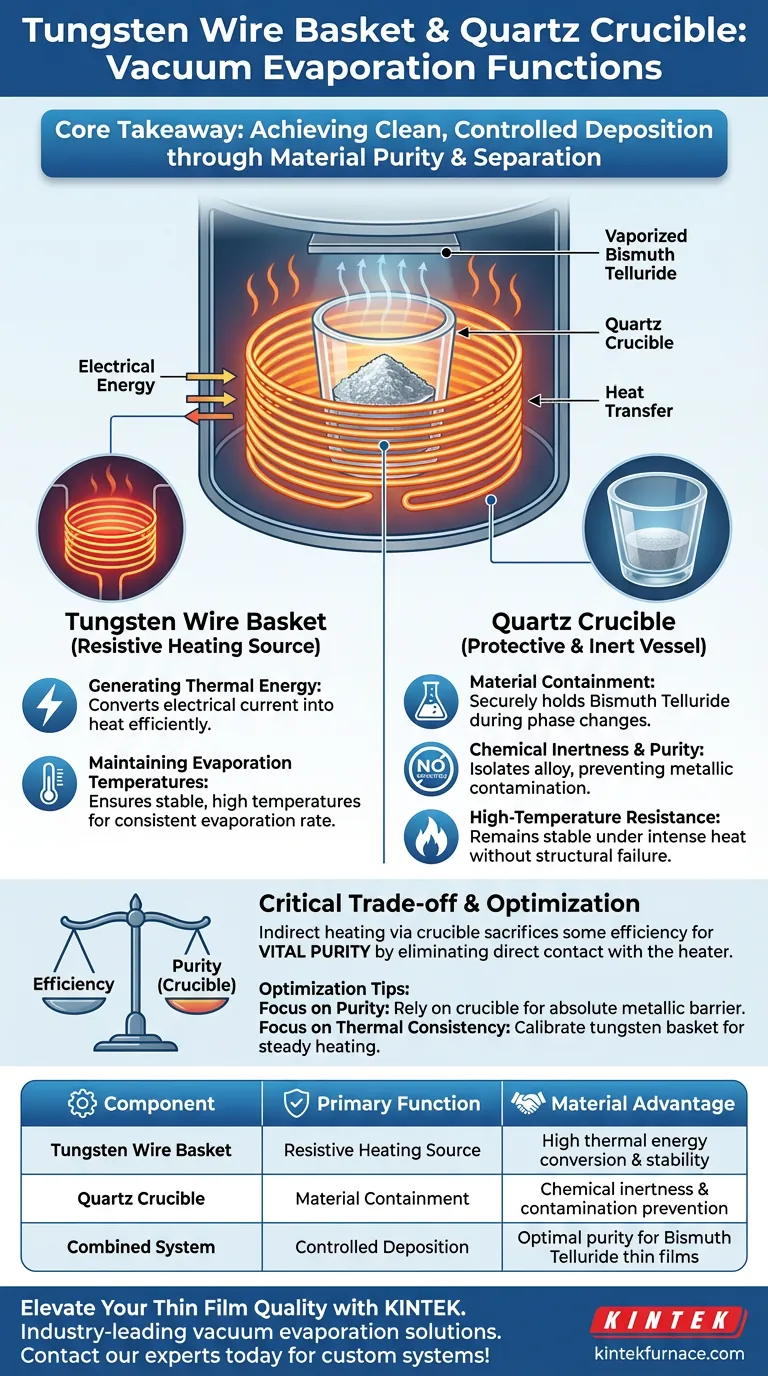
In a vacuum evaporation system, the tungsten wire basket and quartz crucible function as a complementary unit to achieve clean, controlled deposition. The tungsten wire basket serves as the primary resistive heating source, converting electrical energy into the heat required for evaporation, while the quartz crucible acts as a protective container that isolates the source material—specifically Bismuth Telluride—to prevent contamination.
