prep where contamination would invalidate results.
- If your primary focus is altering material properties: A muffle furnace provides the precise thermal control needed for heat treating metals or firing ceramics and glasses.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, rapid heating: A direct-fired furnace might be a better choice, provided sample contamination from combustion gases is not a concern.
Ultimately, understanding the function of the muffle itself is the key to leveraging this powerful tool for any high-temperature application that demands precision and purity.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Analytical Laboratories | Ashing, gravimetric analysis, sample preparation | Contaminant-free heating, precise temperature control |
| Metallurgy and Material Science | Heat treating (hardening, annealing), sintering, brazing | Uniform temperature, property alteration |
| Manufacturing | Firing ceramics, enamel coatings, quality control | Pure environment, defect prevention |
Need a high-temperature furnace tailored to your unique needs? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise performance for applications such as ashing, heat treating, and ceramics. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve contaminant-free results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















