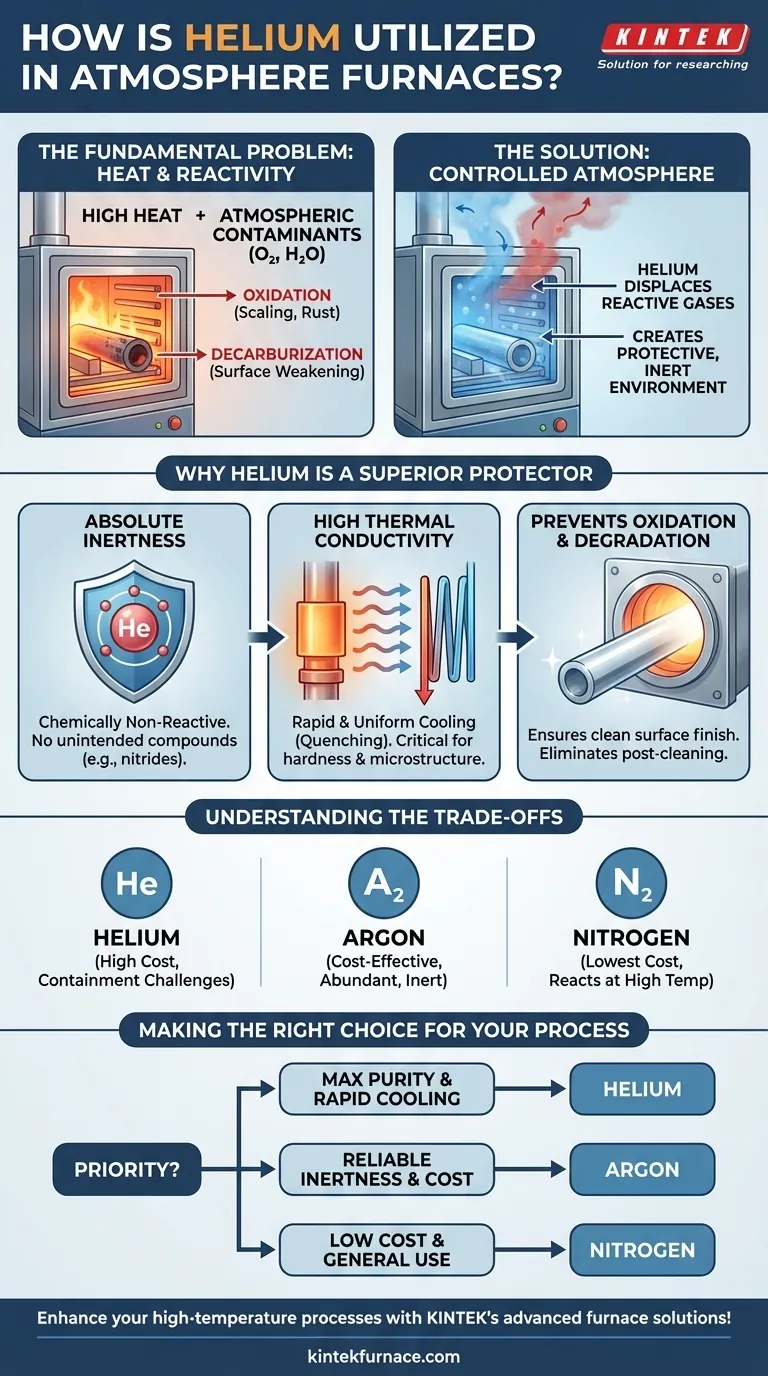
In atmosphere furnaces, helium's primary function is to serve as a high-purity, completely inert gas. It displaces reactive atmospheric gases like oxygen and water vapor, creating a protective environment that prevents unwanted chemical reactions such as oxidation and decarburization during high-temperature processes like heat treating and brazing.
The core purpose of using helium is not merely to fill the furnace, but to precisely control the chemical environment. This control is essential for preventing material degradation at high temperatures, ensuring the final product achieves its required metallurgical and structural properties.

The Fundamental Problem: Heat and Reactivity
At room temperature, most materials are relatively stable in the open air. However, introducing intense heat fundamentally changes their behavior, making them highly susceptible to chemical reactions with their surroundings.
