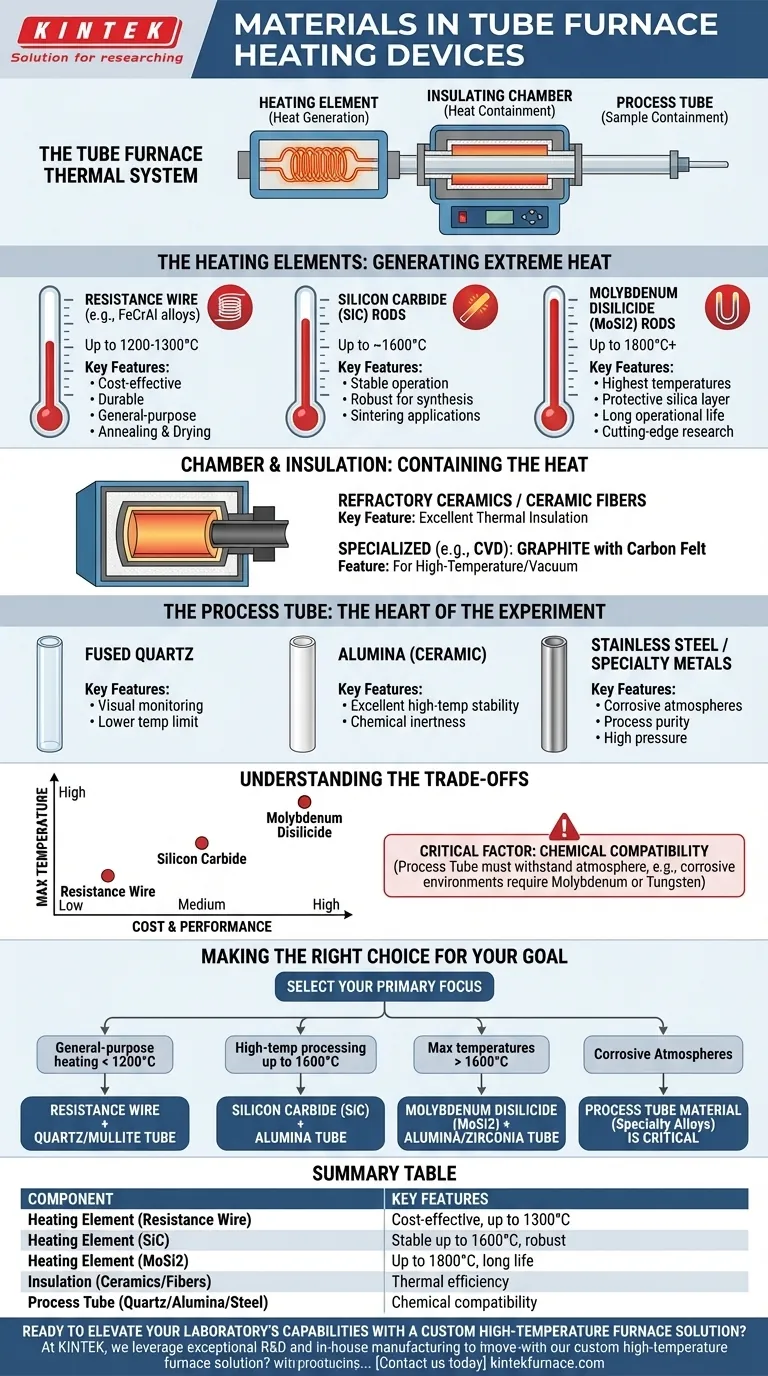
The heating device in a tube furnace relies on a select group of materials chosen for their ability to generate extreme heat reliably. The most common materials for the heating elements themselves are resistance wire alloys, silicon carbide (SiC) rods, and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) rods. These materials are selected for their high-temperature stability and electrical properties that allow for efficient resistive heating.
Understanding a tube furnace requires looking beyond just the heating element. The furnace's true capability is defined by a system of three components working in concert: the heating element that generates the heat, the insulating chamber that contains it, and the process tube that holds your sample.

