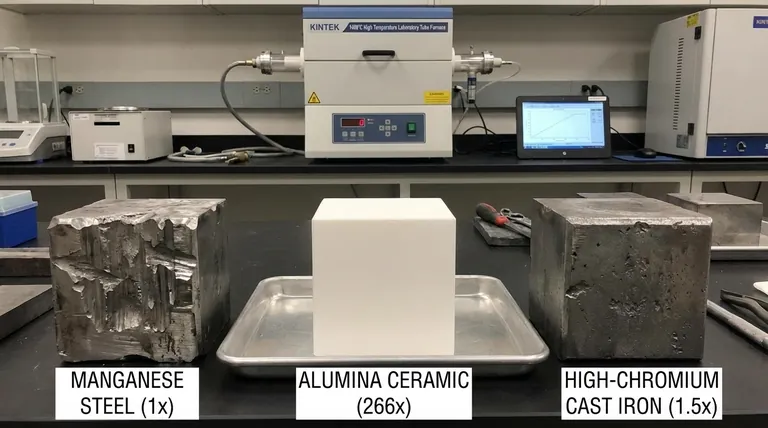
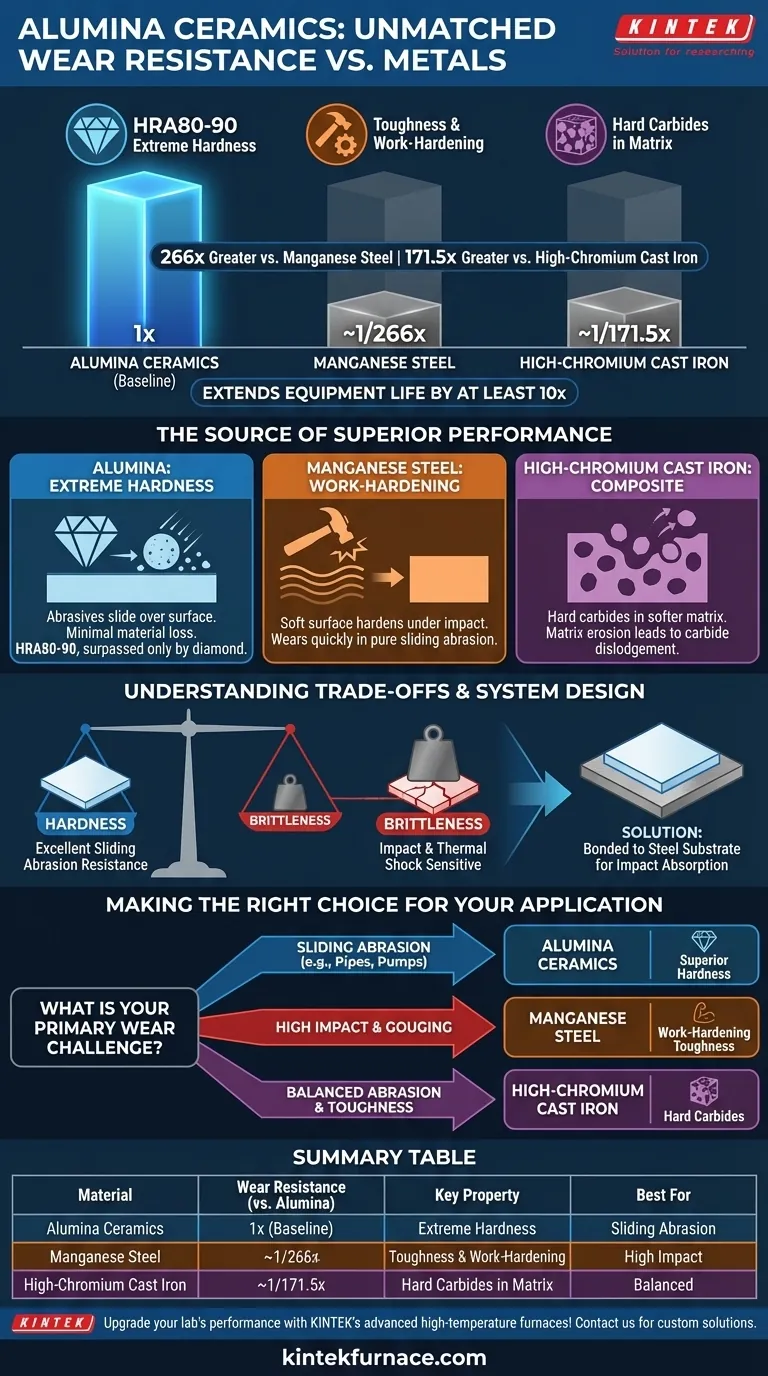
In a direct comparison, alumina ceramics exhibit a wear resistance that is approximately 266 times greater than manganese steel and 171.5 times greater than high-chromium cast iron. This vast difference in performance is due to alumina's extreme hardness, a property that allows it to extend the service life of equipment by at least ten times in many abrasive environments.