The Enemy: Atmospheric Contaminants
The ambient air we live in is approximately 21% oxygen and contains variable amounts of water vapor. At the high temperatures found inside a furnace, these components become aggressive contaminants.
Oxygen will rapidly bond with hot metals, causing oxidation (scaling or rust) that degrades the surface finish and can compromise the part's integrity. For certain steels, it can also lead to decarburization, where carbon leaches out of the surface, making the material softer and weaker than intended.
The Solution: A Controlled Atmosphere
An atmosphere furnace solves this problem by allowing operators to completely purge the ambient air from the heating chamber and replace it with a specific, engineered gas or gas mixture.
This controlled atmosphere blankets the material, physically shielding it from contact with oxygen and other reactive elements throughout the heating and cooling cycle.
Why Helium Is a Superior Protector
While several gases can be used to create a protective atmosphere, helium possesses a unique combination of properties that make it ideal for the most demanding applications.
Absolute Inertness
Helium is a noble gas, meaning it is chemically non-reactive. It will not react with any material, even at the most extreme temperatures used in metallurgy and material science. This guarantees a truly pure environment, free from the risk of forming unintended compounds like nitrides, which can occur with less inert gases like nitrogen.
High Thermal Conductivity
Helium transfers heat more effectively than any other gas except hydrogen. This high thermal conductivity provides a key process advantage: it allows for more rapid and uniform cooling (quenching) of parts. This fast, even cooling is critical for achieving specific hardness levels and microstructures in many heat-treating processes.
Preventing Oxidation and Degradation
By displacing every trace of oxygen, helium provides absolute protection against oxidation. This ensures components emerge from the furnace with a clean, bright surface, often eliminating the need for subsequent cleaning or machining operations. This is critical in processes like brazing, where surfaces must be perfectly clean for the filler metal to bond correctly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Helium is an engineered solution with distinct advantages, but its use involves important considerations. Acknowledging these trade-offs is key to making an informed process decision.
The Primary Factor: Cost
Helium is significantly more expensive than other common atmosphere gases like argon or nitrogen. Its price is driven by its relative scarcity, as it is a finite resource extracted from natural gas deposits.
Viable Alternatives: Argon and Nitrogen
Argon, another noble gas, is also completely inert and is the most common alternative to helium. It is much more abundant in the atmosphere and therefore more cost-effective, making it the standard choice for many general-purpose inerting applications.
Nitrogen is even less expensive and is widely used. However, it is not truly inert at high temperatures. It can react with certain metals, such as titanium and some stainless steels, to form undesirable nitrides on the surface.
Containment Challenges
Helium atoms are extremely small and light, making the gas notoriously difficult to contain. Furnaces using helium require exceptionally high-integrity seals and construction to prevent leaks, which can be both costly and a process control issue.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The selection of an atmosphere gas is a critical decision based on material requirements, process goals, and budget.
- If your primary focus is maximum material purity and rapid cooling rates: Helium's absolute inertness and high thermal conductivity make it the superior choice, particularly for sensitive materials like reactive metals or for applications requiring precise quenching.
- If your primary focus is a reliable inert environment at a lower cost: Argon provides nearly all the inerting benefits of helium and is the more economical and practical option for a wide range of heat treatment and brazing processes.
- If you are processing materials not susceptible to nitriding and budget is the main driver: A nitrogen-based atmosphere offers a highly cost-effective solution for general annealing and inerting applications where absolute purity is not the highest priority.
Ultimately, choosing the right atmosphere gas is a strategic engineering decision that directly dictates the quality, integrity, and performance of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Helium's Role |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Serves as a high-purity, inert gas to displace reactive atmospheric gases like oxygen and water vapor |
| Key Benefits | Absolute inertness (no chemical reactions), high thermal conductivity for rapid and uniform cooling, prevents oxidation and decarburization |
| Common Applications | Heat treating, brazing, processes requiring precise quenching and material purity |
| Trade-offs | Higher cost compared to argon and nitrogen, requires excellent furnace seals to prevent leaks |
Enhance your laboratory's high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, such as optimizing atmosphere control with gases like helium for superior material outcomes. Ready to achieve unparalleled purity and efficiency? Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of inert atmosphere furnaces? Essential for Metal Processing, Electronics, and Additive Manufacturing
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment



















