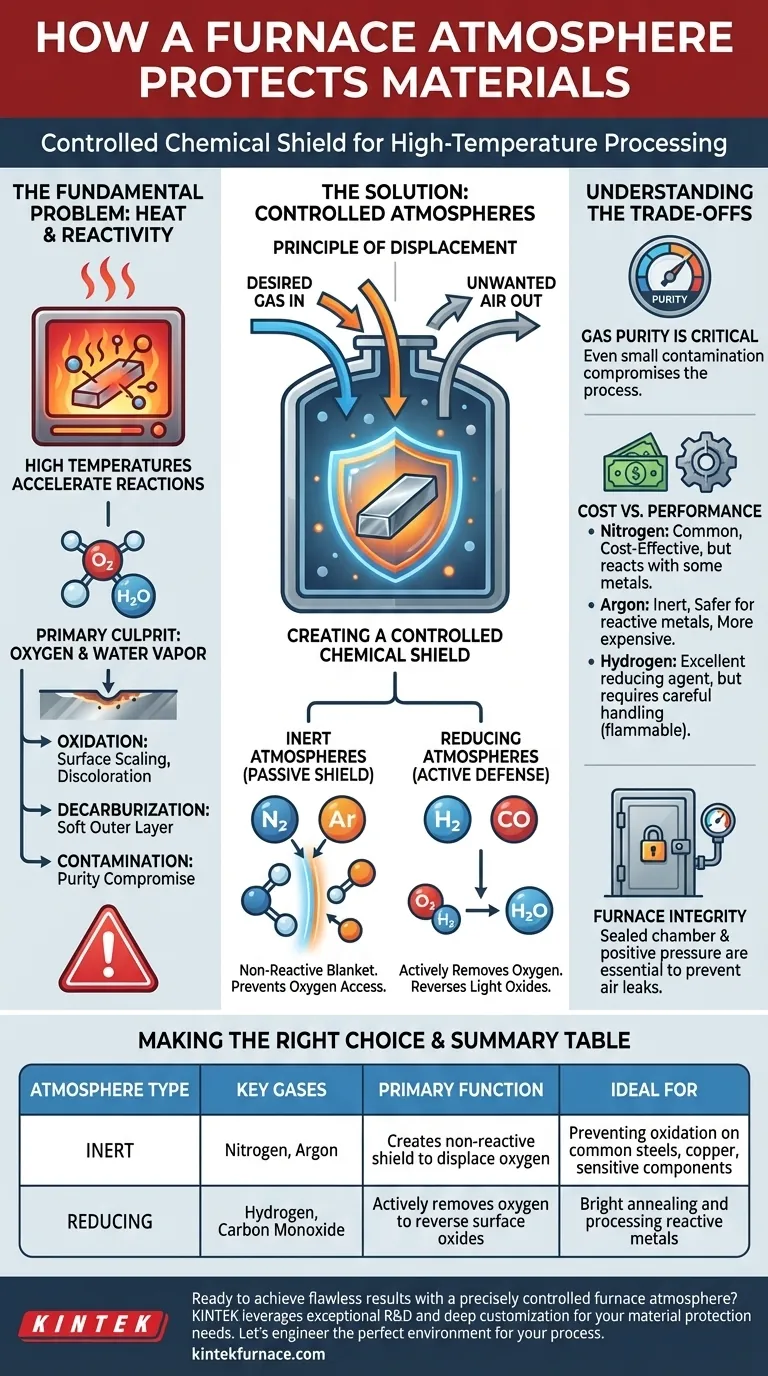
In essence, a furnace atmosphere protects a material by creating a controlled chemical shield around it during high-temperature processing. This shield displaces the reactive ambient air—primarily oxygen and water vapor—with a specific gas or gas mixture that prevents unwanted surface reactions like oxidation, contamination, or decarburization.
The fundamental goal is to control the chemical environment at the material's surface, not just its temperature. A furnace atmosphere achieves this by replacing unpredictable air with a predictable gas composition, ensuring the material's integrity remains intact throughout the heating process.

