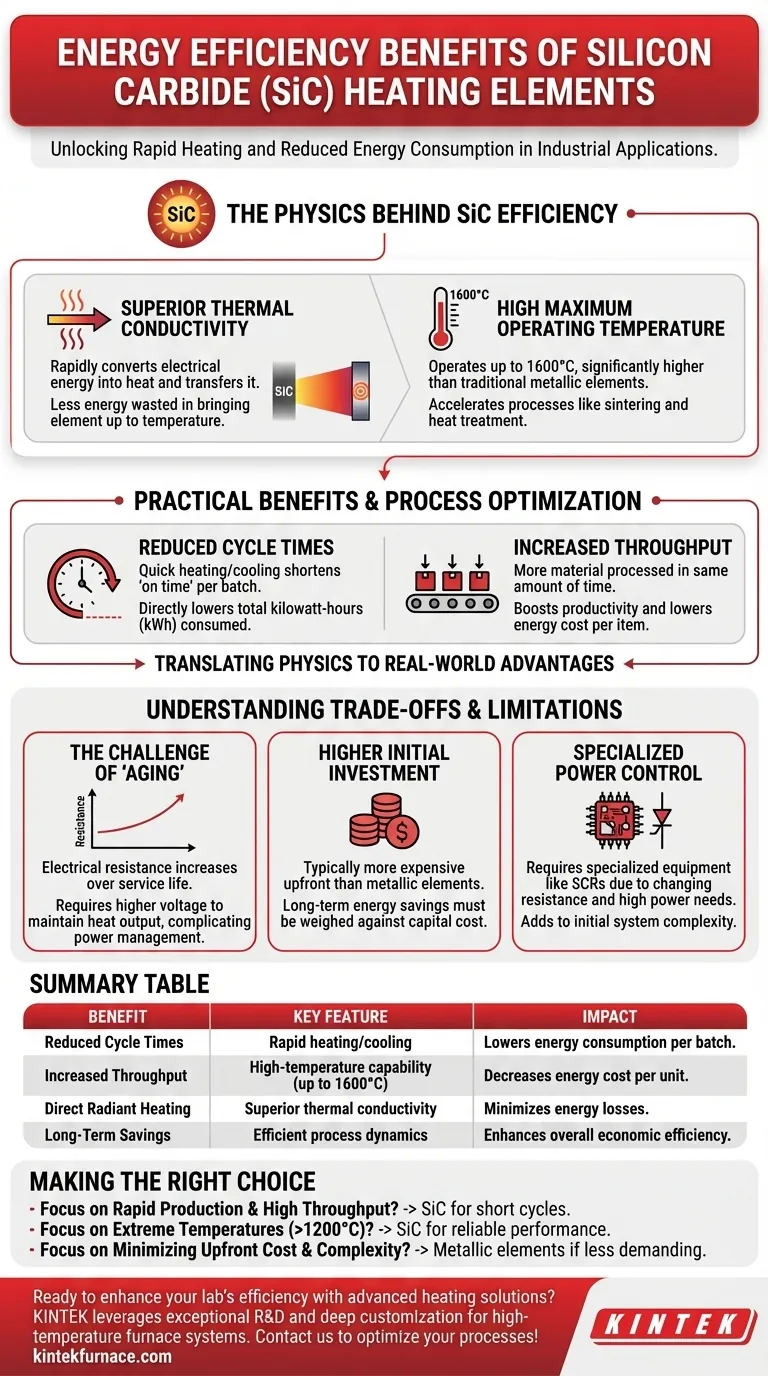
The primary energy efficiency benefits of silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements are rooted in their exceptional thermal conductivity and ability to operate at extremely high temperatures. This combination enables rapid heating and cooling cycles, which reduces the energy consumed per process and significantly increases production throughput in demanding industrial environments.
SiC heating elements achieve energy efficiency not just through lower power draw, but by fundamentally changing the process dynamics. Their ability to heat up and cool down quickly shortens cycle times, directly translating to less energy wasted and higher productivity.