The core distinction lies in the material's fundamental properties: Alumina's exceptional wear resistance is derived from its extreme hardness, while metals like manganese steel rely on toughness and work-hardening. Understanding this difference is the key to selecting the right material for either high-abrasion or high-impact conditions.

The Source of Alumina's Superior Performance
To understand the dramatic performance gap, we must look beyond the simple wear numbers and examine the underlying material science. The way these materials handle friction and wear is fundamentally different.
The Defining Trait of Alumina: Extreme Hardness
Alumina ceramic's defining characteristic is its exceptional hardness. With a Rockwell hardness rating of HRA80-90, its hardness is surpassed only by diamond.
This means that abrasive particles, such as sand, coal, or other minerals, struggle to cut, gouge, or scratch the ceramic surface. Instead of wearing away the material, the abrasive media simply slides over it, resulting in minimal material loss over time.
The Wear Mechanism of Manganese Steel
Manganese steel is known for its legendary toughness, not its initial hardness. It has a unique ability to work-harden under repeated impact.
When subjected to impact or high-pressure stress, its surface transforms from relatively soft to extremely hard and durable. However, in pure sliding abrasion scenarios without significant impact, it remains in its softer state and wears down relatively quickly.
The Wear Mechanism of High-Chromium Cast Iron
High-chromium cast iron represents a middle ground. Its wear resistance comes from hard chromium carbide particles embedded within a softer, more ductile iron matrix.
While these carbides provide good resistance to abrasion—far superior to manganese steel in low-impact wear—the surrounding matrix can still erode. Over time, this can lead to the hard carbides being dislodged, accelerating the wear rate. Alumina, by contrast, is a uniformly hard, monolithic material.
Translating Resistance into Operational Value
A 266x improvement in wear resistance is not just an academic figure; it translates directly into significant operational and financial benefits.
Extending Equipment Service Life
The claim of extending equipment life by at least ten times is realistic for applications dominated by sliding abrasion. Components like pipe elbows, slurry pumps, chutes, and cyclone liners see this level of improvement consistently.
Reducing Downtime and Maintenance Costs
Longer-lasting components directly lead to fewer shutdowns for replacement and repair. This reduction in downtime increases plant availability and productivity while cutting labor and material costs associated with frequent maintenance cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Hardness vs. Brittleness
No material is perfect for every application. The extreme hardness of alumina ceramic comes with a critical trade-off: brittleness.
Impact Sensitivity
While alumina excels at resisting abrasion, it is susceptible to fracture from direct, high-energy impacts. A sharp, heavy impact that would merely dent or deform manganese steel could shatter an unprotected alumina ceramic liner.
The Importance of System Design
Because of this brittleness, alumina is rarely used as a standalone structural component. It is typically manufactured as tiles or custom shapes that are bonded to a steel substrate. The steel casing provides structural integrity and absorbs impact energy, protecting the brittle ceramic wear face.
Thermal Shock Limitations
Rapid and extreme temperature fluctuations (thermal shock) can also induce stress and cause cracking in ceramics. Metals are generally far more resilient to this type of stress. Therefore, the thermal environment must be a key consideration during material selection.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The optimal material is the one whose properties best counter the specific wear phenomena in your equipment.
- If your primary challenge is sliding abrasion: Alumina ceramic is the definitive choice due to its superior hardness, offering a service life that can be an order of magnitude greater than wear-resistant steels.
- If your application involves high impact and gouging: Manganese steel is the superior option, as its ability to work-harden and resist fracture is more critical than pure surface hardness.
- If you need a balance of abrasion resistance and toughness: High-chromium cast iron provides a significant upgrade over standard steels for abrasive wear without the impact sensitivity concerns of pure ceramics.
By correctly matching the material's properties to the specific wear mechanism, you can transition from a cycle of frequent repairs to one of long-term operational reliability.
Summary Table:
| Material | Wear Resistance Multiplier (vs. Alumina) | Key Property | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina Ceramics | 1x (Baseline) | Extreme Hardness (HRA80-90) | Sliding Abrasion |
| Manganese Steel | ~1/266x | Toughness & Work-Hardening | High Impact |
| High-Chromium Cast Iron | ~1/171.5x | Hard Carbides in Matrix | Balanced Abrasion & Toughness |
Upgrade your lab's performance with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems tailored for diverse laboratories. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and durability. Contact us today to discuss how our products can help you achieve superior results in abrasive and high-impact environments!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
















