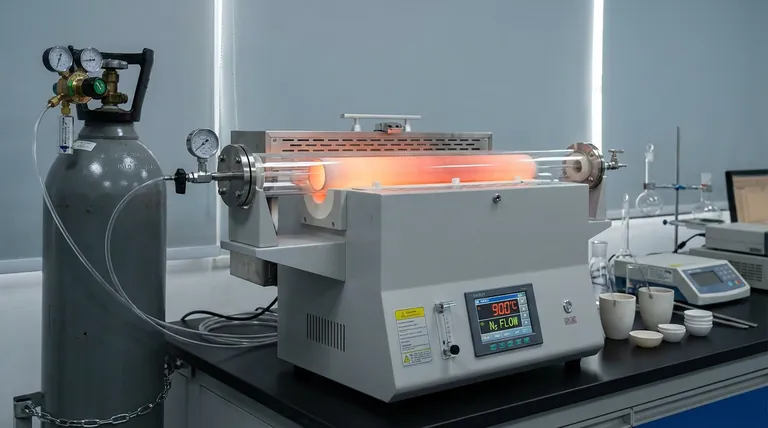
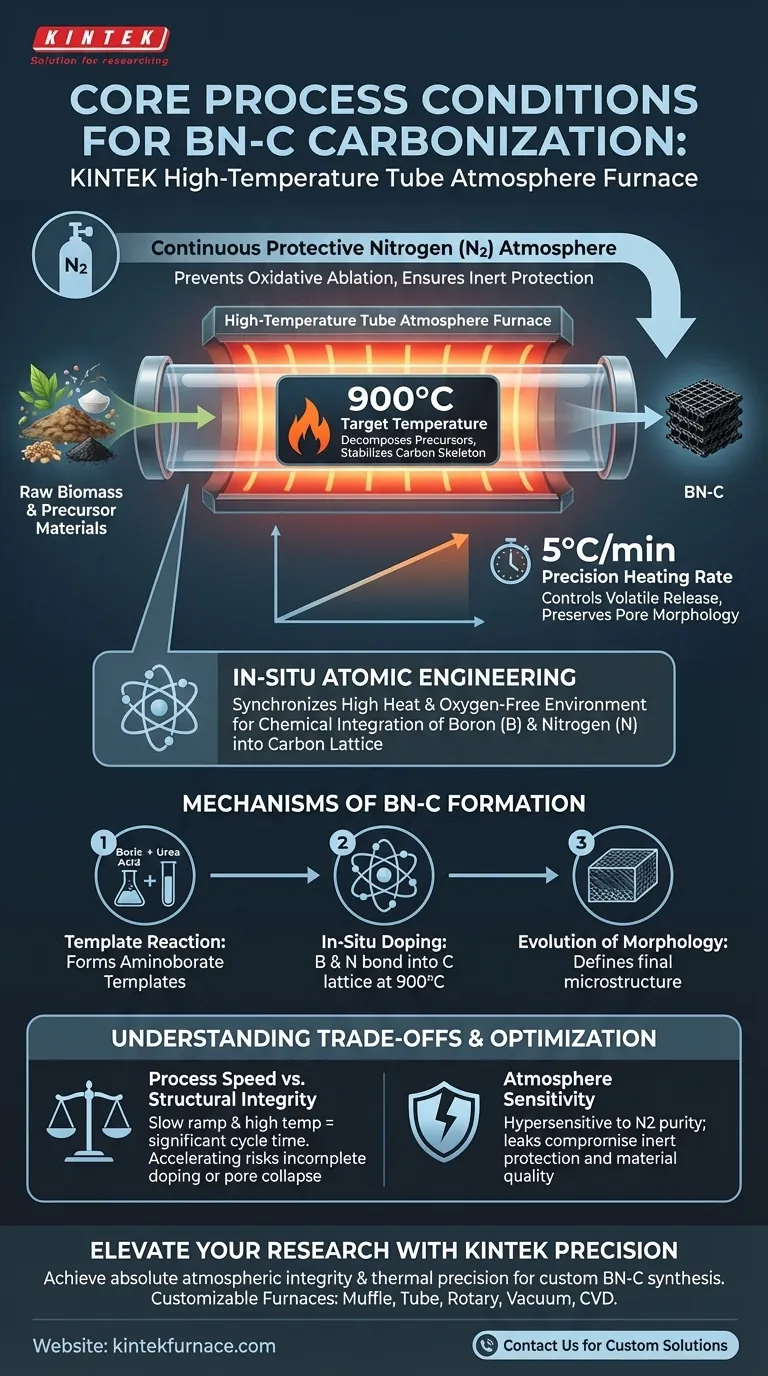
High-temperature tube atmosphere furnaces provide a strictly controlled thermal environment defined by temperatures reaching 900°C under a continuous protective nitrogen atmosphere.
For the carbonization of BN-C (Boron-Nitrogen-Carbon) materials, this equipment maintains a precise heating rate, typically 5°C per minute. This specific combination of temperature, inert gas flow, and ramp rate creates the necessary conditions for simultaneous thermal decomposition and chemical doping.