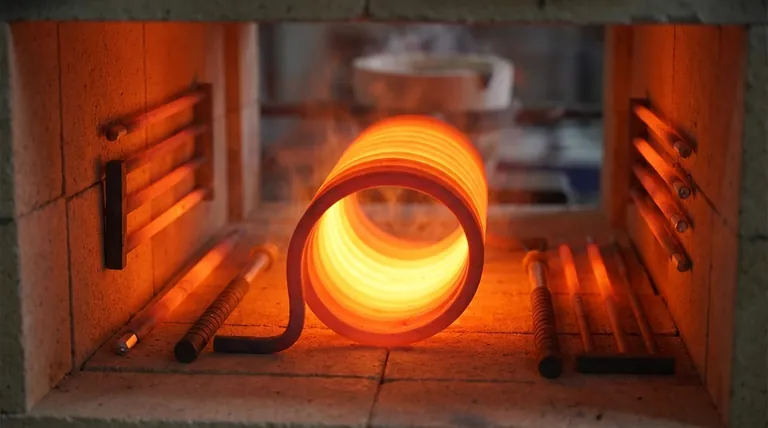

The Physics Behind SiC Efficiency
To understand the benefits, it's essential to look at the material's core properties. The efficiency gains are a direct result of how SiC behaves when electricity is applied.
Superior Thermal Conductivity
Silicon carbide possesses excellent thermal conductivity. This means it can convert electrical energy into heat and transfer that heat to the target environment with remarkable speed.
This property is the reason for the rapid heating capabilities mentioned in industrial applications. Less energy is wasted bringing the element itself up to temperature.
High Maximum Operating Temperature
SiC elements can operate at temperatures up to 1600°C. This is significantly higher than many traditional metallic elements.
Operating at higher temperatures can accelerate many industrial processes, such as sintering or heat treatment. Completing a process faster is a direct form of energy efficiency on a per-unit basis.
Direct Radiant Heating
The heating mechanism is straightforward: an electric current passes through the element, which generates heat due to its resistance. This heat is then radiated directly to the object or furnace chamber.
This direct form of energy transfer is highly efficient, minimizing intermediate losses and allowing for precise control by simply adjusting the electrical current.
How Efficiency Translates to Practical Benefits
The physical properties of SiC create tangible advantages in real-world industrial settings, moving beyond simple power consumption to overall process optimization.
Reduced Cycle Times
The ability to heat up and cool down quickly is the most significant practical benefit. Shorter cycles mean the furnace or kiln is energized for less time per batch.
This reduction in "on time" directly lowers the total kilowatt-hours consumed, leading to immediate energy cost savings.
Increased Throughput
By shortening the time required for each heating cycle, a facility can process more material or parts in the same amount of time.
This boost in productivity means the energy cost per item produced is lower, enhancing the overall economic efficiency of the operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly efficient, SiC elements are not a universal solution. Acknowledging their specific requirements and drawbacks is critical for making an informed decision.
The Challenge of "Aging"
Over their service life, SiC elements experience a phenomenon known as aging, where their electrical resistance gradually increases.
To maintain the same heat output, the power supply must deliver a higher voltage. This not only complicates power management, often requiring transformers with multiple taps, but it can also diminish efficiency over time if not properly managed.
Higher Initial Investment
SiC heating elements are typically more expensive than their common metallic counterparts. The upfront capital cost is a significant factor that must be weighed against the potential long-term energy savings.
Specialized Power Control
The changing resistance and high power requirements of SiC elements necessitate specialized power control equipment, such as SCRs (Silicon-Controlled Rectifiers). This adds to the system's initial cost and complexity compared to simpler metallic element setups.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if SiC elements are the right fit, you must weigh their operational benefits against their initial cost and long-term management requirements.
- If your primary focus is rapid production and high throughput: The short cycle times enabled by SiC's rapid heating make them an excellent choice for maximizing output and reducing energy cost per unit.
- If your primary focus is operating at extreme temperatures (above 1200°C): SiC elements are one of the few viable technologies that can perform reliably and efficiently in these demanding conditions.
- If your primary focus is minimizing upfront cost and maintenance complexity: A traditional metallic element may be more suitable, provided your temperature and cycle time requirements are less demanding.
Ultimately, choosing SiC is an investment in process speed and high-temperature capability, which delivers significant energy savings when properly implemented and managed.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Feature | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced Cycle Times | Rapid heating/cooling | Lowers energy consumption per batch |
| Increased Throughput | High-temperature capability (up to 1600°C) | Decreases energy cost per unit |
| Direct Radiant Heating | Superior thermal conductivity | Minimizes energy losses |
| Long-Term Savings | Efficient process dynamics | Enhances overall economic efficiency |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency with advanced heating solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, helping you achieve faster cycle times, higher throughput, and significant energy savings. Contact us today to discuss how our SiC heating elements and other solutions can optimize your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance



















