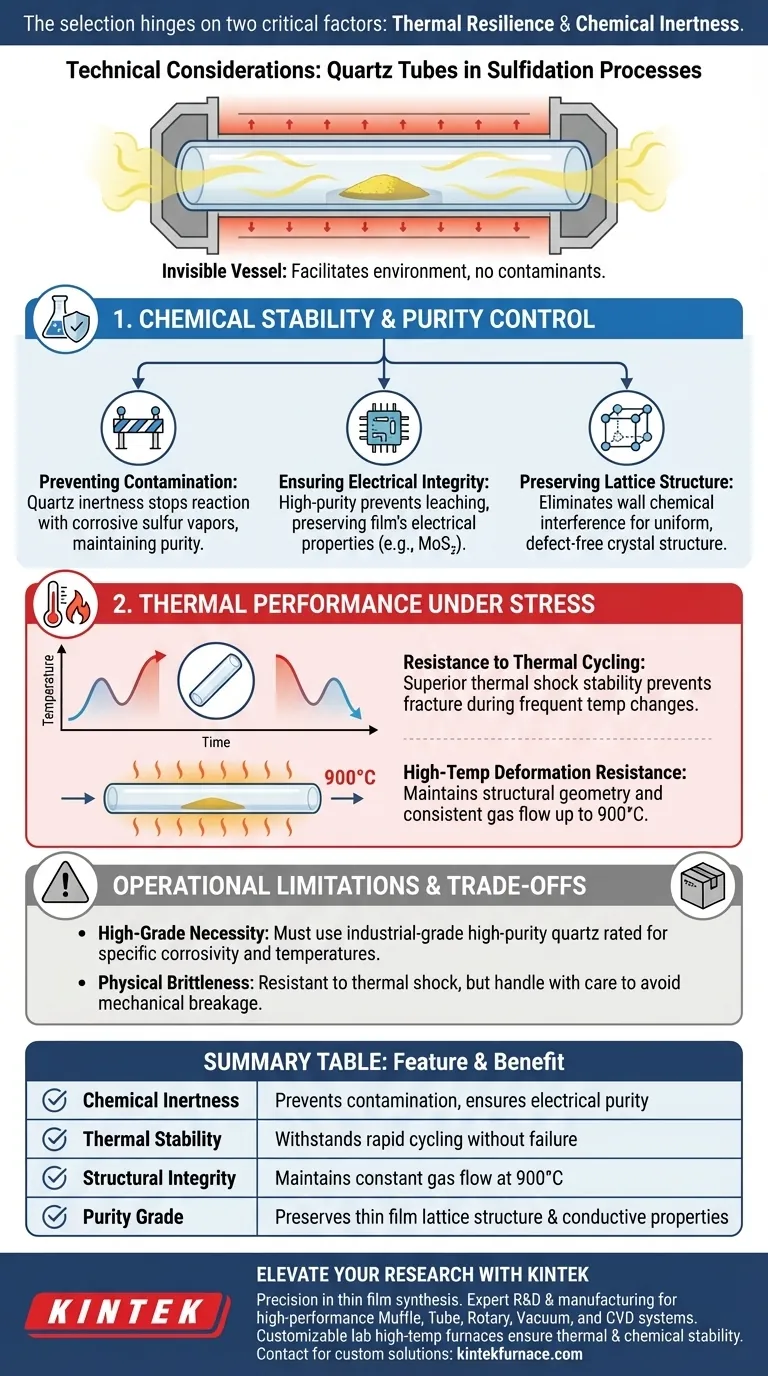
The selection of quartz tubes for sulfidation hinges on two critical factors: thermal resilience and chemical inertness. When designing a reaction chamber, you must prioritize materials that can endure rapid temperature changes without deformation while remaining neutral to aggressive sulfur vapors.
Ideally, a reaction chamber acts as an invisible vessel; quartz is chosen because it facilitates the necessary heat and chemical environment without contributing contaminants that would compromise the electrical purity or lattice structure of the final thin film.
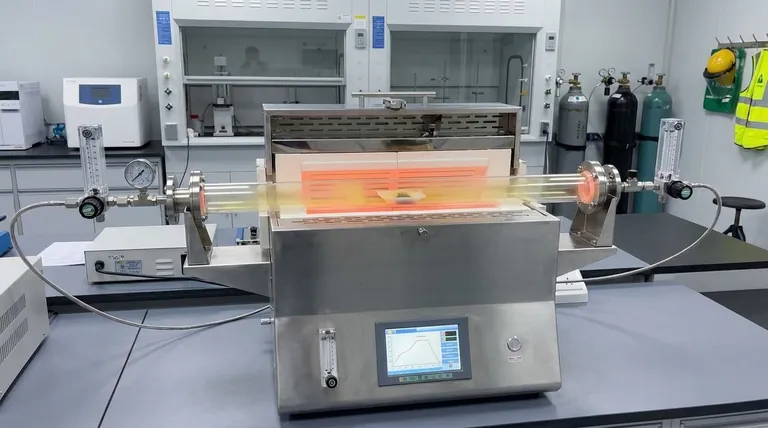

Chemical Stability and Purity Control
preventing Contamination
The most significant risk in sulfidation processes is the introduction of foreign impurities into the synthesized material.