Core Takeaway The tube furnace functions as more than a heat source; it acts as a reactor for in-situ atomic engineering. By synchronizing high heat with an oxygen-free environment, it forces the chemical integration of boron and nitrogen into the carbon lattice while preventing the oxidative destruction of the developing material framework.

The Critical Process Parameters
Thermal Stability and Target Temperature
To successfully synthesize BN-C materials, the furnace must maintain a stable environment up to 900°C.
This high thermal plateau is required to fully decompose precursors like sodium lignosulfonate. At this temperature, the organic components are stripped away, leaving behind a stable carbonaceous skeleton.
Protective Atmosphere Control
A strict nitrogen atmosphere is non-negotiable during this process.
The furnace maintains a continuous flow of inert gas to displace oxygen. Without this protection, the carbon framework and the doping agents would suffer from oxidative ablation (burning off) rather than forming a solid structure.
Precision Heating Rates
The standard heating protocol involves a controlled ramp rate of 5°C per minute.
This gradual increase is critical for managing the release of volatile components. A controlled rate ensures that the evolution of gases does not destroy the material's developing morphology or pore structure.
Mechanisms of BN-C Formation
Template Reaction Facilitation
The furnace environment induces specific chemical reactions between doping precursors.
Under these conditions, boric acid and urea react to form aminoborate templates. This intermediate step is essential for structuring the final material and cannot occur efficiently if the thermal profile is erratic.
In-Situ Doping
The core advantage of this process is the in-situ doping of the carbon framework.
As the carbonization proceeds at 900°C, boron and nitrogen atoms are chemically bonded into the carbon lattice. This transforms a simple carbon material into a functionalized BN-C composite with enhanced electronic or catalytic properties.
Evolution of Morphology
The combination of gas flow and heat determines the physical shape of the material.
The process drives the final evolution of the material's morphology. By carefully removing volatiles while stabilizing the skeleton, the furnace ensures the creation of a distinct microstructure rather than an amorphous char.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Speed vs. Structural Integrity
There is an inherent trade-off between throughput and material quality.
The requirement for a slow ramp rate (5°C/min) and a high final temperature (900°C) means the cycle time is significant. Accelerating this process to increase production speed risks incomplete doping or the collapse of the pore structure due to rapid gas release.
Atmosphere Sensitivity
The quality of the final BN-C material is hypersensitive to the purity of the inert atmosphere.
Even minor leaks or impurities in the nitrogen flow can lead to partial oxidation. This compromises the "strict inert protection" required to preserve the carbon mass and ensures the stability of the crystalline phases.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When configuring a tube furnace for BN-C synthesis, align your process parameters with your specific material objectives.
- If your primary focus is Doping Efficiency: Prioritize maintaining the 900°C temperature plateau to ensure maximum reaction between boric acid, urea, and the carbon source for optimal B and N incorporation.
- If your primary focus is Microstructural Control: Strictly adhere to the 5°C/min ramp rate to prevent structural collapse caused by the rapid exit of volatile components.
Mastering the balance between thermal intensity and atmospheric protection is the key to converting raw biomass and salts into high-performance BN-C materials.
Summary Table:
| Process Parameter | Required Specification | Role in BN-C Synthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Target Temperature | 900°C | Decomposes precursors & stabilizes carbon skeleton |
| Atmosphere Type | Nitrogen (N2) | Prevents oxidative ablation & ensures inert protection |
| Heating Rate | 5°C per minute | Controls volatile release & preserves pore morphology |
| Doping Mechanism | In-situ Atomic Engineering | Facilitates B and N integration into the carbon lattice |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect BN-C composite requires more than just heat; it demands absolute atmospheric integrity and thermal precision. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance laboratory solutions backed by expert R&D and advanced manufacturing.
Whether you need Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, or CVD systems, our high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique carbonization and doping requirements.
Ready to optimize your synthesis process? Contact us today to find your custom furnace solution and experience the KINTEK difference in material science.
Visual Guide
References
- Dichao Wu, Kang Sun. Lignin‐derived carbon with pyridine N‐B doping and a nanosandwich structure for high and stable lithium storage. DOI: 10.1002/cey2.511
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- How does a furnace atmosphere protect materials from surface reactions? Master Controlled Heat Treatment
- How does an atmospheric furnace work? Understanding Efficiency & Safety Risks
- How do chemically active metals behave when heated in an air furnace? Understand the risks and solutions.
- What is an atmosphere box furnace and what are its primary uses? Essential for Controlled Heat Processing
- How does the box type annealing atmosphere furnace ensure accurate temperature control? Discover Precision Heating Solutions
- How does a continuous controlled atmosphere furnace operate? Unlock High-Volume Precision in Material Processing
- How is helium utilized in atmosphere furnaces? Unlock Purity and Rapid Cooling for Superior Results
- What are the primary applications of retort furnaces? Unlock Precision in High-Temperature Processing



