Core Takeaway This configuration prioritizes material purity by physically separating the heating element from the source alloy. While the tungsten basket provides the necessary thermal energy, the quartz crucible acts as an inert barrier, ensuring that no metallic impurities degrade the quality or performance of the resulting thermoelectric thin films.
The Role of the Tungsten Wire Basket
Generating Thermal Energy
The tungsten wire basket functions as a high-resistance heating source. Its primary role is to efficiently convert electrical current into thermal energy.
Maintaining Evaporation Temperatures
By generating substantial heat, the basket ensures the system reaches and maintains the specific temperatures required to melt and vaporize the source material. This thermal consistency is critical for a stable evaporation rate.
The Function of the Quartz Crucible
Material Containment
The quartz crucible serves as the physical vessel for the Bismuth Telluride alloy. It holds the material securely during the phase change from solid to liquid to vapor.
Chemical Inertness and Purity
The most critical function of the quartz crucible is its chemical inertness. By effectively isolating the alloy, it ensures that no metallic impurities are introduced into the film during the heating process.
High-Temperature Resistance
Quartz allows the system to operate at high temperatures without structural failure. This resistance ensures the container remains stable throughout the intense melting and vaporization cycles.
Understanding the Critical Trade-off
Efficiency vs. Contamination Risk
In vacuum evaporation, placing source material directly onto a metallic heater often leads to contamination. This setup accepts a slight layer of complexity—using indirect heating through a crucible—to secure a vital advantage: purity.
The Necessity of Isolation
If the Bismuth Telluride were to touch the tungsten directly, metallic impurities could compromise the film's thermoelectric properties. The crucible eliminates this risk entirely, preserving the integrity of the deposited thin film.
Optimizing for Film Quality
To ensure the success of your vacuum evaporation process, consider the following based on your specific requirements:
- If your primary focus is maintaining high purity: rely on the quartz crucible to act as an absolute barrier against metallic contamination during the melt.
- If your primary focus is thermal consistency: ensure the tungsten wire basket is calibrated to provide steady resistive heating to the crucible surface.
This dual-component approach ensures that thermal efficiency never comes at the cost of material integrity.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Material Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Tungsten Wire Basket | Resistive Heating Source | High thermal energy conversion & stability |
| Quartz Crucible | Material Containment | Chemical inertness & contamination prevention |
| Combined System | Controlled Deposition | Optimal purity for Bismuth Telluride thin films |
Elevate Your Thin Film Quality with KINTEK
Don't let metallic contamination compromise your research or production. KINTEK provides industry-leading vacuum evaporation solutions backed by expert R&D and manufacturing. Whether you need precise Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, or CVD systems, our equipment is fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory requirements.
Ensure the integrity of your materials—Contact our experts today to find the perfect high-temp furnace for your needs!
Visual Guide
References
- N.G. Imam, Abd El‐Hady B. Kashyout. Comprehensive study of nanostructured Bi <sub>2</sub> Te <sub>3</sub> thermoelectric materials – insights from synchrotron radiation XRD, XAFS, and XRF techniques. DOI: 10.1039/d3ra06731a
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a carrier gas flow control system necessary for thermal sludge treatment? Ensure Precision & Protect Equipment
- What is the wear resistance of alumina ceramics compared to manganese steel and high-chromium cast iron? Discover the Superior Choice for Abrasive Environments
- What is the recommended cooling rate for the alumina furnace tube? Prevent Thermal Shock and Extend Tube Life
- What roles do the high-purity graphite crucible and lid play in PVT AlN growth? Optimize Your Crystal Production
- What makes high-purity alumina crucibles the preferred choice for BZT synthesis? Ensure Purity & Thermal Stability
- What is the purpose of applying Boron Nitride (BN) to graphite molds in Mg3Sb2 VHP? Ensure Purity & Easy Demolding
- What role does a PTFE-lined high-pressure autoclave play in synthesis of ZnO nanorods? Key Benefits & Growth Factors
- Why is temperature-controlled heating equipment required for calcium perrhenate? Ensure Rhenium Stability at 140 °C



