The Fundamental Problem: Heat and Reactivity
Why High Temperatures Are a Challenge
Heat is an accelerator. As you increase the temperature of a material, you dramatically increase the rate at which it will react with its surroundings.
A process that might take years at room temperature, like the rusting of iron, can happen in mere seconds inside a hot furnace.
The Primary Culprit: Oxygen
For most metals and many ceramics, the most significant threat in the air is oxygen. At high temperatures, oxygen aggressively bonds with materials to form oxides.
This process, known as oxidation, can result in undesirable surface scaling, discoloration, and a change in the material's physical properties.
Beyond Oxidation
Other unwanted reactions can also occur. For steels, the carbon near the surface can react with oxygen, leading to decarburization and a soft outer layer.
Furthermore, contaminants from the air or the furnace itself can deposit onto the material, compromising its purity and performance.
How Controlled Atmospheres Provide Protection
The Principle of Displacement
The core mechanism of any protective atmosphere is displacement. By filling the furnace chamber with a desired gas, you physically push out the unwanted air.
This ensures that the material is only exposed to the gases you have intentionally introduced, giving you complete control over the surface chemistry.
Inert Atmospheres: The Non-Reactive Shield
The simplest form of protection uses an inert gas, such as Argon or Nitrogen. These gases are chemically stable and do not readily react with other elements, even at high temperatures.
They act like a "blanket of gas," forming a neutral barrier that simply prevents oxygen from reaching the material's surface. This is a passive but highly effective form of protection.
Reducing Atmospheres: The Active Defense
A reducing atmosphere goes a step further. These atmospheres, which often contain Hydrogen (H₂) or Carbon Monoxide (CO), actively remove oxygen from the environment.
Hydrogen, for example, will react with any free oxygen (O₂) to form water vapor (H₂O), which is then flushed from the furnace. This not only prevents oxidation but can even reverse light surface oxides that may have been present before heating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Gas Purity is Critical
The effectiveness of a furnace atmosphere is entirely dependent on its purity. Even small amounts of contamination, such as moisture or oxygen in the gas supply lines, can compromise the entire process.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct trade-off between gas cost and effectiveness. Nitrogen is a common and affordable choice, but it can react with certain metals like titanium at high temperatures.
Argon is more inert and safer for reactive metals but is significantly more expensive. Hydrogen is an excellent reducing agent but requires careful handling due to its flammability.
Furnace Integrity
The most sophisticated gas mixture is useless if the furnace itself leaks. A sealed chamber and positive pressure are essential to prevent ambient air from being drawn in, which would defeat the purpose of the controlled atmosphere.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Choosing the correct atmosphere is a critical decision based on your material, your process, and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is preventing basic oxidation on common steels or copper: A cost-effective inert atmosphere like Nitrogen is typically sufficient.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive metals like titanium or sensitive electronic components: A high-purity inert gas like Argon is necessary to avoid any potential side reactions.
- If your primary focus is actively bright-annealing parts or reversing surface oxides: A reducing atmosphere containing Hydrogen is the most effective choice.
Mastering the furnace atmosphere transforms heat treatment from simple heating into precise surface engineering.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Key Gases | Primary Function | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inert | Nitrogen, Argon | Creates a non-reactive shield to displace oxygen | Preventing oxidation on common steels, copper, and sensitive components |
| Reducing | Hydrogen, Carbon Monoxide | Actively removes oxygen to reverse surface oxides | Bright annealing and processing reactive metals |
Ready to achieve flawless results with a precisely controlled furnace atmosphere?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions for your specific needs. Whether you require a standard Muffle Furnace or a custom-designed Atmosphere or Vacuum Furnace, our deep customization capabilities ensure your material is protected from oxidation, decarburization, and contamination.
Let's engineer the perfect environment for your process. Contact our experts today to discuss your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance



















