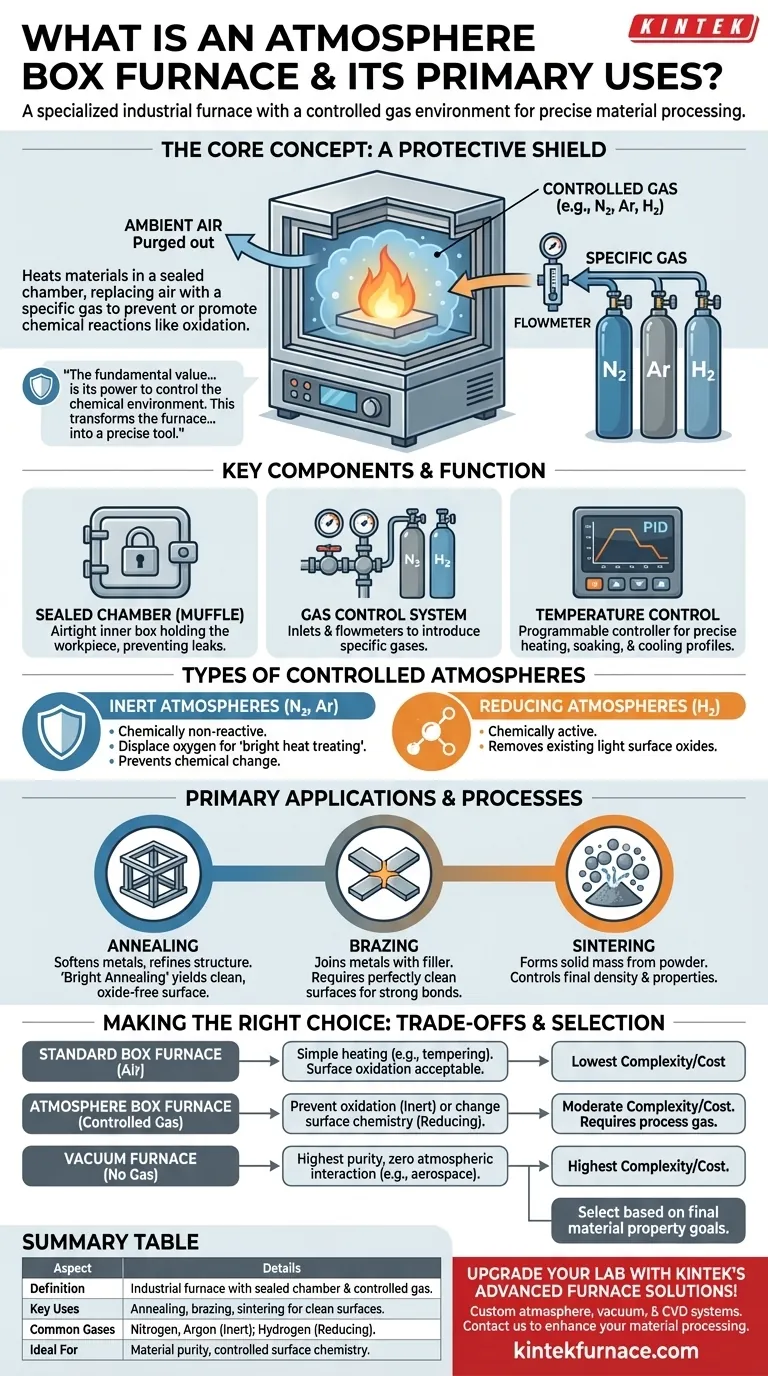
At its core, an atmosphere box furnace is a specialized type of industrial furnace that heats materials inside a sealed chamber filled with a specific, controlled gas. Unlike a standard furnace that heats in ambient air, this controlled environment is the key feature, designed to prevent or promote specific chemical reactions, such as oxidation, during the heating process. This capability is critical for achieving desired properties in metallurgy, electronics, and advanced materials research.
The fundamental value of an atmosphere furnace is not just its ability to heat, but its power to control the chemical environment. This transforms the furnace from a simple oven into a precise tool for manipulating a material's final integrity, surface finish, and internal structure.

Deconstructing the Atmosphere Box furnace
An atmosphere box furnace builds upon the design of a standard box (or "muffle") furnace by adding a crucial layer of environmental control. Understanding its components reveals its purpose.