Deconstructing the Furnace's Thermal System
A tube furnace is more than just a hot box. To understand its material composition, you must see it as an integrated system where each part plays a distinct and critical role.
The Heating Element: The Source of Heat
This is the component that converts electrical energy into thermal energy. The choice of material here directly dictates the furnace's maximum operating temperature.
- Resistance Wire (e.g., FeCrAl alloys): Used for lower-temperature applications, typically up to 1200-1300°C. These are cost-effective and durable within their temperature range.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) Rods: The next step up, allowing for stable operation up to approximately 1600°C. They are a common choice for many high-temperature lab and production processes.
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Rods: These are the standard for the highest temperature applications, capable of reaching 1800°C or even higher. They form a protective silica layer at high temperatures, ensuring a long operational life.
The Chamber & Insulation: Containing the Heat
The heating elements are housed within a chamber designed to maximize thermal efficiency and protect the outer furnace body.
The primary materials are high-temperature refractory ceramics or ceramic fibers. These provide excellent thermal insulation, ensuring the heat is focused on the process tube and energy is not wasted.
In specialized furnaces, such as those for Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), the hot zone may be constructed from graphite with carbon felt insulation.
The Process Tube: The Heart of the Experiment
This is the tube that passes through the center of the furnace and contains the sample and process atmosphere. Its material is chosen based on chemical compatibility and temperature requirements.
Common materials include fused quartz, alumina (a ceramic), and stainless steel. Quartz is useful for visually monitoring a process but has a lower temperature limit than alumina. Alumina tubes offer excellent high-temperature stability and chemical inertness.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
The selection of a heating element is a direct trade-off between maximum temperature and cost. Each material occupies a specific performance tier.
Up to ~1200°C: Resistance Wire
This is the workhorse for general-purpose heat treatment, annealing, and drying. It offers the best balance of performance and cost for applications that do not require extreme temperatures.
Up to ~1600°C: Silicon Carbide (SiC)
When your process requires temperatures beyond the limits of wire elements, SiC is the logical choice. It is a robust and reliable material for many advanced materials synthesis and sintering applications.
Above 1600°C: Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2)
For cutting-edge research and processing of high-performance ceramics and alloys, MoSi2 elements are non-negotiable. They represent the peak of resistive heating technology but come at a higher price point.
The Critical Factor: Chemical Compatibility
The heating element's temperature rating is meaningless if your process tube cannot withstand the chemical environment.
For highly corrosive atmospheres, standard quartz or even alumina tubes may degrade. In these cases, specialty tubes made of metals like molybdenum or tungsten are required to ensure process purity and safety.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right materials means matching the entire furnace system to your specific application.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating below 1200°C: A furnace with resistance wire elements and a quartz or mullite tube is the most cost-effective and practical solution.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing up to 1600°C: Look for a system with Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements and a high-purity alumina tube for robust performance.
- If your primary focus is reaching maximum temperatures above 1600°C: A furnace with Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements is necessary, paired with a high-grade alumina or zirconia tube.
- If your primary focus is processing in corrosive atmospheres: The process tube material (e.g., specialty metal alloys) becomes the most critical factor, dictating the rest of the system's design.
By understanding how these components and materials function as a system, you can confidently select a furnace that precisely matches your technical requirements.
Summary Table:
| Component | Common Materials | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Element | Resistance Wire (FeCrAl alloys) | Cost-effective, up to 1200-1300°C |
| Heating Element | Silicon Carbide (SiC) Rods | Stable up to 1600°C, robust for synthesis |
| Heating Element | Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Rods | Up to 1800°C, long life with protective layer |
| Insulation | Refractory Ceramics / Fibers | Excellent thermal efficiency, contains heat |
| Process Tube | Fused Quartz, Alumina, Stainless Steel | Chemical compatibility, sample containment |
Ready to elevate your laboratory's capabilities with a custom high-temperature furnace solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, whether you're working with general heat treatment or cutting-edge materials at extreme temperatures. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