Quartz provides exceptional chemical inertness, meaning it does not react with the corrosive sulfur vapors generated during the process. This neutrality is essential for maintaining the purity of the reaction environment.
Ensuring Electrical Integrity
For applications such as producing Molybdenum Disulfide ($MoS_2$) thin films, even trace impurities can degrade performance.
High-purity quartz prevents the leaching of contaminants that would otherwise alter the electrical purity of the film. This ensures the final product retains its intended conductive or semi-conductive properties.
Preserving Lattice Structure
Beyond chemical composition, the structural quality of the thin film is paramount.
By eliminating chemical interference from the chamber walls, quartz helps maintain the lattice integrity of the developing crystal structure. This results in a more uniform and defect-free material.
Thermal Performance Under Stress
Resistance to Thermal Cycling
Sulfidation processes often require raising and lowering temperatures repeatedly.
Quartz tubes possess superior thermal shock stability, allowing them to withstand these frequent temperature fluctuations without fracturing. This durability prevents catastrophic failure of the reaction chamber during operation.
High-Temperature Deformation Resistance
The material must hold its shape under extreme heat to ensure consistent gas flow and pressure.
Quartz offers excellent resistance to deformation at high temperatures, maintaining its structural geometry even in experimental environments reaching up to 900°C. This rigidity ensures that the physical parameters of the reaction zone remain constant.
Operational Limitations and Trade-offs
The Necessity of High-Grade Material
Not all quartz is created equal; the benefits discussed here rely on the use of industrial-grade high-purity quartz.
Using lower-grade quartz may introduce the very impurities you are trying to avoid or fail under thermal stress. You must verify that the specific grade selected is rated for the corrosivity of sulfur vapor and the specific temperature range of your experiment.
Physical Brittleness
While quartz is resistant to thermal shock, it remains physically brittle.
Care must be taken during the loading and unloading of samples to avoid mechanical breakage. The "toughness" of quartz refers to its thermal and chemical properties, not its resistance to impact.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your sulfidation process, align your material selection with your specific technical outcomes:
- If your primary focus is Electronic Grade Quality: Prioritize high-purity quartz to prevent atomic-level contamination and ensure the electrical purity required for high-performance Molybdenum Disulfide films.
- If your primary focus is Process Durability: Select industrial-grade quartz rated for temperatures up to 900°C to ensure the chamber withstands frequent thermal cycling without deformation or fracture.
By treating the reaction chamber as a critical component of the synthesis chemistry rather than just a container, you ensure reproducible, high-quality results.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Technical Requirement | Benefit to Sulfidation Process |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resistance to sulfur vapor | Prevents contamination and ensures electrical purity |
| Thermal Stability | High shock resistance | Withstands rapid cycling without fracturing or failure |
| Structural Integrity | Low deformation at 900°C | Maintains constant gas flow and reaction zone geometry |
| Purity Grade | Industrial-grade quartz | Preserves thin film lattice structure and conductive properties |
Elevate Your Sulfidation Research with KINTEK
Precision in thin film synthesis starts with the right environment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of chemical vapor deposition and sulfidation. Whether you are producing MoS₂ films or specialized semiconductors, our customizable lab high-temp furnaces ensure the thermal and chemical stability your project requires.
Ready to optimize your reaction chamber performance?
Contact KINTEK today for a custom solution and let our experts help you achieve superior material integrity.
Visual Guide
References
- Md Shariful Islam, Nowshad Amin. Pressure-dependent sulfurization of molybdenum thin films for high-quality MoS<sub>2</sub> formation. DOI: 10.1088/1755-1315/1500/1/012020
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- What is the primary function of a tube resistance furnace in g-C3N4 synthesis? Achieve Precise Thermal Condensation
- What materials are commonly used in the heating device of a tube furnace? Optimize Your High-Temp Processes
- Why is high-vacuum encapsulation in quartz tubes required? Ensure Precision for Sn-Ag-Bi-Se-Te Composites
- What is the function of a tube furnace in pRF preparation? Optimize Carbonization & Conductivity
- How does a laboratory tube annealing furnace contribute to the final formation of CNT-Al2O3-Ag-TiO2 composite materials?
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace contribute to the atmosphere-controlled sintering of Mn-Zn ferrites?
- What are the roles of a vacuum tube furnace and a CCD camera in high-temperature wettability testing? Key Insights



