The Core Function: A Protective Shield
At high temperatures, most metals and many other materials react readily with the oxygen in the air. This reaction, oxidation, creates a layer of scale on the surface that can ruin a part's finish, alter its dimensions, and compromise its structural integrity.
An atmosphere furnace prevents this by first purging the air from the chamber and replacing it with a carefully selected gas. This gas acts as a protective shield during the entire heating and cooling cycle.
Key Components That Enable Control
The ability to manage the atmosphere depends on several integrated systems:
- The Sealed Chamber: Often called a "muffle," this is the inner box that holds the workpiece. It must be airtight to prevent the controlled atmosphere from escaping or outside air from leaking in.
- The Gas Control System: This is the heart of the furnace's special capability. It includes inlets and flowmeters to introduce specific gases like Nitrogen, Argon, or Hydrogen into the chamber.
- The Temperature Control System: A programmable controller, typically a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller, executes precise heating, soaking, and cooling profiles as required by the process.
Types of Controlled Atmospheres
The choice of gas determines the effect on the material:
- Inert Atmospheres: Gases like Nitrogen and Argon are chemically non-reactive. They are used simply to displace oxygen and prevent any chemical change, a process often called bright heat treating.
- Reducing Atmospheres: Gases like Hydrogen (or a mix of Hydrogen and Nitrogen called "forming gas") are chemically active. They not only prevent oxidation but can actively remove existing light surface oxides.
Primary Applications and Processes
The ability to prevent unwanted chemical reactions makes atmosphere furnaces essential for processes where surface quality and material purity are paramount.
Annealing
Annealing is a process used to soften metals, relieve internal stresses, and refine their grain structure. When performed in an atmosphere furnace (bright annealing), the part emerges with a clean, bright, and oxide-free surface, often eliminating the need for post-process cleaning.
Brazing
Brazing joins two pieces of metal using a filler material that melts at a lower temperature than the base metals. For the filler to flow properly and create a strong bond, the surfaces must be perfectly clean. An atmosphere furnace prevents oxide formation during heating, ensuring a sound joint.
Sintering
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat and pressure without melting it to the point of liquefaction. Used extensively in powder metallurgy and ceramics, a controlled atmosphere is vital for bonding the particles and controlling the final density and properties of the component.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace requires weighing process needs against equipment complexity and cost.
Atmosphere Furnace vs. Standard Box Furnace
The primary difference is process intent. A standard box furnace is sufficient for applications where surface oxidation is acceptable or even desired, such as hardening some tool steels or performing burn-off processes. An atmosphere furnace is chosen when surface chemistry must be preserved or controlled.
This control comes at the cost of increased equipment complexity, the ongoing expense of process gases, and stricter operational and safety protocols.
Atmosphere Furnace vs. Vacuum Furnace
A vacuum furnace represents the next level of atmospheric control. While an atmosphere furnace replaces air with a specific gas, a vacuum furnace removes virtually all gases.
Vacuum is superior for the most sensitive materials where even trace impurities from a process gas are unacceptable. However, vacuum furnaces are generally more expensive to purchase and operate than atmosphere furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your choice of thermal processing equipment must be driven by the final material properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is simple heating without surface chemistry concerns (e.g., tempering, basic stress relief): A standard, air-atmosphere box furnace is the most direct and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation to maintain a clean surface (e.g., bright annealing, clean brazing, copper processing): An atmosphere furnace using an inert gas like Nitrogen or Argon is necessary.
- If your primary focus is actively changing surface chemistry or processing sensitive powders (e.g., sintering, decarburization-sensitive steels): An atmosphere furnace with a reducing gas like Hydrogen is often the correct tool.
- If your primary focus is achieving the absolute highest purity with zero atmospheric interaction (e.g., medical implants, aerospace alloys): A vacuum furnace is the required technology.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace is about matching the tool's capability to your specific material transformation goal.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Industrial furnace with sealed chamber and controlled gas environment for precise heating. |
| Key Uses | Annealing, brazing, sintering to prevent oxidation and control material properties. |
| Common Gases | Nitrogen (inert), Argon (inert), Hydrogen (reducing) for specific chemical reactions. |
| Ideal For | Applications requiring clean surfaces, material purity, and controlled atmospheres. |
Upgrade your lab's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable atmosphere box furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, such as bright annealing or sintering. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your material processing efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage



















